Lithologic Reservoirs ›› 2026, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (1): 13-25.doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20260102
• PETROLEUM EXPLORATION • Previous Articles Next Articles
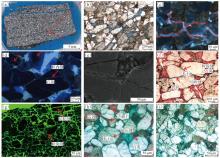
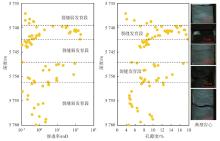
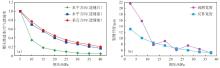
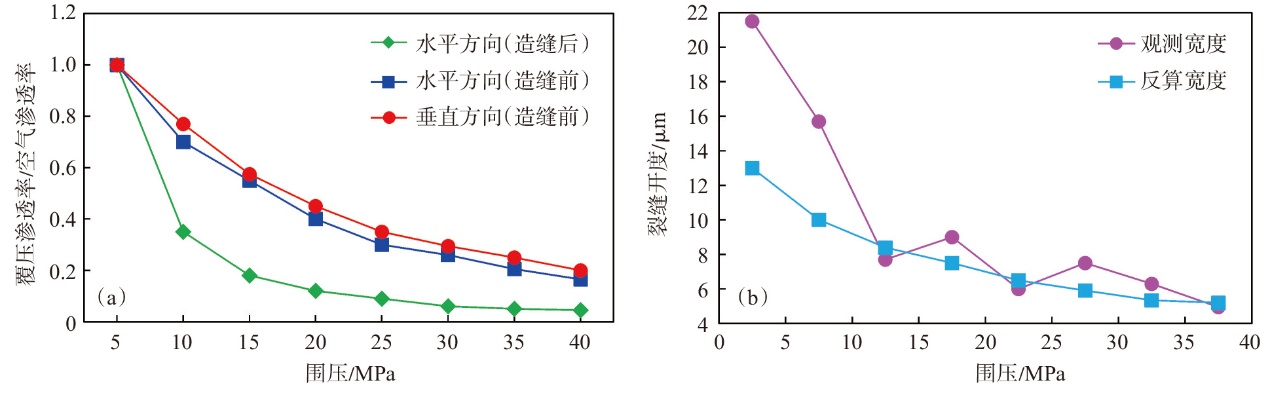
Development characteristics and main controlling factors of natural fractures of Jurassic Qigu Formation in Yongjin area, Junggar Basin
MENG Yang1( ), CAO Xiaopeng2, ZHAO Hao2,3(
), CAO Xiaopeng2, ZHAO Hao2,3( ), YANG Minglin2, LI Zhipeng4, TIAN Zhenlei2, WU Hongcui2, JIANG Yue2
), YANG Minglin2, LI Zhipeng4, TIAN Zhenlei2, WU Hongcui2, JIANG Yue2
- 1
Shengli Oilfield Company ,Sinopec Dongying 257000, Shandong, China
2Exploration and Development Research Institute ,Shengli Oilfield Company, Sinopec Dongying 257015, Shandong, China
3Postdoctoral Work Station of Shengli Oilfield ,Sinopec Dongying 257015, Shandong, China
4Xinjiang Xinchun Petroleum Development Co. ,Ltd., Sinopec Dongying 257000, Shandong, China
CLC Number:
- TE122
| [1] | 邹才能, 杨智, 朱如凯, 等. 中国非常规油气勘探开发与理论技术进展[J]. 地质学报, 2015, 89(6):979-1007. |
| ZOU Caineng, YANG Zhi, ZHU Rukai, et al. Progress in China’s unconventional oil & gas exploration and development and theo-retical technologies[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2015, 89(6):979-1007. | |
| [2] |
丁文龙, 王兴华, 胡秋嘉, 等. 致密砂岩储层裂缝研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 2015, 30(7):737-750.
doi: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2015.07.0737 |
| DING Wenlong, WANG Xinghua, HU Qiujia, et al. Progress in tight sandstone reservoir fractures research[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2015, 30(7):737‑750. | |
| [3] |
ZENG Lianbo, SU Hui, TANG Xiaomei, et al. Fractured tight sandstone oil and gas reservoirs:A new play type in the Dongpu depression,Bohai Bay Basin,China[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2013, 97(3):363-377.
doi: 10.1306/09121212057 |
| [4] | 李新景, 胡素云, 程克明. 北美裂缝性页岩气勘探开发的启示[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2007, 34(4):392-400. |
| LI Xinjing, HU Suyun, CHENG Keming. Suggestions from the development of fractured shale gas in North America[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2007, 34(4):392-400. | |
| [5] |
ZENG Lianbo, GONG Lei, ZHANG Yunzhao, et al. A review of the genesis,evolution,and prediction of natural fractures in deep tight sandstones of China[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2023, 107(10):1687-1721.
doi: 10.1306/07052322120 |
| [6] | 曾联波, 巩磊, 宿晓岑, 等. 深层—超深层致密储层天然裂缝分布特征及发育规律[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2024, 45(1):1-14. |
| ZENG Lianbo, GONG Lei, SU Xiaocen, et al. Natural fractures in deep to ultra-deep tight reservoirs:Distribution and development[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2024, 45(1):1-14. | |
| [7] |
ZENG Lianbo, TANG Xiaomei, WANG Tiecheng, et al. The influence of fracture cements in tight Paleogene saline lacustrine carbonate reservoirs,western Qaidam Basin,northwest China[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2012, 96(11):2003-2017.
doi: 10.1306/04181211090 |
| [8] | SANDERSON D J, NIXON C W. Topology,connectivity and percolation in fracture networks[J]. Journal of Structural Geo-logy, 2018, 115:167-177. |
| [9] | 梁晓伟, 韩永林, 王海红, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地姬塬地区上三叠统延长组裂缝特征及其地质意义[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2009, 21(2):49-53. |
| LIANG Xiaowei, HAN Yonglin, WANG Haihong, et al. Fracture characteristics and geological significance of Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation in Jiyuan area,Ordos Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2009, 21(2):49-53. | |
| [10] | 巩磊, 程宇琪, 高帅, 等. 库车前陆盆地东部下侏罗统致密砂岩储层裂缝连通性表征及其主控因素[J]. 地球科学, 2023, 48(7):2475-2488. |
| GONG Lei, CHENG Yuqi, GAO Shuai, et al. Fracture connectivity characterization and its controlling factors in Lower Jurassic tight sandstone reservoirs of eastern Kuqa Foreland Basin[J]. Earth Science, 2023, 48(7):2475-2488. | |
| [11] |
曾联波, 漆家福, 王永秀. 低渗透储层构造裂缝的成因类型及其形成地质条件[J]. 石油学报, 2007, 28(4):52-56.
doi: 10.7623/syxb200704010 |
|
ZENG Lianbo, QI Jiafu, WANG Yongxiu. Origin type of tectonic fractures and geological conditions in low-permeability reservoirs[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2007, 28(4):52-56.
doi: 10.7623/syxb200704010 |
|
| [12] | 曾联波, 高春宇, 漆家福, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地陇东地区特低渗透砂岩储层裂缝分布规律及其渗流作用[J]. 中国科学 D 辑:地球科学, 2008, 38(增刊1):41-47. |
| ZENG Lianbo, GAO Chunyu, QI Jiafu, et al. Fracture distribution and its effect on seepage in the ultra low-permeability sandstone reservoirs in Longdong area,Ordos Basin[J]. Science in China Series D:Earth Sciences, 2008, 38(Suppl 1):41-47. | |
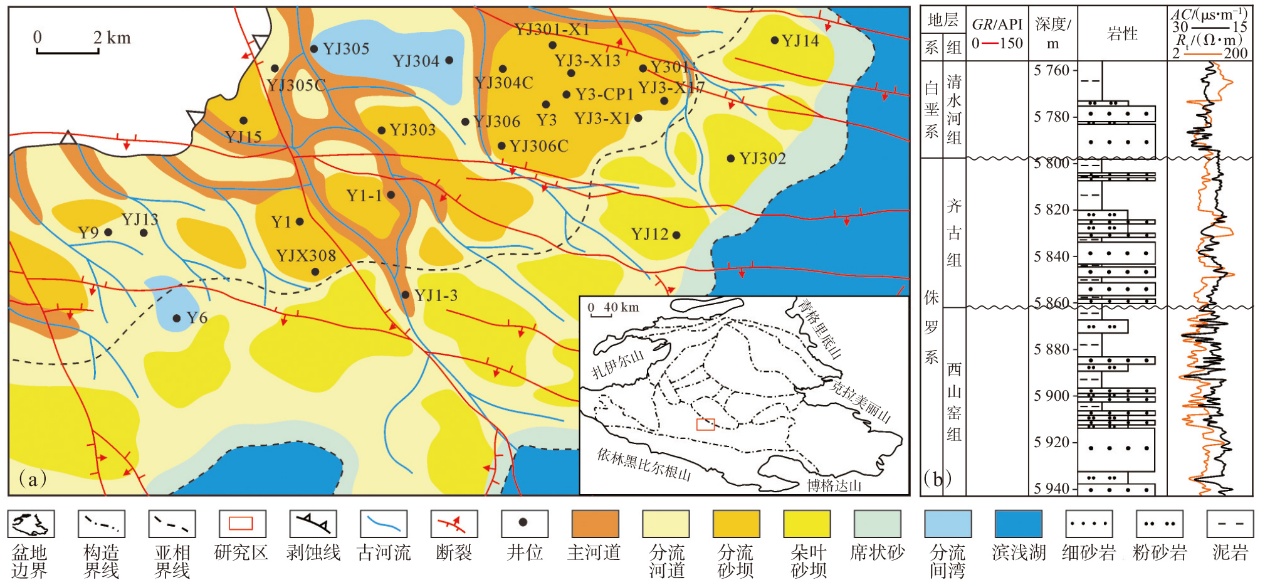
| [13] | 王树华. 准噶尔盆地永进地区隐蔽油气藏识别与预测[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2009. |
| WANG Shuhua. Identification and prediction for the subtle oil reservoir developed at Yongjin area in Junggar Basin[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2009. | |
| [14] | 王金铎, 曾治平, 宫亚军, 等. 深部超压储层发育机制及控制因素:以准噶尔盆地永进油田为例[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2020, 27(3):13-19. |
| WANG Jinduo, ZENG Zhiping, GONG Yajun, et al. Development mechanism and controlling factors of deep overpressured reservoir:A case study of Yongjin Oilfield in Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2020, 27(3):13-19. | |
| [15] | 贺振建, 刘宝军, 王朴. 准噶尔盆地永进地区侏罗系层理缝成因及其对储层的影响[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2011, 18(1):15-17. |
| HE Zhenjian, LIU Baojun, WANG Pu. Genesis of bedding fractures and its influences on reservoirs in Jurassic,Yongjin area,Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2011, 18(1):15-17. | |
| [16] | 刘浩杰, 盖姗姗, 于文政, 等. 准噶尔盆地永进油田超深层致密砂岩裂缝测井识别[J]. 测井技术, 2022, 46 (5):592-598. |
| LIU Haojie, GAI Shanshan, YU Wenzheng, et al. Fracture identification in super-deeply buried tight sandstone reservoirs in Yongjin Oilfield,Junggar Basin,China[J]. Well Logging Techno-logy, 2022, 46(5):592-598. | |
| [17] |
胡鑫, 朱筱敏, 金绪铃, 等. 准噶尔盆地永进地区侏罗系齐古组浅水辫状河三角洲沉积特征[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2025, 37(2):115-126.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20250211 |
|
HU Xin, ZHU Xiaomin, JIN Xuling, et al. Sedimentary characteristics of the shallow-water braided river delta of Jurassic Qigu Formation in Yongjin area,Junggar Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2025, 37(2):115-126.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20250211 |
|
| [18] | 胡海燕, 李平平, 王国建. 准噶尔永进地区深层次生孔隙带发育机理[J]. 地质科技情报, 2008, 27(3):21-25. |
| HU Haiyan, LI Pingping, WANG Guojian. Mechanism of secon-dary porosity development of Xishanyao Formation(J2x) in Yongjin Block,Junggar Basin[J]. Geological Science and Techno-logy Information, 2008, 27(3):21-25. | |
| [19] |
朱美衡, 李茂榕, 朱凤云, 等. 永进地区西山窑组成岩作用及储层影响因素[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 33(1):31-36.
doi: 10.3863/j.issn.1674-5086.2011.01.006 |
| ZHU Meiheng, LI Maorong, ZHU Fengyun, et al. Sandstone diagenesis and the influence factors on reservoir of Xishanyao Formation in Yongjin area[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University (Science & Technology Edition), 2011, 33(1):31-36. | |
| [20] | 刘浩杰, 张昌民, 盖姗姗, 等. 准噶尔盆地永进油田侏罗系超深层致密砂岩储层成岩相识别及分布预测[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2024, 31(1):13-22 |
| LIU Haojie, ZHANG Changmin, GAI Shanshan, et al. Diagenetic facies identification and distribution prediction of Jurassic ultra-deep tight sandstone reservoirs in Yongjin Oilfield,Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2024, 31(1):13-22. | |
| [21] | 何登发, 张磊, 吴松涛, 等. 准噶尔盆地构造演化阶段及其特征[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2018, 39(5):845-861. |
| HE Dengfa, ZHANG Lei, WU Songtao, et al. Tectonic evolution stages and features of the Junggar Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geo-logy, 2018, 39(5):845-861. | |
| [22] | 李平平, 邹华耀, 郝芳. 准噶尔盆地腹部侏罗系顶部风化壳的发育机制及其油气成藏效应[J]. 沉积学报, 2006, 24(6):889-896. |
| LI Pingping, ZOU Huayao, HAO Fang. Formation mechanism and effect on petroleum accumulation of the weathering crust,top of Jurassic,in the hinterland of Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Sedi-mentologica Sinica, 2006, 24(6):889-896. | |
| [23] |
吕文雅, 曾联波, 周思宾, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南部致密砂岩储层微观裂缝特征及控制因素:以红河油田长8储层为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2020, 31(1):37-46.
doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2019.08.006 |
| LYU Wenya, ZENG Lianbo, ZHOU Sibin, et al. Microfracture characteristics and its controlling factors in the tight oil sandstones in the southwest Ordos Basin:Case study of the eighth member of the Yanchang Formation in Honghe Oilfield[J]. Na-tural Gas Geoscience, 2020, 31(1):37-46. | |
| [24] | 罗群, 魏浩元, 刘冬冬, 等. 层理缝在致密油成藏富集中的意义、研究进展及其趋势[J]. 石油实验地质, 2017, 39(1):1-7 |
| LUO Qun, WEI Haoyuan, LIU Dongdong, et al. Research signi-ficance,advances and trends on the role of bedding fracture in tight oil accumulation[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2017, 39(1):1-7. | |
| [25] | 鞠玮, 尤源, 冯胜斌, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地延长组长7油层组致密砂岩储层层理缝特征及成因[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2020, 41(3):596-605. |
| JU Wei, YOU Yuan, FENG Shengbin, et al. Characteristics and genesis of bedding-parallel fractures in tight sandstone reservoirs of Chang 7 oil layer,Ordos Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geo-logy, 2020, 41(3):596-605. | |
| [26] | 毛哲, 曾联波, 刘国平, 等. 准噶尔盆地南缘侏罗系深层致密砂岩储层裂缝及其有效性[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2020, 41 (6):1212-1221 |
| MAO Zhe, ZENG Lianbo, LIU Guoping, et al. Characterization and effectiveness of natural fractures in deep tight sandstones at the south margin of the Junggar Basin,northwestern China[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2020, 41(6):1212-1221. | |
| [27] | 于雷, 陈建文, 李元, 等. 姬塬油田堡子湾南长4+5储层裂缝特征及其影响因素分析[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2011, 23(6):69-72. |
| YU Lei, CHEN Jianwen, LI Yuan, et al. Characteristics and influencing factors of fractures of Chang 4+5 reservoir in southern Puziwan area,Jiyuan Oilfield[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2011, 23(6):69-72. | |
| [28] |
曾联波, 吕文雅, 徐翔, 等. 典型致密砂岩与页岩层理缝的发育特征、形成机理及油气意义[J]. 石油学报, 2022, 43(2):180-191.
doi: 10.7623/syxb202202002 |
|
ZENG Lianbo, LYU Wenya, XU Xiang, et al. Development characteristics,formation mechanism and hydrocarbon significance of bedding fractures in typical tight sandstone and shale[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2022, 43(2):180-191.
doi: 10.7623/syxb202202002 |
|
| [29] | 司学强, 彭博, 庞志超, 等. 储集层多尺度裂缝特征及控制因素:以准噶尔盆地南缘侏罗系—白垩系为例[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2022, 51(4):731-741. |
| SI Xueqiang, PENG Bo, PANG Zhichao, et al. Characteristics and controlling factors of multi-scale fractures in reservoir:A Jurassic-Cretaceous case from the southern margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2022, 51(4):731-741. | |
| [30] | NELSON R A. Geologic analysis of naturally fractured reservoirs[M]. Gulf Professional Publishing, 1985. |
| [31] | 王瑞飞, 孙卫. 鄂尔多斯盆地姬塬油田上三叠统延长组超低渗透砂岩储层微裂缝研究[J]. 地质论评, 2009, 55(3):444-448. |
| WANG Ruifei, SUN Wei. A study on micro cracks in super-low permeability sandstone reservoir of the Upper Triassic Yanchang Formation in the Ordos Basin[J]. Geological Review, 2009, 55(3):444-448. | |
| [32] | 蒋有录, 李明阳, 王良军, 等. 川东北巴中—通南巴地区须家河组致密砂岩储层裂缝发育特征及控制因素[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(5):1525-1537. |
| JIANG Youlu, LI Mingyang, WANG Liangjun, et al. Characteri-stics and controlling factors of tight sandstone reservoir fractures of the Xujiahe Formation in the Bazhong-Tongnanba area,Northeast Sichuan[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(5):1525-1537. | |
| [33] | 赵向原, 曾联波, 祖克威, 等. 致密储层脆性特征及对天然裂缝的控制作用:以鄂尔多斯盆地陇东地区长7致密储层为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2016, 37(1):62-71. |
| ZHAO Xiangyuan, ZENG Lianbo, ZU Kewei, et al. Brittleness characteristics and its control on natural fractures in tight reservoirs:A case study from Chang7 tight reservoir in Longdong area of the Ordos Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2016, 37(1):62-71. | |
| [34] |
LAI Jin, LIU Bingchang, LI Hongbin, et al. Bedding parallel fractures in fine-grained sedimentary rocks:Recognition,formation mechanisms,and prediction using well log[J]. Petroleum Science, 2022, 19(2):554-569.
doi: 10.1016/j.petsci.2021.10.017 |
| [35] |
LI Zilong, FAN Changyu, SUN Bo, et al. Characteristics,logging identification and major controlling factors of bedding-parallel fractures in tight sandstones[J]. Geoenergy Science and Engineering, 2023, 228:211956.
doi: 10.1016/j.geoen.2023.211956 |
| [36] |
卫欢, 单长安, 朱松柏, 等. 库车坳陷克深地区白垩系巴什基奇克组致密砂岩裂缝发育特征及地质意义[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2025, 37(1):149-160.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20250113 |
|
WEI Huan, SHAN Changan, ZHU Songbai, et al. Fracture deve-lopment characteristics and geological significance of tight sand-stone of Cretaceous Bashijiqike Formation in Keshen area,Kuqa Depression[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2025, 37(1):149-160.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20250113 |
|
| [37] | 吕文雅, 曾联波, 刘静, 等. 致密低渗透储层裂缝研究进展[J]. 地质科技情报, 2016, 35(4):74-83. |
| LYU Wenya, ZENG Lianbo, LIU Jing, et al. Fractures research progress in low permeability tight reservoirs[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2016, 35(4):74-83. | |
| [38] |
杨旭, 白鸣生, 龚汉渤, 等. 川西新场地区三叠系须二段构造裂缝特征及定量预测[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2025, 37(3):73-83.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20250307 |
|
YANG Xu, BAI Mingsheng, GONG Hanbo, et al. Characteristics and quantitative prediction of structural fractures in the second member of Triassic Xujiahe Formation in Xinchang area,western Sichuan Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2025, 37(3):73-83.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20250307 |
|
| [39] |
徐思慧, 赵军, 赵新建, 等. 库车山前克拉苏构造带白垩系亚格列木组致密储层裂缝有效性评价[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2025, 37(5):155-165.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20250514 |
|
XU Sihui, ZHAO Jun, ZHAO Xinjian, et al. Fracture effectiveness evaluation of tight reservoir of Cretaceous Yageliemu Formation in Kelasu structural belt,Kuqa piedmont[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2025, 37(5):155-165.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20250514 |
|
| [40] | ROUCHET J D. Stress fields,a key to oil migration[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1981, 65(1):74-85. |
| [41] | 吴志均, 唐红君, 安凤山. 川西新场致密砂岩气藏层理缝成因探讨[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2003, 30(2):109-111. |
| WU Zhijun, TANG Hongjun, AN Fengshan. Causes of bedding fractures of tight sand gas-reservoir in Xinchang,West Sichuan region[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2003, 30(2):109-111. | |
| [42] | 韩宏伟, 刘震, 马昕箬, 等. 基于颗粒应力的深层超压预测方法研究:以准噶尔盆地腹部地区为例[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(4):1074-1086. |
| HAN Hongwei, LIU Zhen, MA Xinruo, et al. Distribution prediction of high overpressure in Jurassic Moxizhuang-Yongjin area,central Junggar Basin[J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(4):1074-1086. | |
| [43] | 谭绍泉, 曾治平, 宫亚军, 等. 准噶尔盆地腹部超压控制烃、储演化与油气充注过程[J]. 断块油气田, 2014, 21(3):287-291. |
| TAN Shaoquan, ZENG Zhiping, GONG Yajun, et al. Control of abnormal overpressure on hydrocarbon-reservoir evolution and hydrocarbon filling process in central of Junggar Basin[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2014, 21(3):287-291. | |
| [44] | 章惠, 关达, 向雪梅, 等. 川东北元坝东部须四段裂缝型致密砂岩储层预测[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2018, 30(1):133-139. |
|
ZHANG Hui, GUAN Da, XIANG Xuemei, et al. Prediction for fractured tight sandstone reservoir of Xu 4 member in eastern Yuanba area,northeastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2018, 30(1):133-139.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2018.01.013 |
| [1] | CHEN Xuan, XU Xiongfei, ZHANG Hua, GOU Hongguang, ZHANG Yiting, YOU Fan, CHENG Yi, SUN Yufeng. Carboniferous volcanic reservoirs characteristics and favorable area prediction of the eastern Junggar Basin [J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2025, 37(6): 13-27. |
| [2] | QIU Zhengke, HOU Wenfeng, HUANG Huan, GAO Ruqi, ZHOU Lin, ZHANG Yuanmei, TIAN Jinshan, LI Hao. Characteristics of volcanic edifices and hydrocarbon accumulation models of the 6th and 7th blocks of Ke-Bai fault zone, Junggar Basin [J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2025, 37(6): 48-58. |
| [3] | JIANG Mengya, JIANG Zhongfa, LIU Longsong, WANG Jiangtao, CHEN Hailong, WANG Xueyong, LIU Hailei. Hydrocarbon geochemical characteristics and source of Triassic Baijiantan Formation in Dabasong uplift, Junggar Basin [J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2025, 37(6): 71-87. |
| [4] | SU Shuai, QU Hongjun, YIN Hu, ZHANG Leigang, YANG Xiaofeng. Fractal characteristics of pore throat structure and their influence on reservoir physical properties of tight sandstone reservoir: A case study of Triassic Chang 8 member in Fuxian area, Ordos Basin [J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2025, 37(6): 88-98. |
| [5] | MIAO Zhiwei, LI Shikai, ZHANG Wenjun, XIAO Wei, LIU Ming, YU Tong. Seismic prediction technology for complex network fractures in fault-fracture reservoir of tight sandstones: A case study of Triassic Xujiahe Formation in northern Sichuan Basin [J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2025, 37(6): 140-150. |
| [6] | LIU Guanbo, CHEN Shijia, LI Shihong, ZOU Yang, LI Yong. Gas generation potential and reservoir formation condition of Permian Fengcheng Formation source rock in Mazhong structural belt of Mahu Sag [J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2025, 37(5): 83-96. |
| [7] | YE Hui, ZHU Feng, WANG Guizhong, SHI Wanzhong, KANG Xiaoning, DONG Guoning, Naziyiman, WANG Ren. Paleogeomorphy restoration of Permian-Jurassic and its hydrocarbon implications in Junggar Basin,NW China [J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2025, 37(5): 122-132. |
| [8] | TIAN Jixian, SHI Zhenghao, LI Jian, SHA Wei, JIANG Zhengwen, YANG Lei, YU Xue, PU Yongxia. Reservoir formation conditions and exploration potential of Jurassic coal-rock gas in Qaidam Basin [J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2025, 37(4): 17-25. |
| [9] | WANG Jingzhao, JIN Wei, CHANG Lipeng, DONG Zhongliang, WANG Gaowen. Characteristics and hydrocarbon accumulation process of karst reservoir in the third member of Permian Maokou Formation,Hechuan-Tongnan area,central Sichuan Basin [J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2025, 37(4): 63-72. |
| [10] | LI Zhenming, JIA Cunshan, WANG Bin, SONG Zhenxiang, QIU Qi, WANG Jiyuan, XU Chenjie, CUI Yuyao. Characteristics and resource potential of source rocks of Carboniferous Shiqiantan Formation in Shiqiantan Sag,eastern Junggar Basin [J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2025, 37(4): 115-126. |
| [11] | XIAO Wenhua, YANG Jun, YAN Baonian, WANG Jianguo, LI Shaoyong, MA Qilin, LI Zonglin, XUE Huanzhao. Characteristics and main controlling factors of Triassic Chang 8 tight sandstone reservoir in Huanqing area,Ordos Basin [J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2025, 37(3): 23-32. |
| [12] | YIN Zhaopu, ZHU Feng, ZHOU Zhiyao, WANG Lili, LIU Xiaoye, Nazyman, WANG Yuting, HUANG Darui. Main controlling factors of hydrocarbon accumulation and enrichment of Jurissic Xishanyao Formation in Monan Slope,Junggar Basin [J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2025, 37(3): 33-46. |
| [13] | DENG Gaoshan, DONG Xuemei, YU Haitao, ZHANG Jie, YUE Xiwei, REN Junmin, JIANG Tao. Hydrocarbon accumulation conditions and exploration potential of Triassic Baikouquan Formation in Shawan Sag,Junggar Basin [J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2025, 37(3): 59-72. |
| [14] | YANG Xu, BAI Mingsheng, GONG Hanbo, LI Gao, TAO Zuwen. Characteristics and quantitative prediction of structural fractures in the second member of Triassic Xujiahe Formation in Xinchang area, western Sichuan Basin [J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2025, 37(3): 73-83. |
| [15] | ZHANG Zhaohui, ZHANG Jiaosheng, LIU Jungang, ZOU Jiandong, ZHANG Jianwu, LIAO Jianbo, LI Zhiyong, ZHAO Wenwen. Lithofacies identification using conventional logging curves and its exploration significance,Triassic Chang 81 sub-member,Longdong area,Ordos Basin [J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2025, 37(3): 95-107. |
|
||