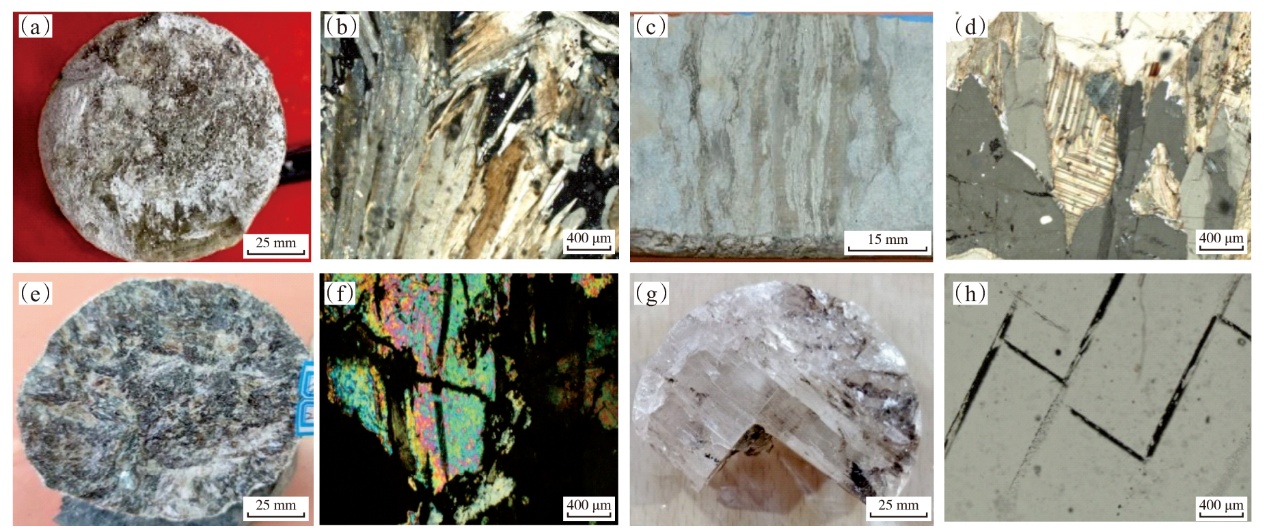
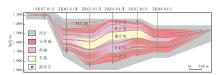
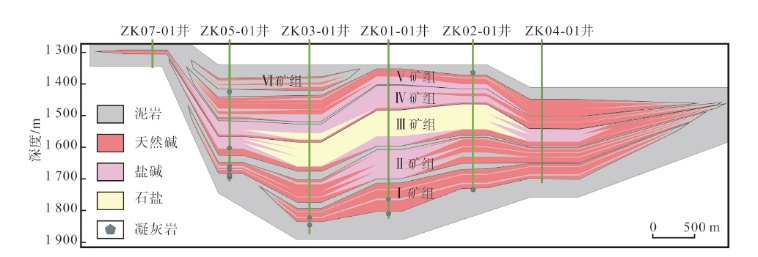
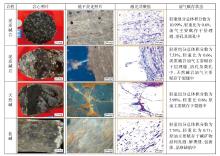
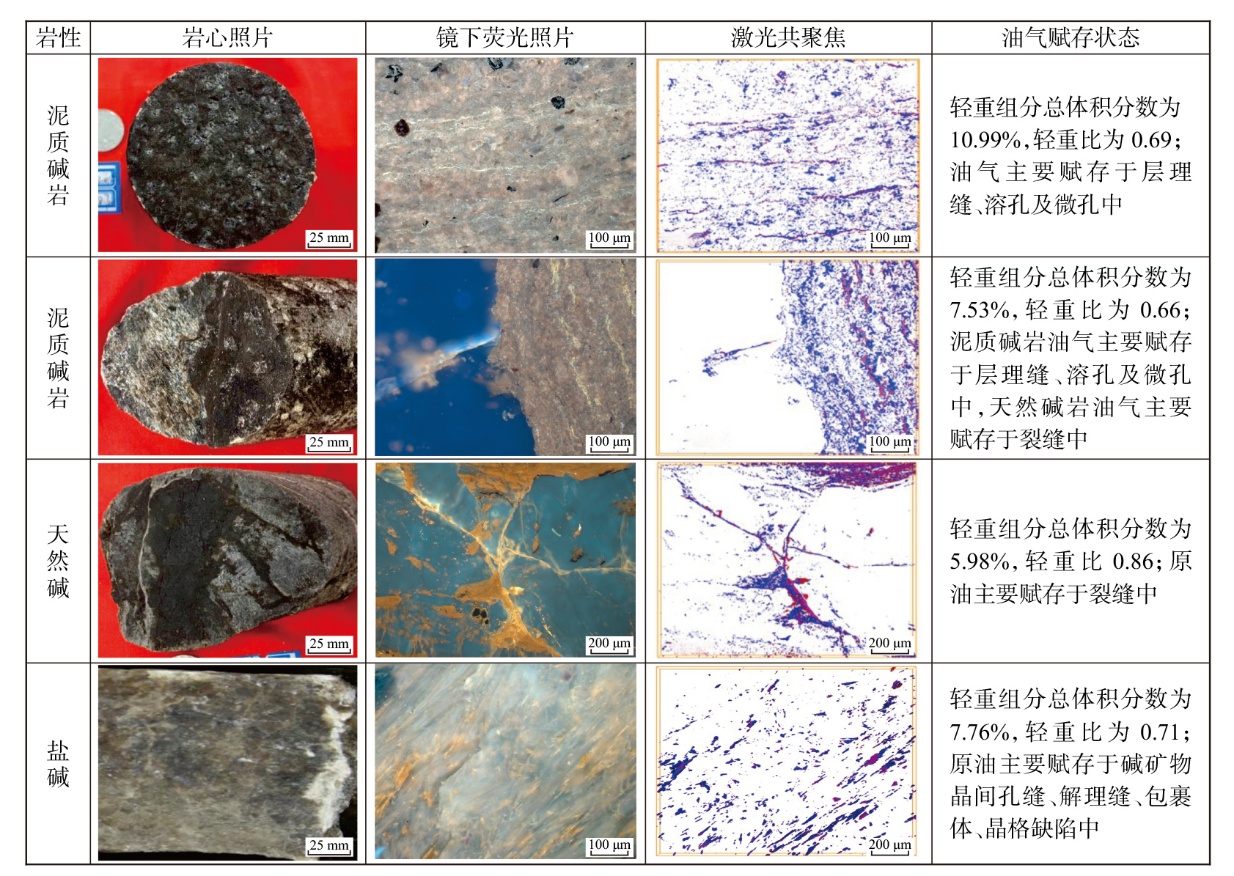
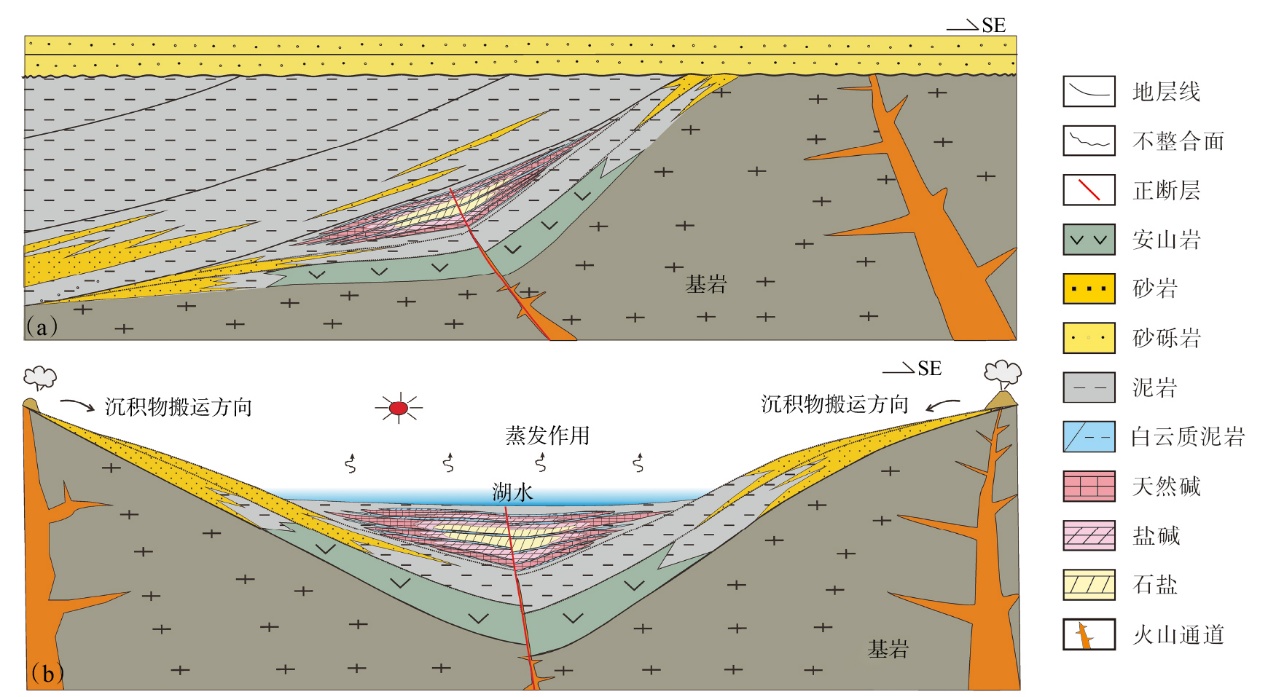
Lithologic Reservoirs ›› 2026, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (1): 1-12.doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20260101
• PETROLEUM EXPLORATION •
Geological characteristics and genesis of trona deposit in Cretaceous Yixian Formation of Naiman Sag, Kailu Basin
HU Changhao1,2( ), PEI Jiaxue2, YANG Xue2, CAI Guogang2, FAN Jiaming2, LI Li2
), PEI Jiaxue2, YANG Xue2, CAI Guogang2, FAN Jiaming2, LI Li2
- 1
School of Geosciences and Info-physics ,Central South University Changsha 410083, China
2Research Institute of Exploration and Development ,PetroChina Liaohe Oilfield Company Panjin 124010, Liaoning, China
CLC Number:
- TE121
| [1] | 陈振红, 陈建立, 王九一, 等. 世界天然碱矿床资源分布、成矿因素及找矿远景[J]. 中国地质, 2023, 50(5):1399-1413. |
| CHEN Zhenhong, CHEN Jianli, WANG Jiuyi, et al. Distribution and genesis of global Na-carbonate deposits and its prospecting potential[J]. Geology in China, 2023, 50(5):1399-1413. | |
| [2] |
黄华, 袁娟梅, 彭伟, 等. 江汉盆地古近系潜江组盐湖沉积特征与成藏模式[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2021, 33(2):9-16.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20210202 |
|
HUANG Hua, YUAN Juanmei, PENG Wei, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and reservoir accumulation model of salt lake of Paleogene Qianjiang Formation in Jianghan Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2021, 33(2):9-16.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20210202 |
|
| [3] | 李文涛, 陈建立, 孙建涛. 河南桐柏县安棚一带曹庄天然碱矿芒硝矿地质特征及成因分析[J]. 矿产与地质, 2022, 36(4):759-767. |
| LI Wentao, CHEN Jianli, SUN Jiantao. Geological characteristics and genesis analysis of Caozhuang natural alkali deposit and mirabilite deposit in Anpeng area,Tongbai County,Henan[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 2022, 36(4):759-767. | |
| [4] | 戴朝成, 钟炽涛, 刘晓东, 等. 内蒙古巴音戈壁盆地塔木素碱矿Na-碳酸盐成因模式[J]. 地球科学, 2024, 49(4):1207-1223. |
| DAI Chaocheng, ZHONG Chitao, LIU Xiaodong, et al. Genetic model of Na-cabonate in Tamusu Trona Deposit,Bayinggobi Basin,Inner Mongolia[J]. Earth Science, 2024, 49(4):1207-1223. | |
| [5] | 徐少康, 石秋圆. 中国油页岩型天然碱矿床成因研究[J]. 化工矿产地质, 2023, 45(2):121-131. |
| XU Shaokang, SHI Qiuyuan. Genesis study on oil shale type of natural soda deposit in China[J]. Geology of Chemical Minerals, 2023, 45(2):121-131. | |
| [6] |
向龙, 刘晓东, 刘平辉, 等. 内蒙古巴音戈壁盆地因格井坳陷下白垩统湖相热水沉积岩特征及成因[J]. 古地理学报, 2019, 21(5):709-726.
doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2019.05.048 |
| XIANG Long, LIU Xiaodong, LIU Pinghui, et al. Genesis and characteristics of lacustrine hydrothermal-sedimentary rock of the Lower Cretaceous in Yingejing Sag of Bayan Gebi Basin,Inner Mongolia[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography (Chinese Edition), 2019, 21(5):709-726. | |
| [7] | 周珍琦, 董清水, 厚刚福, 等. 与盐碱矿共生的油页岩形成环境及沉积演化:以桐柏吴城盆地油页岩矿床为例[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2006, 36(6):1001-1005. |
| ZHOU Zhenqi, DONG Qingshui, HOU Gangfu, et al. The forming environment and sedimentary evolution of the oil shale intergrowthing with salt alkali mine:With the oil shale deposit of Wucheng,Tongbai Basin as an example[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2006, 36(6):1001-1005. | |
| [8] |
吕正祥, 廖哲渊, 李岳峰, 等. 玛湖凹陷二叠系风城组碱湖云质岩储层成岩作用[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2022, 34(5):26-37.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20220502 |
|
LYU Zhengxiang, LIAO Zheyuan, LI Yuefeng, et al. Diagenesis of alkaline lacustrine dolomitic reservoirs of Permian Fengcheng Formation in Mahu Sag[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2022, 34(5):26-37.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20220502 |
|
| [9] | 舒丽娟. 奈曼凹陷九佛堂组非烃流体地质意义及控制因素[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2015, 27(3):75-81. |
|
SHU Lijuan. Geological significance and controlling factors of nonhydrocarbon fluid of Jiufotang Formation in Naiman Sag[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2015, 27(3):75-81.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2015.03.011 |
|
| [10] |
户昶昊, 裴家学, 蔡国钢. 开鲁盆地陆东凹陷白恶系九佛堂组油气连续成藏条件[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2025, 37(3):1-12.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20250301 |
|
HU Changhao, PEI Jiaxue, CAI Guogang. Continuous accumulation conditions of Cretaceous Jiufotang Formation in Ludong Depression in Kailu Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2025, 37(3):1-12.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20250301 |
|
| [11] | 周建民. 古碱矿中几种岩石矿物的地质意义[J]. 化工地质, 1987, 9(2):62-67. |
| ZHOU Jianmin. The geological significance of several rock minerals in paleo-alkaline deposits[J]. Geology of Chemical Minerals, 1987, 9(2):62-67. | |
| [12] | 范萌萌, 卜军, 赵筱艳, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东南部延长组微量元素地球化学特征及环境指示意义[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 49(4):633-642. |
| FAN Mengmeng, BU Jun, ZHAO Xiaoyan, et al. Geochemical characteristics and environmental implications of trace elements of Yanchang formation in southeastern Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 49(4):633-642. | |
| [13] | 王峰, 刘玄春, 邓秀芹, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地纸坊组微量元素地球化学特征及沉积环境指示意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2017, 35(6):1265-1273. |
| WANG Feng, LIU Xuanchun, DENG Xiuqin, et al. Geochemical characteristics and environmental implications of trace elements of Zhifang Formation in Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2017, 35(6):1265-1273. | |
| [14] | 刘安, 陈林, 陈孝红, 等. 湘中坳陷泥盆系碳氧同位素特征及其古环境意义[J]. 地球科学, 2021, 46(4):1269-1281. |
| LIU An, CHEN Lin, CHEN Xiaohong, et al. Carbon and oxygen isotopic characteristics of Devonian in central Hunan depression and its paleoenvironmental significance[J]. Earth Science, 2021, 46(4):1269-1281. | |
| [15] | 刘庆. 渤海湾盆地东营凹陷烃源岩碳氧同位素组成及地质意义[J]. 石油实验地质, 2017, 39(2):247-252. |
| LIU Qing. Composition and geologic significance of carbon and oxygen isotopes in hydrocarbon source rocks,Dongying Sag,Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2017, 39(2):247-252. | |
| [16] | 伊海生, 林金辉, 周恳恳, 等. 青藏高原北部新生代湖相碳酸盐岩碳氧同位素特征及古环境意义[J]. 古地理学报, 2007, 9(3):303-312. |
| YI Haisheng, LIN Jinhui, ZHOU Kenken, et al. Carbon and oxygen isotope characteristics and palaeoenvironmental implication of the Cenozoic lacustrine carbonate rocks in northern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography (Chinese Edition), 2007, 9(3):303-312. | |
| [17] | 刘传联, 赵泉鸿, 汪品先. 湖相碳酸盐氧碳同位素的相关性与生油古湖泊类型[J]. 地球化学, 2001, 30(4):363-367. |
|
LIU Chuanlian, ZHAO Quanhong, WANG Pinxian. Correlation between carbon and oxygen isotopic ratios of lacustrine carbonates and types of oil-producing paleolakes[J]. Geochimica, 2001, 30(4):363-367.
doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(66)90009-3 |
|
| [18] | 曲长胜, 邱隆伟, 杨勇强, 等. 吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组碳酸盐岩碳氧同位素特征及其古湖泊学意义[J]. 地质学报, 2017, 91(3):605-616. |
| QU Changsheng, QIU Longwei, YANG Yongqiang, et al. Carbon and oxygen isotope compositions of carbonatic rock from Permian Lucaogou Formation in the Jimsar Sag,NW China and their paleolimnological significance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2017, 91(3):605-616. | |
| [19] | 刘海艳, 刘兴周, 蔡国刚, 等. 奈曼凹陷北部义县组—九佛堂组沉积-地球化学环境恢复及其意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2025, 44(2):325-344. |
| LIU Haiyan, LIU Xingzhou, CAI Guogang, et al. Sedimentary geochemical environment restoration of Yixian Formation and Jiufotang Formation in the northern part of Naiman sag and its signification[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2025, 44(2):325-344. | |
| [20] |
JOMES B, MANNING D A C. Comparison of geochemical indices used for the interpretation of palaeoredox conditions in ancient mudstones[J]. Chemical Geology, 1994, 111(1):111-129.
doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(94)90085-X |
| [21] | 李作臣. 奈曼凹陷奈1区块CO2地球化学特征及成因分析[J]. 长江大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 8(6):25-28. |
| LI Zuochen. Characteristics and genetic analysis of CO2 in block Nai1 of Naiman Depression[J]. Journal of Yangtze University (Nature Science Edition), 2011, 8(6):25-28. | |
| [22] | 刘晋龙, 王国芝, 李娜, 等. 准噶尔盆地风城组硅硼钠石中包裹体特征及其地质意义[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2024, 44(2):326-338. |
| LIU Jinlong, WANG Guozhi, LI Na, et al. Characteristics and geological significance of inclusions in searlesite from the Fengcheng Formation in the Junggar Basin,China[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2024, 44(2):326-338. | |
| [23] | 张幼勋. 河南吴城天然碱矿床地质特征及成因探讨[J]. 化工地质, 1980, 2(3):66-88. |
| ZHANG Youxun. Geological characteristics and genesis of the Wucheng natural soda deposit in Henan[J]. Geology of Chemical Minerals, 1980, 2(3):66-88. | |
| [24] | 李玉堂, 袁标, 刘成林, 等. 国内水硅硼钠石的首次发现[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 1990, 9(2):170-174. |
| LI Yutang, YUAN Biao, LIU Chenglin, et al. Searlesite disco-vered for the first time in China[J]. Acta Petrologica et Minera-logica, 1990, 9(2):170-174. |
|
||