岩性油气藏 ›› 2026, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (1): 100–114.doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20260109
• 地质勘探 • 上一篇
下扬子地区萍乐坳陷二叠系乐平组煤系页岩储层特征及勘探潜力
肖富强1,2,3( ), 肖卫东2, 姜智东2, 高磊3, 赵正威3, 潘晓飞3, 陈富贵2, 邹勇军1,2(
), 肖卫东2, 姜智东2, 高磊3, 赵正威3, 潘晓飞3, 陈富贵2, 邹勇军1,2( )
)
- 1
关键矿产资源勘查与开发江西省重点实验室 南昌 330001
2江西省煤田地质勘察研究院 南昌 330001
3新疆维吾尔自治区地质局 煤田地质中心 乌鲁木齐 830009
Coal measure shale reservoir characteristics and exploration potential of Permian Leping Formation in Pingle Depression of Lower Yangtze region
XIAO Fuqiang1,2,3( ), XIAO Weidong2, JIANG Zhidong2, GAO Lei3, ZHAO Zhengwei3, PAN Xiaofei3, CHEN Fugui2, ZOU Yongjun1,2(
), XIAO Weidong2, JIANG Zhidong2, GAO Lei3, ZHAO Zhengwei3, PAN Xiaofei3, CHEN Fugui2, ZOU Yongjun1,2( )
)
- 1
Jiangxi Key Laboratory of Critical Mineral Resources Exploration and Development Nanchang 330001, China
2Jiangxi Coalfield Geological Survey Institute Nanchang 330001, China
3Coalfield Geological Center of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region Geological Bureau Urumqi 830000, China
摘要:
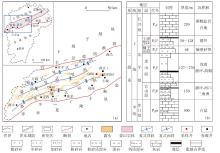
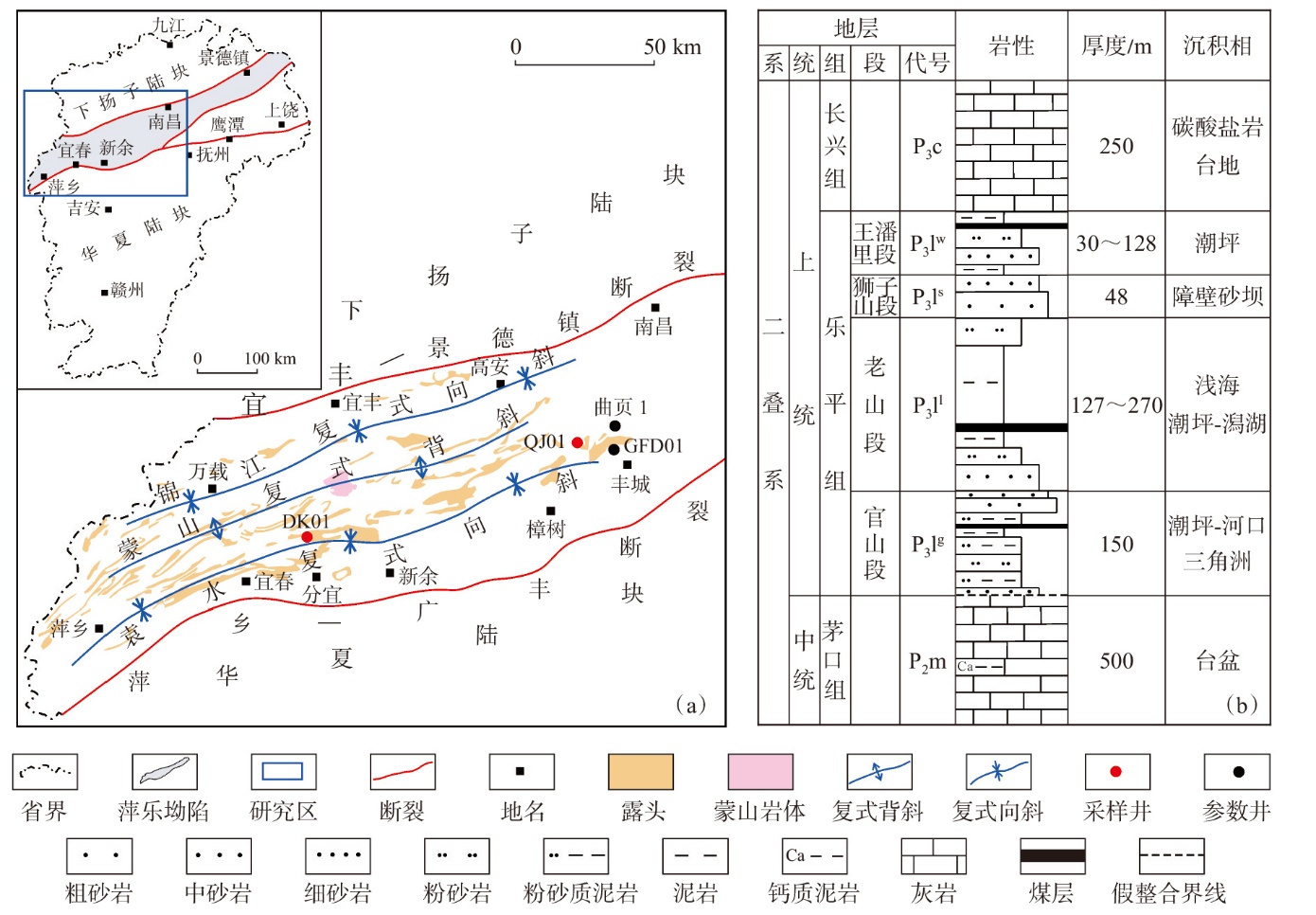
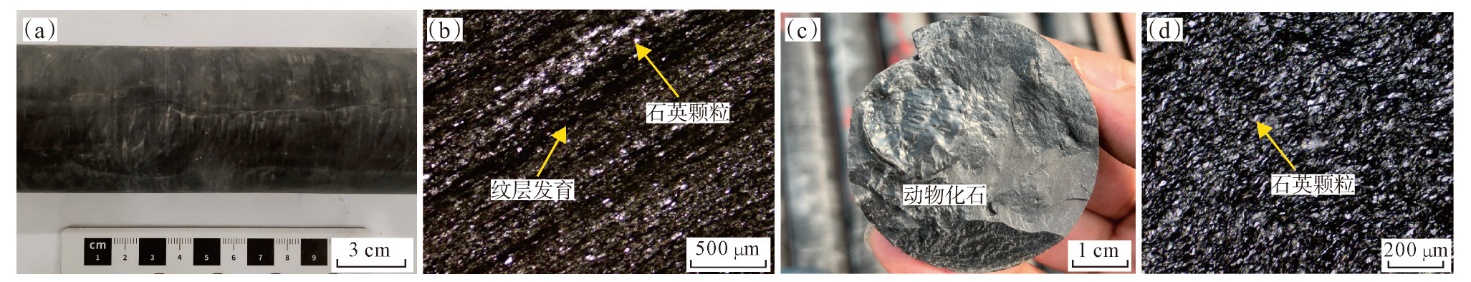
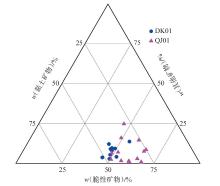
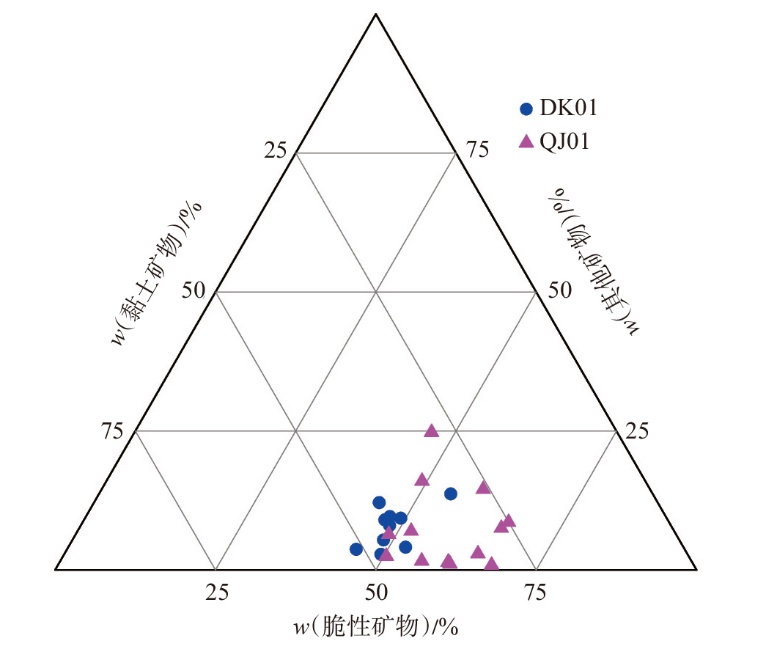
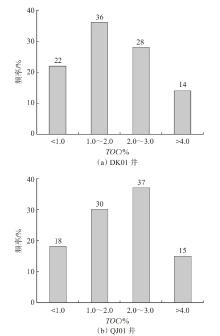
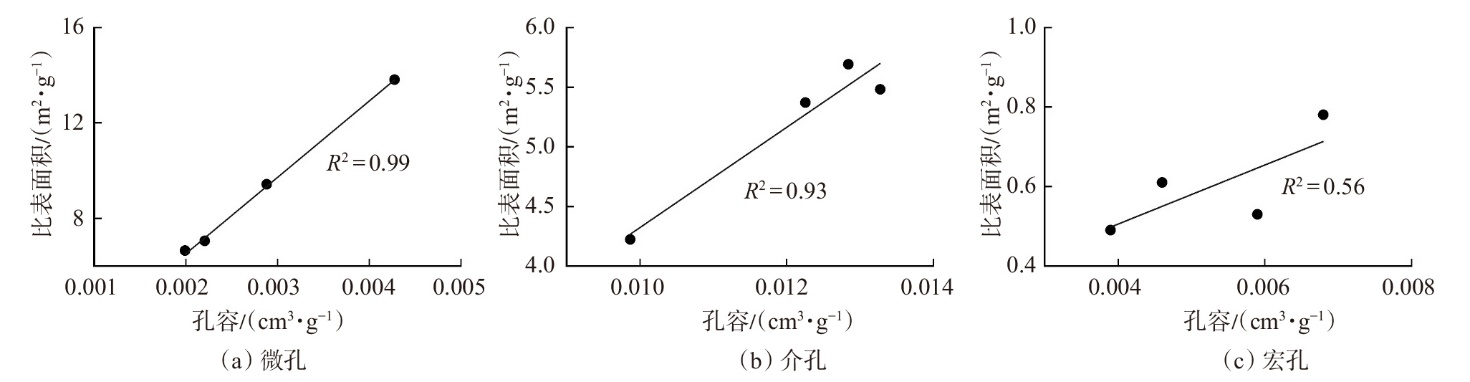
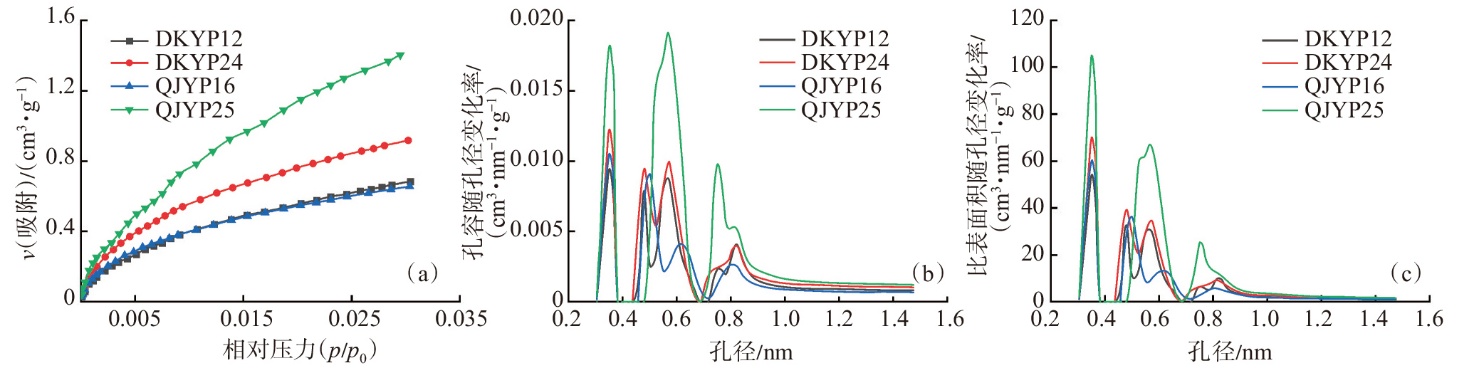
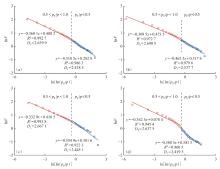
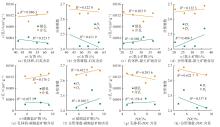
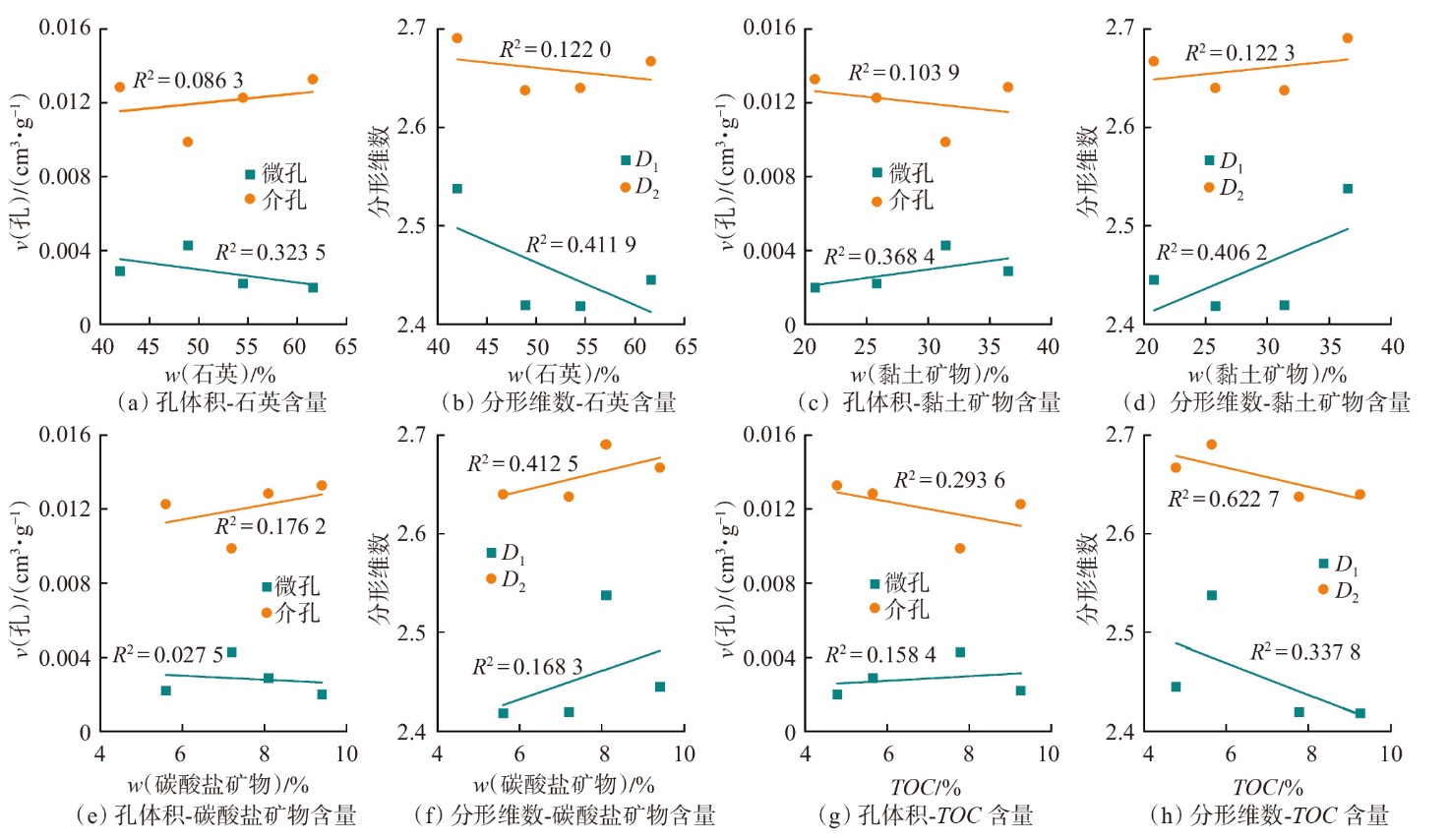
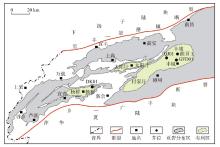
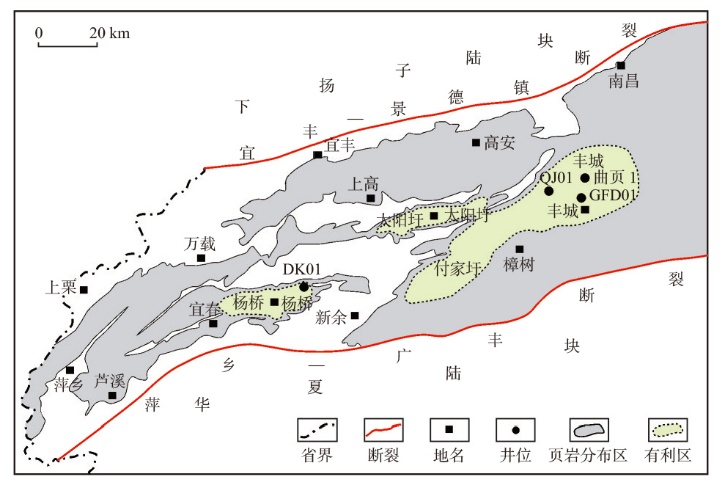
萍乐坳陷上二叠统乐平组是华南地区重要的含煤地层,具有较好的煤系页岩气成藏条件。采用薄片鉴定、X射线衍射、有机地球化学分析、扫描电镜、高压压汞、低温N2和CO2吸附等多种测试手段,对萍乐坳陷西段乐平组煤系页岩储层矿物组成、有机地球化学特征、孔隙类型、孔隙结构及孔隙发育影响因素等进行了研究,并探讨了页岩气勘探前景。研究结果表明:①下扬子地区萍乐坳陷二叠系乐平组煤系页岩主要由碎屑颗粒、泥质和炭质构成,脆性矿物含量较高,可压裂性较好;TOC含量较高,干酪根类型为Ⅱ1,Ⅲ型,热演化达到高成熟—过成熟阶段。②页岩孔隙度大多为3.75%~4.67%,渗透率大多为0.006 2~0.009 1 mD,具有低孔、低渗特征;孔隙类型以粒间孔、粒内孔及微裂缝为主,有机质孔较少。③页岩平均孔容为0.020 2 cm3/g,平均比表面积为15.02 m2/g,介孔对总孔容的贡献最大,微孔对总比表面积的贡献最大,孔径具有“多峰态”分布特征。④石英和碳酸盐矿物能促进介孔、抑制微孔的发育,石英含量增加降低了孔隙非均质性,碳酸盐矿物增加则提高孔隙非均质性;黏土矿物和有机质均能促进微孔、抑制介孔的发育,黏土矿物增加提高了孔隙非均质性,有机质则增强了孔隙均质性。⑤研究区煤系页岩的可压裂性、生烃潜力和储集能力均较好,且保存条件良好,优选出杨桥、丰城、付家圩、太阳圩为煤系页岩气勘探有利区,其中丰城地区可作为下一步勘探重点目标区。
中图分类号:
- TE121.31
| [1] | 邹才能, 陶士振, 白斌, 等. 论非常规油气与常规油气的区别和联系[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2015, 20(1):1-16. |
| ZOU Caineng, TAO Shizhen, BAI Bin, et al. Differences and relations between unconventional and conventional oil and gas[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2015, 20(1):1-16. | |
| [2] |
邹才能, 杨智, 黄士鹏, 等. 煤系天然气的资源类型、形成分布与发展前景[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2019, 46(3):433-442.
doi: 10.11698/PED.2019.03.02 |
| ZOU Caineng, YANG Zhi, HUANG Shipeng, et al. Resource types,formation,distribution and prospects of coal-measure gas[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2019, 46(3):433-442. | |
| [3] | 李阳阳, 李贤庆, 张学庆, 等. 沁水盆地阳泉区块上古生界煤系页岩气储层特征[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2021, 49(2):142-151. |
| LI Yangyang, LI Xianqing, ZHANG Xueqing, et al. Characteri-stics of shale gas reservoir in Upper Paleozoic coal measures in Yangquan block,Qinshui Basin[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2021, 49(2):142-151. | |
| [4] |
CAO Taotao, DENG Mo, XIAO Juanyi, et al. Reservoir characteristics of marine-continental transitional shale and gas-bearing mechanism: Understanding based on comparison with marine shale reservoir[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Geoscience, 2023, 8(3):169-185.
doi: 10.1016/j.jnggs.2023.03.004 |
| [5] |
杨学锋, 赵圣贤, 刘勇, 等. 四川盆地宁西地区奥陶系五峰组—志留系龙马溪组页岩气富集主控因素[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2024, 36(5):99-110.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20240510 |
|
YANG Xuefeng, ZHAO Shengxian, LIU Yong, et al. Main controlling factors of shale gas enrichment of Ordovician Wufeng Formation-Silurian Longmaxi Formation in Ningxi area,Sichuan Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2024, 36(5):99-110.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20240510 |
|
| [6] |
郭旭升, 王濡岳, 申宝剑, 等. 中国页岩气地质特征、资源潜力与发展方向[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2025, 52(1):15-28.
doi: 10.11698/PED.20240380 |
| GUO Xusheng, WANG Ruyue, SHEN Baojian, et al. Geological characteristics,resource potential,and development direction of shale gas in China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2025, 52(1):15-28. | |
| [7] | 邹才能, 董大忠, 熊伟, 等. 中国页岩气新区带、新层系和新类型勘探进展、挑战及对策[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2024, 45(2):309-326. |
| ZOU Caineng, DONG Dazhong, XIONG Wei, et al. Advances, challenges, and countermeasures in shale gas exploration of underexplored plays,sequences and new types in China[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2024, 45(2):309-326. | |
| [8] | 林腊梅, 张金川, 唐玄, 等. 中国陆相页岩气的形成条件[J]. 天然气工业, 2013, 33(1):35-40. |
| LIN Lamei, ZHANG Jinchuan, TANG Xuan, et al. Conditions of continental shale gas accumulation in China[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2013, 33(1):35-40. | |
| [9] | 胡宗全, 王濡岳, 路菁, 等. 陆相页岩及其夹层储集特征对比与差异演化模式[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2023, 44(6):1393-1404. |
| HU Zongquan, WANG Ruyue, LU Jing, et al. Storage characteri-stic comparison of pores between lacustrine shales and their interbeds and differential evolutionary patterns[J]. Oil & Gas Geo-logy, 2023, 44(6):1393-1404. | |
| [10] |
YANG Xiaoguang, GUO Shaobin. Reservoirs characteristics and environments evolution of lower permian transitional shale in the Southern North China Basin:Implications for shale gas exploration[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2021, 96:104282.
doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2021.104282 |
| [11] | 郭少斌, 付娟娟, 高丹, 等. 中国海陆交互相页岩气研究现状与展望[J]. 石油实验地质, 2015, 37(5):535-540. |
| GUO Shaobin, FU Juanjuan, GAO Dan, et al. Research status and prospects for marine-continental shale gases in China[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2015, 37(5):535-540. | |
| [12] | 马新华, 张晓伟, 熊伟, 等. 中国页岩气发展前景及挑战[J]. 石油科学通报, 2023, 8(4):491-501. |
| MA Xinhua, ZHANG Xiaowei, XIONG Wei, et al. Prospects and challenges of shale gas development in China[J]. Petroleum Science Bulletin, 2023, 8(4):491-501. | |
| [13] | 肖富强, 章双龙, 祁星. 萍乐坳陷地区吴家坪期沉积环境的元素地球化学指示[J]. 东华理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 43(3) :231-239. |
| XIAO Fuqiang, ZHANG Shuanglong, QI Xing. Elemental geochemical indication of sedimentary environment in Wujiaping period of Pingle depression area[J]. Journal of East China University of Technology (Natural Science), 2020, 43(3):231-239. | |
| [14] | 俞宽坤. 萍乐坳陷上二叠统乐平组泥页岩储层特征[J]. 中国地质, 2016, 43(2):520-530. |
| YU Kuankun. Reservoir characteristics of Upper Permian Leping Formation shale in Pingle Depression[J]. Geology in China, 2016, 43(2):520-530. | |
| [15] | 谢德湘, 靳凯, 易志东, 等. 江西萍乐坳陷曲江向斜乐平组页岩储层特征[J]. 非常规油气, 2018, 5(3):1-7. |
| XIE Dexiang, JIN Kai, YI Zhidong, et al. Reservoir characteristics of shale gas reservoir of Leping Group in Qujiang Syncline,Ping-Le Depression,Jiangxi Province[J]. Unconventional Oil & Gas, 2018, 5(3):1-7. | |
| [16] | 吴小力, 李荣西, 李尚儒, 等. 下扬子地区海陆过渡相页岩气成藏条件与主控因素:以萍乐坳陷二叠系乐平组为例[J]. 地质科技情报, 2018, 37(1):160-168. |
| WU Xiaoli, LI Rongxi, LI Shangru, et al. Accumulation conditions and main factors of marine-continental transitional shale gas in the Lower Yangtze Area of China:A case of Permian Le-ping Formation in the Pingle Depression[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2018, 37(1):160-168. | |
| [17] | 王修齐, 滕龙, 郑红军, 等. 下扬子丰城—乐平地区二叠系乐平组页岩气潜力综合评价[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2019, 49(1):248-260. |
| WANG Xiuqi, TENG Long, ZHENG Hongjun, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of shale gas potential of Permian Leping Formation in Fengcheng-Leping area of Lower Yangtze Region[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2019, 49(1):248-260. | |
| [18] | 陈哲, 王中鹏, 李尚儒. 萍乐坳陷曲页1井乐平组页岩气和煤层气地质条件分析[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2019, 26(4):50-55. |
| CHEN Zhe, WANG Zhongpeng, LI Shangru. Geological condition analysis of shale gas and coalbed methane of Leping Formation in Well Quye1 of Pingle Depression[J]. Petroleum Geo-logy and Recovery Efficiency, 2019, 26(4):50-55. | |
| [19] | 滕龙, 沈雪华, 方朝刚, 等. 萍乐坳陷中部GFD1井页岩气富集模式[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2020, 50(3):757-767. |
| TENG Long, SHEN Xuehua, FANG Chaogang, et al. Shale gas enrichment model of Well GFD01 in Middle Pingle Depression,Jiangxi province[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Sci-ence Edition), 2020, 50(3):757-767. | |
| [20] | 蒋裕强, 董大忠, 漆麟, 等. 页岩气储层的基本特征及其评价[J]. 天然气工业, 2010, 30(10):7-12. |
| JIANG Yuqiang, DONG Dazhong, QI Lin, et al. Basic features and evaluation of shale gas reservoirs[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2010, 30(10):7-12. | |
| [21] | 张曼婷, 付炜, 姜秉仁, 等. 黔北煤田上二叠统龙潭组煤系页岩气储层特征与勘探潜力评价[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2022, 50(8):133-139. |
| ZHANG Manting, FU Wei, JIANG Bingren, et al. Shale gas reser-voir characteristics and exploration potential analysis of Longtan Formation of the upper Permian Series in Qianbei Coalfield[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2022, 50(8):133-139. | |
| [22] | 许德如, 王力, 王智琳, 等. 江西萍乐凹陷构造-沉积演化的基本特征及对找煤预测的启示[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2011, 25(4):513-524. |
| XU Deru, WANG Li, WANG Zhilin, et al. Tectonic-sedimentary characteristics of the Ping (Pingxiang)-Le (Leping) Depression in Jiangxi Province and its implications on coal mineral resource prospecting[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2011, 25(4):513-524. | |
| [23] | 王昆, 吴安国, 张玉清. 江西省区域地质概况[J]. 中国区域地质, 1993(3):200-210. |
| WANG Kun, WU Anguo, ZHANG Yuqing. A brief account of regional geology of Jiangxi Province[J]. Regional Geology of China, 1993(3):200-210. | |
| [24] | 陶传奇, 王延斌, 倪小明, 等. 临兴地区下二叠统太原组页岩气地质特征及勘探潜力[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2023, 51(5):140-148. |
| TAO Chuanqi, WANG Yanbin, NI Xiaoming, et al. Shale gas geological characteristics and exploration potential of lower Permian Taiyuan Formation in Linxing area[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2023, 51(5):140-148. | |
| [25] |
杨跃明, 张少敏, 金涛, 等. 川南地区二叠系龙潭组页岩储层特征及勘探潜力[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2023, 35(1):1-11.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20230101 |
|
YANG Yueming, ZHANG Shaomin, JIN Tao, et al. Characteristics and exploration potential of shale reservoirs of Permian Longtan Formation in southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2023, 35(1):1-11.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20230101 |
|
| [26] |
卢树藩, 陈厚国. 黔南地区麻页1井寒武系牛蹄塘组页岩特征及页岩气勘探前景[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2017, 22(3):81-87.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2017.03.010 |
|
LU Shufan, CHEN Houguo. Shale characteristics and shale gas exploration prospect in Cambrian Niutitang Formation in Well MY-1,southern Guizhou[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2017, 22(3):81-87.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2017.03.010 |
|
| [27] |
WANG Yang, QIN Yong, YANG Liu, et al. Organic geochemical and petrographic characteristics of the coal measure source rocks of Pinghu Formation in the Xihu Sag of the East China sea shelf basin:Implications for coal measure gas potential[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 2020, 94(2):364-375.
doi: 10.1111/acgs.v94.2 |
| [28] | 王文强, 何金先, 曹文杰. 织纳地区龙潭组煤系页岩气储层特征与勘探潜力评价[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2024, 24(20):8409-8418. |
| WANG Wenqiang, HE Jinxian, CAO Wenjie. Evaluation of shale gas reservoir characteristics and exploration potential of Longtan Formation in Zhina area[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2024, 24(20):8409-8418. | |
| [29] | BOYER C, KIESCHNICK J, SUAREZ-RIVERA R, et al. Producing gas from its source[J]. Oilfield Review, 2006, 18:36-49. |
| [30] |
白玉彬, 李梦瑶, 朱涛, 等. 玛湖凹陷二叠系风城组烃源岩地球化学特征及页岩油“甜点”评价[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2024, 36(6):110-121.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20240611 |
|
BAI Yubin, LI Mengyao, ZHU Tao, et al. Geochemical characteristics of source rocks and evaluation of shale oil “sweet spot” of Permian Fengcheng Formation in Mahu Sag[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2024, 36(6):110-121.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20240611 |
|
| [31] | 郭旭升, 胡东风, 刘若冰, 等. 四川盆地二叠系海陆过渡相页岩气地质条件及勘探潜力[J]. 天然气工业, 2018, 38(10):11-18. |
| GUO Xusheng, HU Dongfeng, LIU Ruobing, et al. Geological conditions and exploration potential of Permian marine-continent transitional facies shale gas in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2018, 38(10):11-18. | |
| [32] |
仇秀梅, 刘亚东, 董学林. 鄂西建始地区大隆组页岩有机地球化学特征[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2019, 31(2):96-104.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20190211 |
|
QIU Xiumei, LIU Yadong, DONG Xuelin. Organic geochemical characteristics of shale from Dalong Formation in Jianshi area,western Hubei[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2019, 31(2):96-104.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20190211 |
|
| [33] | 肖富强, 夏为平, 肖卫东, 等. 江西丰城矿区二叠系乐平组B4煤层气地质条件与勘探前景[J]. 东华理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2025, 48(2):142-154. |
| XIAO Fuqiang, XIA Weiping, XIAO Weidong, et al. Geological conditions and exploration prospects of coalbed methane in the B4coal seam of the Permian Leping Formation in Fengcheng mining area,Jiangxi Province[J]. Journal of East China University of Technology (Natural Science), 2025, 48(2):142-154. | |
| [34] |
陆江, 王健, 吴楠, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地西缘奥陶系乌拉力克组页岩气勘探潜力[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2025, 37(5):34-48.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20250504 |
|
LU Jiang, WANG Jian, WU Nan, et al. Exploration potential of shale gas in Ordovician Wulalike Formation in the western margin of Ordos Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2025, 37(5):34-48.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20250504 |
|
| [35] | 贾立龙, 舒建生, 姜在炳, 等. 黔西海陆过渡相煤系页岩气成藏条件及储层特征研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2021, 49(10):201-207. |
| JIA Lilong, SHU Jiansheng, JIANG Zaibing, et al. Study on formation conditions and reservoir characteristics of marine-terri-genous facies coal measures shale gas in western Guizhou[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2021, 49(10):201-207. | |
| [36] |
LOUCKS R G, REED R M, RUPPEL S C, et al. Spectrum of pore types and networks in mudrocks and a descriptive classification for matrix-related mudrock pores[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2012, 96(6):1071-1098.
doi: 10.1306/08171111061 |
| [37] |
罗冰, 文华国, 廖义沙, 等. 川东北地区二叠系吴家坪组二段页岩储层特征及有利区分布[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2025, 37(1):1-12.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20250101 |
|
LUO Bing, WEN Huaguo, LIAO Yisha, et al. Shale reservoirs characteristics and favorable areas distribution of the second member of Permian Wujiaping Formation in northeastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2025, 37(1):1-12.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20250101 |
|
| [38] | 杨峰, 宁正福, 胡昌蓬, 等. 页岩储层微观孔隙结构特征[J]. 石油学报, 2013, 34(2):301-311. |
|
YANG Feng, NING Zhengfu, HU Changpeng, et al. Characteri-zation of microscopic pore structures in shale reservoirs[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2013, 34(2):301-311.
doi: 10.7623/syxb201302012 |
|
| [39] |
ROUQUEROL J, AVNIR D, FAIRBRIDGE C W, et al. Recommendations for the characterization of porous solids (Technical Report)[J]. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 1994, 66(8):1739-1785.
doi: 10.1351/pac199466081739 |
| [40] | 张敏, 李贤庆, 张吉振, 等. 新疆阜康地区八道湾组煤系页岩气储层孔隙结构特征[J]. 地球化学, 2020, 49(1):95-107. |
| ZHANG Min, LI Xianqing, ZHANG Jizhen, et al. Pore structure characteristics of a shale gas reservoir from coal measures in the Badaowan Formation,Fukang area of the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region[J]. Geochimica, 2020, 49(1):95-107. | |
| [41] | 王馨佩, 刘成林, 蒋立伟, 等. 渝西大安地区五峰组—龙马溪组深层页岩微观孔隙结构与含气性控制因素[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2025, 46(1):230-245. |
| WANG Xinpei, LIU Chenglin, JIANG Liwei, et al. Pore microstructure and its controlling effects on gas content of deep shale reservoirs in the Wufeng-Longmaxi formations,Da’an area,western Chongqing[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2025, 46(1):230-245. | |
| [42] |
THOMMES M, KANEKO K, NEIMARK A V, et al. Physisorption of gases,with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report)[J]. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 2015, 87(9/10):1051-1069.
doi: 10.1515/pac-2014-1117 |
| [43] |
BAI Longhui, LIU Bo, FU Xiaofei, et al. A new method for evaluating the oil mobility based on the relationship between pore structure and state of oil[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 2023, 14(6):101684.
doi: 10.1016/j.gsf.2023.101684 |
| [44] | 徐勇, 吕成福, 陈国俊, 等. 川东南龙马溪组页岩孔隙分形特征[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2015, 27(4):32-39. |
|
XU Yong, LYU Chengfu, CHEN Guojun, et al. Fractal characteristics of shale pores of Longmaxi Formation in southeast Sichuan Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2015, 27(4):32-39.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2015.04.005 |
|
| [45] | 顾天甫, 孙豪飞, 张雪莹, 等. 川东地区吴家坪组页岩储层孔隙结构及发育控制因素[J]. 断块油气田, 2025, 32(1):1-9. |
| GU Tianfu, SUN Haofei, ZHANG Xueying, et al. Pore structure and development control factors of shale reservoirs in Wujiaping Formation,eastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2025, 32(1):1-9. | |
| [46] | 陈居凯, 朱炎铭, 崔兆帮, 等. 川南龙马溪组页岩孔隙结构综合表征及其分形特征[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2018, 30(1):55-62. |
|
CHEN Jukai, ZHU Yanming, CUI Zhaobang, et al. Pore structure and fractal characteristics of Longmaxi shale in southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2018, 30(1):55-62.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2018.01.006 |
|
| [47] | 贺小标, 罗群, 李鑫, 等. 陆相混积页岩不同岩相孔隙差异特征及影响机制:以吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系芦草沟组为例[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2024, 53(1):141-157. |
| HE Xiaobiao, LUO Qun, LI Xin, et al. Characteristics of pore differences between different lithofacies of continental mixed shale and the influencing mechanism:An example from the Permian Lucaogou Formation in the Jimusar Depression[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2024, 53(1):141-157. | |
| [48] |
罗思聪, 张南希, 王保保, 等. 川南下寒武统筇竹寺组页岩孔隙结构特征及其主控因素[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 46(6):91-106.
doi: 10.11885/j.issn.1674-5086.2024.12.05.04 |
| LUO Sicong, ZHANG Nanxi, WANG Baobao, et al. Pore structure characteristics and main controlling factors of Qiongzhusi Formation shales of Lower Cambrian, Southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University (Science & Technology Edition), 2024, 46(6):91-106. | |
| [49] |
郭旭升, 胡东风, 李宇平, 等. 涪陵页岩气田富集高产主控地质因素[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2017, 44(4):481-491.
doi: 10.11698/PED.2017.04.01 |
|
GUO Xusheng, HU Dongfeng, LI Yuping, et al. Geological factors controlling shale gas enrichment and high production in Fuling shale gas field[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2017, 44(4):481-491.
doi: 10.11698/PED.2017.04.01 |
|
| [50] | 倪冬梅. 松辽盆地梨树断陷陆相页岩储层地质特征及地质意义[J]. 非常规油气, 2021, 8(3):33-42. |
| NI Dongmei. Geological features of continental shale reservoir in Lishu fault depression of Songliao Basin[J]. Unconventional Oil & Gas, 2021, 8(3):33-42. | |
| [51] |
何贵松, 何希鹏, 高玉巧, 等. 中国南方3套海相页岩气成藏条件分析[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2019, 31(1):57-68.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20190107 |
|
HE Guisong, HE Xipeng, GAO Yuqiao, et al. Analysis of accu-mulation conditions of three sets of marine shale gas in southern China[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2019, 31(1):57-68.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20190107 |
|
| [52] | 李世臻, 周志, 李飞, 等. 鄂西—渝东地区上二叠统大隆组页岩气富集条件与勘探有利区[J]. 天然气工业, 2024, 44(5):1-15. |
| LI Shizhen, ZHOU Zhi, LI Fei, et al. Shale gas enrichment conditions and favorable exploration areas of Upper Permian Dalong Formation in the western Hubei and eastern Chongqing region[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2024, 44(5):1-15. | |
| [53] | 中华人民共和国自然资源部. [S]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2021. |
| Ministry of Natural Resources,People’s Republic of China. [S]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2021. |
| [1] | 刘冠伯, 陈世加, 李世宏, 邹阳, 李勇. 玛湖凹陷玛中构造带二叠系风城组烃源岩生气潜力及成藏条件[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2025, 37(5): 83-96. |
| [2] | 叶慧, 朱峰, 王贵重, 石万忠, 康晓宁, 董国宁, 娜孜依曼, 王任. 准噶尔盆地二叠纪—侏罗纪古地貌恢复及其油气地质意义[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2025, 37(5): 122-132. |
| [3] | 詹淋, 范存辉, 唐雯, 杨西燕, 刘冬玺, 李博, 杨昕睿. 四川盆地东部南雅地区二叠系吴家坪组构造特征及其控藏机制[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2025, 37(5): 133-144. |
| [4] | 王青, 田冲, 罗超, 张景缘, 杨雪, 吴伟, 陶夏妍. 四川盆地遂宁—合江地区二叠系龙潭组煤岩气储层特征及勘探前景[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2025, 37(4): 26-37. |
| [5] | 王敬朝, 金玮, 常立朋, 董忠良, 王高文. 川中合川—潼南地区二叠系茅三段岩溶储层特征及油气成藏过程[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2025, 37(4): 63-72. |
| [6] | 杨雪, 杨雨然, 张景缘, 田鹤, 王青, 宋芳, 张赛柯, 陈瑶. 川北地区开江—梁平海槽二叠系海相页岩特征及优质储层形成机制[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2025, 37(3): 108-119. |
| [7] | 赵艾琳, 赖强, 樊睿琦, 吴煜宇, 陈杰, 严双栏, 张家伟, 廖广志. 基性火山岩核磁共振响应机理及孔隙结构评价方法——以四川盆地西南部二叠系峨眉山玄武岩组为例[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2025, 37(3): 153-164. |
| [8] | 林鹤, 杜金玲, 徐刚, 容娇君, 梁雪莉, 衡峰, 郭俊宁, 马梦茜. 随机森林算法在水力压裂套管变形预测中的应用[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2025, 37(3): 185-193. |
| [9] | 李亚, 王尉, 赵立可, 刘冉, 张玺华, 陈延贵, 黄天海, 肖笛. 四川盆地德阳—绵阳凹陷南缘二叠系栖霞组沉积演化及有利储层分布[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2025, 37(2): 81-91. |
| [10] | 罗冰, 文华国, 廖义沙, 张兵, 姚永君, 温思宇, 杨凯. 川东北地区二叠系吴家坪组二段页岩储层特征及有利区分布[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2025, 37(1): 1-12. |
| [11] | 钱永新, 赵毅, 刘新龙, 刘鸿, 刘国梁, 朱涛, 邹阳, 陈方文. 玛湖凹陷二叠系风城组页岩油储层特征及高产主控因素[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2025, 37(1): 115-125. |
| [12] | 余琪祥, 罗宇, 段铁军, 李勇, 宋在超, 韦庆亮. 准噶尔盆地环东道海子凹陷侏罗系煤层气成藏条件及勘探方向[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2024, 36(6): 45-55. |
| [13] | 白玉彬, 李梦瑶, 朱涛, 赵靖舟, 任海姣, 吴伟涛, 吴和源. 玛湖凹陷二叠系风城组烃源岩地球化学特征及页岩油“甜点”评价[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2024, 36(6): 110-121. |
| [14] | 王义凤, 田继先, 李剑, 乔桐, 刘成林, 张景坤, 沙威, 沈晓双. 玛湖凹陷西南地区二叠系油气藏相态类型及凝析油气地球化学特征[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2024, 36(6): 149-159. |
| [15] | 洪智宾, 吴嘉, 方朋, 余进洋, 伍正宇, 于佳琦. 纳米限域下页岩中可溶有机质的非均质性及页岩油赋存状态[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2024, 36(6): 160-168. |
|
||








 甘公网安备 62010202002827号
甘公网安备 62010202002827号