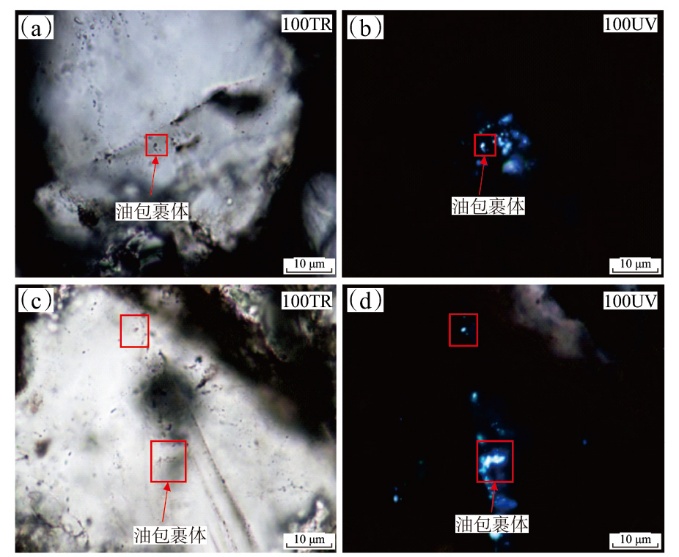
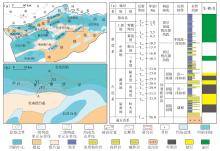
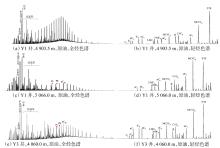
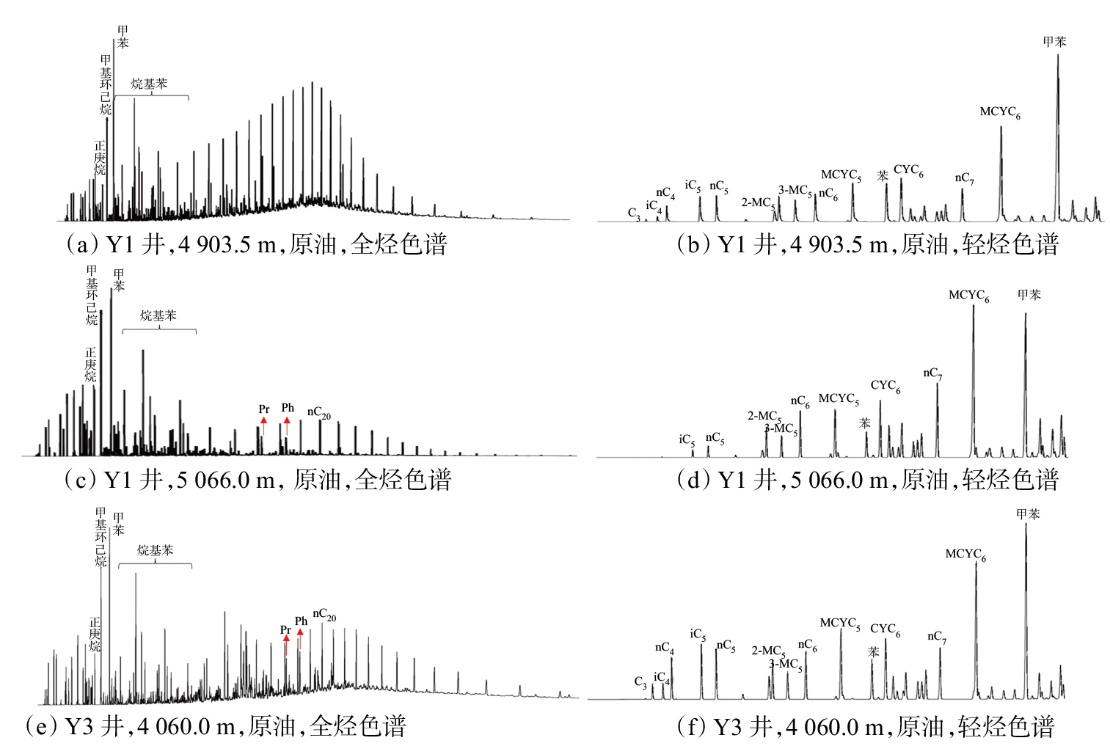
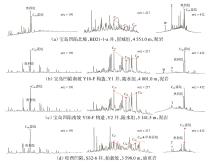
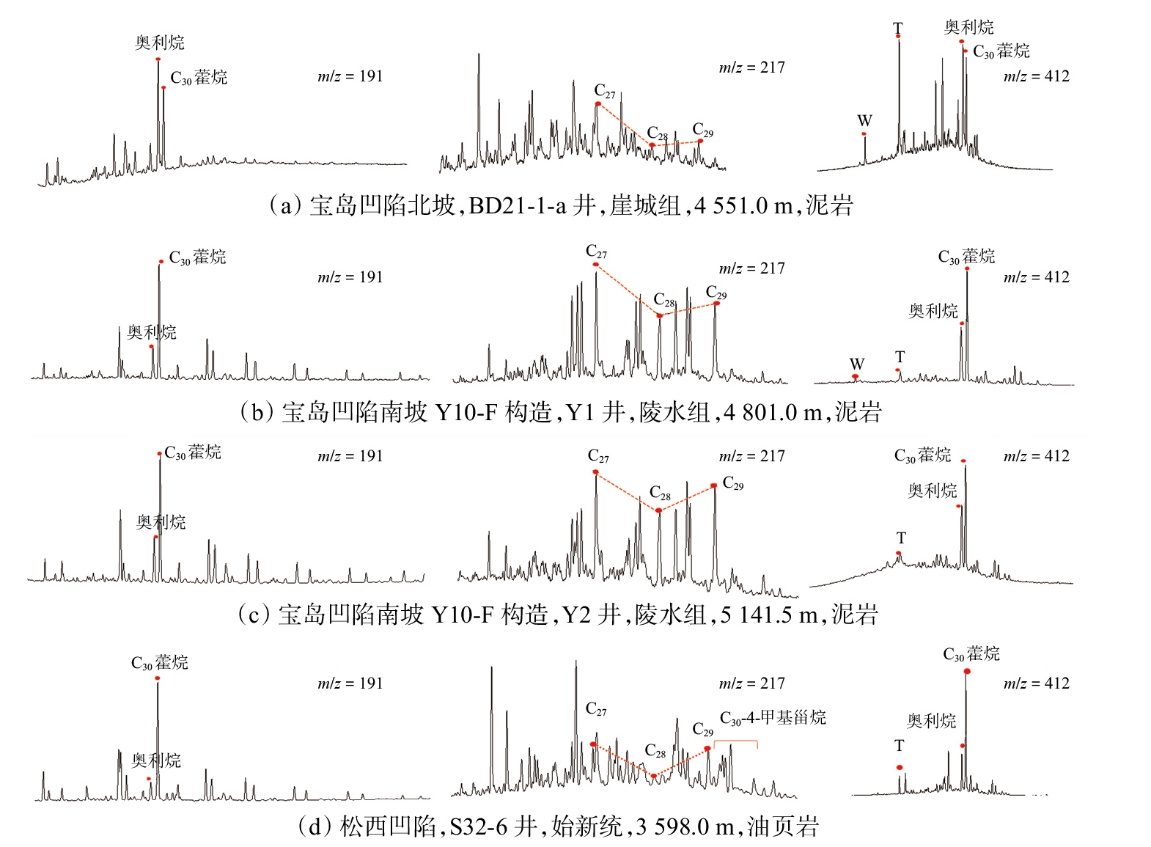
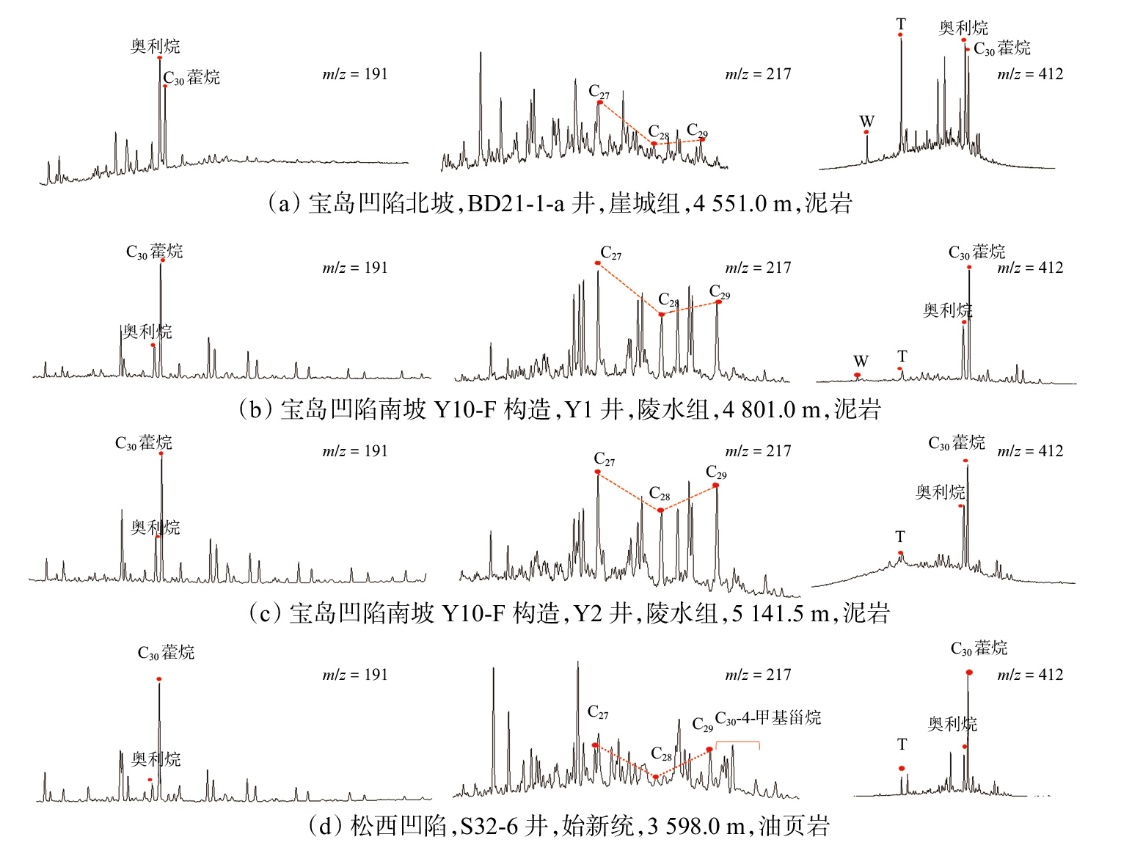
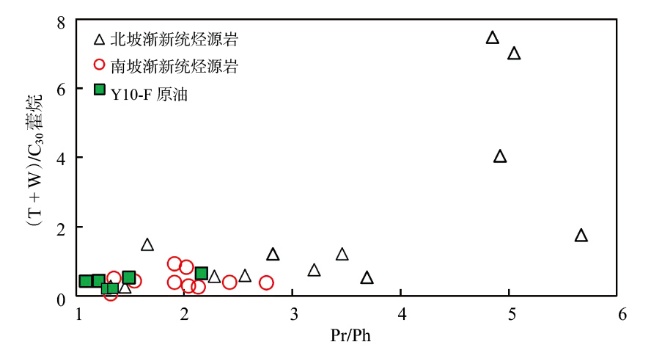
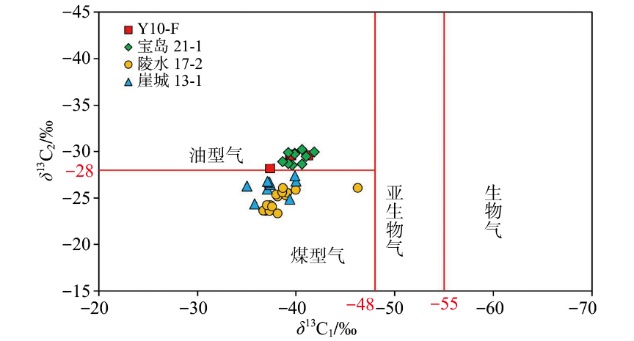
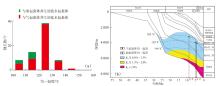
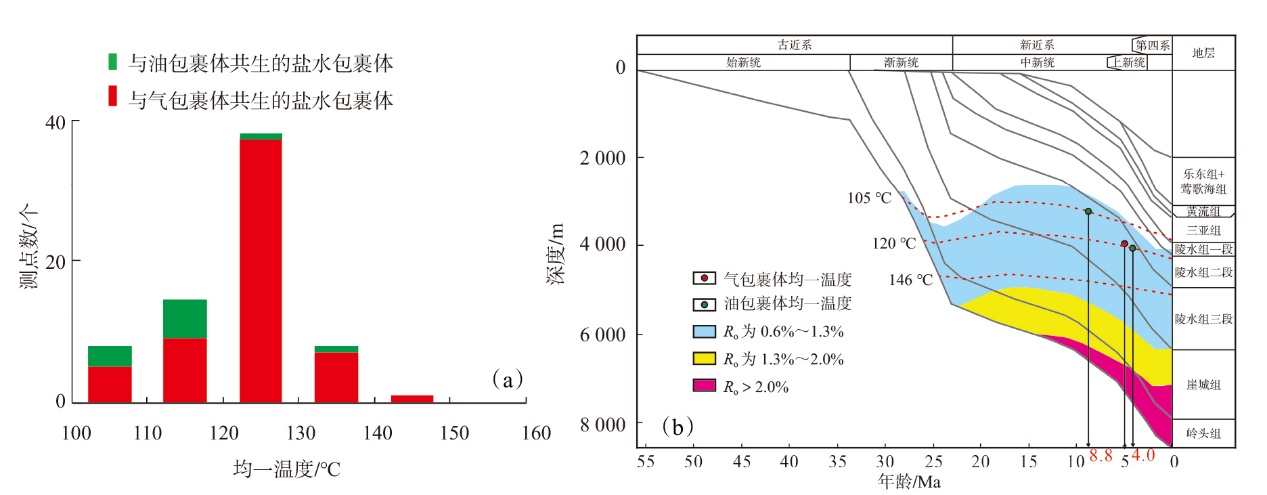
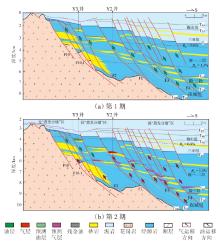
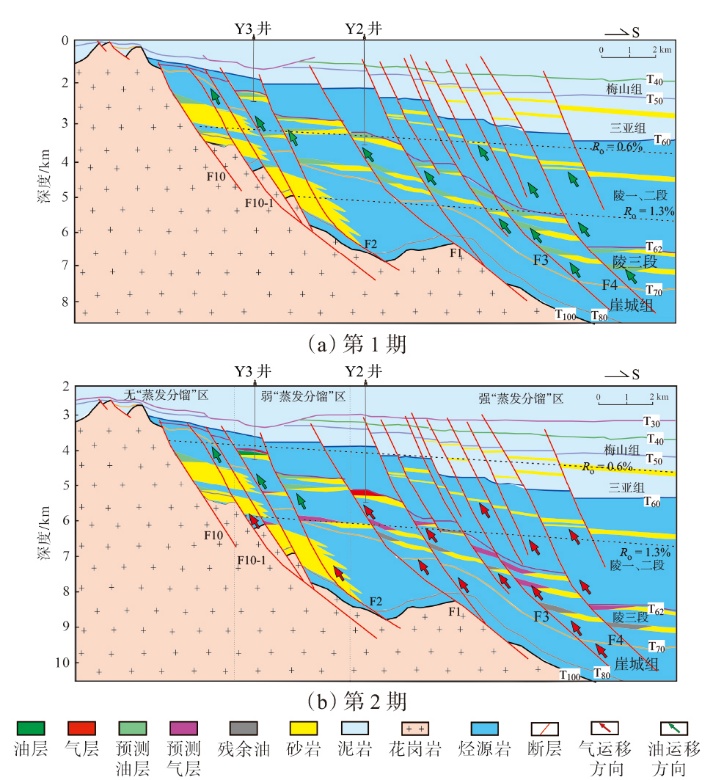
Lithologic Reservoirs ›› 2026, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (1): 89-99.doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20260108
• PETROLEUM EXPLORATION • Previous Articles Next Articles
Origin and accumulation mechanism of hydrocarbon of Oligocene Lingshui Formation in the southern slope of Baodao Sag, Qiongdongnan Basin
LIU Haiyu( ), LI Shanshan, GUO Xiaoxiao, LUO Wei, LIANG Gang, WANG Biwei
), LI Shanshan, GUO Xiaoxiao, LUO Wei, LIANG Gang, WANG Biwei
Hainan Branch of CNOOC Ltd. Haikou 570100, China
CLC Number:
- TE122.1
| [1] | 尤丽, 权永彬, 庹雷, 等. 琼东南盆地深水区宝岛21-1气田天然气来源及输导体系[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2023, 44(5):1270-1278. |
| YOU Li, QUAN Yongbin, TUO Lei, et al. Natural gas sources and migration pathways of the Baodao 21-1 gas field in the deep-water area of the Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geo-logy, 2023, 44(5):1270-1278. | |
| [2] | 甘军, 张亚震, 林璐, 等. 琼东南盆地宝岛凹陷天然气差异聚集主控因素与成藏模式[J]. 地球科学, 2023, 48(2):439-450. |
| GAN Jun, ZHANG Yazhen, LIN Lu, et al. Main controlling factors of natural gas differential accumulation model,in Baodao Sag,Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Earth Science, 2023, 48(2):439-450. | |
| [3] | 甘军, 张迎朝, 梁刚, 等. 琼东南盆地深水区天然气成藏过程及动力机制研究[J]. 地质学报, 2018, 92(11):2359-2362. |
| GAN Jun, ZHANG Yingzhao, LIANG Gang, et al. On accumulation process and dynamic mechanism of natural gas in the deep water area of central canyon,Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2018, 92(11):2359-2362. | |
| [4] | 吴飘, 侯读杰, 甘军, 等. 琼东南盆地深水东区渐新统烃源岩发育模式[J]. 沉积学报, 2019, 37(3):633-644. |
| WU Piao, HOU Dujie, GAN Jun, et al. Development model of Oligocene source rock in the eastern deep-water area of Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2019, 37(3):633-644. | |
| [5] | 黄保家, 李绪深, 王振峰, 等. 琼东南盆地深水区烃源岩地球化学特征与天然气潜力[J]. 中国海上油气, 2012, 24(4):1-7. |
| HUANG Baojia, LI Xushen, WANG Zhenfeng, et al. Source rock geochemistry and gas potential in the deep water area,Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2012, 24(4):1-7. | |
| [6] | 刘显阳, 邓秀芹, 赵彦德, 等. 姬塬地区长9油层组油气运移规律及模式探讨[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2011, 23(5):9-15. |
| LIU Xianyang, DENG Xiuqin, ZHAO Yande, et al. Hydrocarbon migration law and model of Chang 9 reservoir in Jiyuan area,Ordos Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2011, 23(5):9-15. | |
| [7] | 张明峰, 妥进才, 张小军, 等. 柴达木盆地乌南油田油源及油气运移探讨[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2012, 24(2):61-66. |
| ZHANG Mingfeng, TUO Jincai, ZHANG Xiaojun, et al. Discussion on oil sources and petroleum migration in the Wunan Oilfield,Qaidam Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2012, 24(2):61-66. | |
| [8] |
程焱, 王波, 张铜耀, 等. 渤中凹陷渤中A-2区新近系明化镇组岩性油气藏油气运移特征[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2024, 36(5):46-55.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20240505 |
|
CHENG Yan, WANG Bo, ZHANG Tongyao, et al. Oil and gas migration characteristics of lithologic reservoirs of Neogene Minghuazhen Formation in Bozhong A-2 area,Bozhong Sag[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2024, 36(5):46-55.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20240505 |
|
| [9] |
朱扬明, 苏爱国, 梁狄刚, 等. 柴达木盆地北缘南八仙油气藏的蒸发分馏作用[J]. 石油学报, 2003, 24(4):31-35.
doi: 10.7623/syxb200304007 |
|
ZHU Yangming, SU Aiguo, LIANG Digang, et al. Evaporative fractionation of oil and gas reservoir in Nanbaxian area of northern Qaidam Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2003, 24(4):31-35.
doi: 10.7623/syxb200304007 |
|
| [10] | 刘金水, 赵洪. 东海陆架盆地西湖凹陷平湖斜坡带差异性气侵的成藏模式[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 46(4):487-496. |
| LIU Jinshui, ZHAO Hong. Characteristics of differential gas invasion on Pinghu Slope of Xihu Sag,East China Sea Basin[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 2019, 46(4):487-496. | |
| [11] | 蔡忠贤, 吴楠, 杨海军, 等. 轮南低凸起凝析气藏的蒸发分馏作用机制[J]. 天然气工业, 2009, 29(4):21-24. |
| CAI Zhongxian, WU Nan, YANG Haijun, et al. Mechanism of evaporative fractionation in condensate gas reservoir in Lunnan low salient[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2009, 29(4):21-24. | |
| [12] |
宋兴国, 陈石, 杨明慧, 等. 塔里木盆地富满油田FⅠ16断裂发育特征及其对油气分布的影响[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2023, 35(3):99-109.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20230309 |
|
SONG Xingguo, CHEN Shi, YANG Minghui, et al. Development characteristics of FⅠ16 fault in Fuman oilfield of Tarim Basin and its influence on oil and gas distribution[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2023, 35(3):99-109.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20230309 |
|
| [13] | 付广, 夏云清. 南堡凹陷东一段油气成藏与分布的主控因素及模式[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2012, 24(6):27-37. |
| FU Guang, XIA Yunqing. Main controlling factors and models of oil and gas accumulation and distribution of Ed1 in Nanpu Depression[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2012, 24(6):27-37. | |
| [14] |
龙国徽, 王艳清, 朱超, 等. 柴达木盆地英雄岭构造带油气成藏条件与有利勘探区带[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2021, 33(1):145-160.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20210114 |
|
LONG Guohui, WANG Yanqing, ZHU Chao, et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation conditions and favorable exploration plays in Yingxiongling structural belt,Qaidam Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2021, 33(1):145-160.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20210114 |
|
| [15] |
张功成, 米立军, 吴时国, 等. 深水区:南海北部大陆边缘盆地油气勘探新领域[J]. 石油学报, 2007, 28(2):15-21.
doi: 10.7623/syxb200206003 |
|
ZHANG Gongcheng, MI Lijun, WU Shiguo, et al. Deepwater area:The new prospecting targets of northern continental margin of South China Sea[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2007, 28(2):15-21.
doi: 10.7623/syxb200206003 |
|
| [16] |
朱伟林, 吴景富, 张功成, 等. 中国近海新生代盆地构造差异性演化及油气勘探方向[J]. 地学前缘, 2015, 22(1):88-101.
doi: 10.13745/j.esf.2015.01.008 |
|
ZHU Weilin, WU Jingfu, ZHANG Gongcheng, et al. Discre-pancy tectonic evolution and petroleum exploration in China offshore Cenozoic basins[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2015, 22(1):88-101.
doi: 10.13745/j.esf.2015.01.008 |
|
| [17] |
施和生, 杨计海, 张迎朝, 等. 琼东南盆地地质认识创新与深水领域天然气勘探重大突破[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2019, 24(6):691-697.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2019.06.001 |
|
SHI Hesheng, YANG Jihai, ZHANG Yingzhao, et al. Geological understanding innovation and major breakthrough to natural gas exploration in deep water in Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2019, 24(6):691-697.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2019.06.001 |
|
| [18] |
徐新德, 张迎朝, 梁刚, 等. 南海北部琼东南盆地深水区烃源条件及天然气成藏机制[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2016, 27(11):1985-1992.
doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2016.11.1985 |
|
XU Xinde, ZHANG Yingzhao, LIANG Gang, et al. Hydrocarbon source condition and accumulation mechanism of natural gas in deepwater area of Qiongdongnan Basin,northern South China Sea[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2016, 27(11):1985-1992.
doi: 10.11764/j.issn.1672-1926.2016.11.1985 |
|
| [19] | 张迎朝, 范彩伟, 徐新德, 等. 南海琼东南盆地东区天然气成因类型与烃源探讨[J]. 石油实验地质, 2015, 37(4):466-472. |
| ZHANG Yingzhao, FAN Caiwei, XU Xinde, et al. Genesis and sources of natural gas in eastern Qiongdongnan Basin,South China Sea[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2015, 37(4):466-472. | |
| [20] |
HAVEN H L, LEEUW J W, RULLKÖTTER J, et al. Restricted utility of the pristane/phytane ratio as a palaeoenvironmental indicator[J]. Nature, 1987, 330(6149):641-643.
doi: 10.1038/330641a0 |
| [21] | PETERS K E, WALTERS C C, MOLDOWAN J M. The biomarker guide[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2005. |
| [22] |
AARSSEN B G, ZHANG Quanxing, LEEUW J W. An unusual distribution of bicadinanes,tricadinanes and oligocadinanes in sediments from the Yacheng gasfield,China[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1992, 18(6):805-812.
doi: 10.1016/0146-6380(92)90049-4 |
| [23] | 潘贤庄, 张国华, 黄义文, 等. 崖13-1气田天然气的混源特征[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 2001, 15(2):99-103. |
| PAN Xianzhuang, ZHANG Guohua, HUANG Yiwen, et al. The mixed gas sources in Yacheng 13-1 gas field[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas(Geology), 2001, 15(2):99-103. | |
| [24] | 胡忠良, 肖贤明, 黄保家, 等. 琼东南盆地崖13-1气田气源区圈定与成藏运聚模式[J]. 地球化学, 2005, 34(1):66-72. |
| HU Zhongliang, XIAO Xianming, HUANG Baojia, et al. Source area determination and gas pool formation model of the Ya13-1 Gasfield from the Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Geochimica, 2005, 34(1):66-72. | |
| [25] | 王振峰, 孙志鹏, 张迎朝, 等. 南海北部琼东南盆地深水中央峡谷大气田分布与成藏规律[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2016, 21(4):54-64. |
| WANG Zhenfeng, SUN Zhipeng, ZHANG Yingzhao, et al. Distribution and hydrocarbon accumulation mechanism of the giant deepwater central canyon gas field in Qiongdongnan Basin,northern South China Sea[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2016, 21(4):54-64. | |
| [26] | 梁刚, 甘军, 李兴. 琼东南盆地陵水凹陷天然气成因类型及来源[J]. 中国海上油气, 2015, 27(4):47-53. |
| LIANG Gang, GAN Jun, LI Xing. Genetic types and origin of natural gas in Lingshui sag,Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2015, 27(4):47-53. | |
| [27] |
黄合庭, 黄保家, 黄义文, 等. 南海西部深水区大气田凝析油成因与油气成藏机制:以琼东南盆地陵水17-2气田为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2017, 44(3):380-388.
doi: 10.11698/PED.2017.03.07 |
|
HUANG Heting, HUANG Baojia, HUANG Yiwen, et al. Condensate origin and hydrocarbon accumulation mechanism of the deepwater giant gas field in western South China Sea:A case study of Lingshui 17-2 Gas Field in Qiongdongnan Basin,South China Sea[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2017, 44(3):380-388.
doi: 10.11698/PED.2017.03.07 |
|
| [28] | 王铁冠. 生物标志物地球化学研究[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1990. |
| WANG Tieguan. Study on biomarker geochemistry[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 1990. | |
| [29] | 侯读杰, 冯子辉. 油气地球化学[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社,2011:168-190. |
| HOU Dujie, FENG Zihui. Petroleum geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press,2011:168-190. | |
| [30] | 戴金星. 天然气碳氢同位素特征和各类天然气鉴别[J]. 天然气地球科学, 1993, 4(2):1-40. |
| DAI Jinxing. Characteristics of natural gas carbon-hydrogen isotope and identification of natural gas[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 1993, 4(2):1-40. | |
| [31] | 戴金星, 邹才能, 张水昌, 等. 无机成因和有机成因烷烃气的鉴别[J]. 中国科学D辑:地球科学, 2008, 38(11):1329-1341. |
| DAI Jinxing, ZOU Caineng, ZHANG Shuichang, et al. Identification origin of inorganic and organic alkane gas[J]. Science in China Series D:Earth Sciences, 2008, 38(11):1329-1341. | |
| [32] | 张水昌. 运移分馏作用:凝析油和蜡质油形成的一种重要机制[J]. 科学通报, 2000, 45(6):667-670. |
| ZHANG Shuichang. Migration fractionation:An important mechanism for the formation of condensate and wax oil[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2000, 45(6):667-670. | |
| [33] |
THOMPSON K F. Fractionated aromatic petroleums and the generation of gas-condensates[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1987, 11(6):573-590.
doi: 10.1016/0146-6380(87)90011-8 |
| [34] | 傅宁, 李友川, 陈桂华, 等. 东海西湖凹陷油气“蒸发分馏”成藏机制[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2003, 30(2):39-42. |
| FU Ning, LI Youchuan, CHEN Guihua, et al. Pooling mechanisms of “evaporating fractionation” of oil and gas in the Xihu Depression,East China Sea[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2003, 30(2):39-42. | |
| [35] | 马柯阳. 凝析油形成新模式:原油蒸发分馏机制研究[J]. 地球科学进展, 1995, 10(6):567-571. |
| MA Keyang. Study on petroleum evaporative fractionation:A new mechanism for the generation of condensate[J]. Advance in Earth Science, 1995, 10(6):567-571. | |
| [36] | 王广源, 牛成民, 王飞龙, 等. 渤海海域渤东低凸起南段原油“蒸发分馏”地球化学特征及成因[J]. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 48(4):466-473. |
| WANG Guangyuan, NIU Chengmin, WANG Feilong, et al. Geochemical characteristics and genesis of“evaporative fraction”of crude oil in the southern section of Bodong low uplift,Bohai Sea,China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Techno-logy (Science & Technology Edition), 2021, 48(4):466-473. | |
| [37] | 牛成民, 王飞龙, 汤国民, 等. 复合油藏形成中的蒸发分馏与生物降解联合控制作用:以渤海海域秦皇岛29-2油田为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2018, 40(3):381-388. |
| NIU Chengmin, WANG Feilong, TANG Guomin, et al. Evaporative fractionation and biodegradation impacts on a complex petroleum system:QHD29-2 oil field,Bohai Sea area[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2018, 40(3):381-388. | |
| [38] | 龙祖烈, 陈聪, 马宁, 等. 珠江口盆地深水区白云凹陷油气成因来源与成藏特征[J]. 中国海上油气, 2020, 32(4):36-45. |
| LONG Zulie, CHEN Cong, MA Ning, et al. Geneses and accumulation characteristics of hydrocarbons in Baiyun sag,deep water area of Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2020, 32(4):36-45. | |
| [39] | 何文祥, 王培荣, 潘贤庄. 莺-琼盆地原油的蒸发分馏作用[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2004, 31(4):52-54. |
| HE Wenxiang, WANG Peirong, PAN Xianzhuang. Evaporative fraction of crude oils in the Ying-Qiong Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2004, 31(4):52-54. | |
| [40] | 刘海钰, 黄保家, 庹雷, 等. 琼东南盆地深水区气田凝析油成熟度判别和成因分析[J]. 中国海上油气, 2018, 30(6):33-40. |
| LIU Haiyu, HUANG Baojia, TUO Lei, et al. Maturity discrimination and genesis analysis of condensate in the deep water gas fields of Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2018, 30(6):33-40. | |
| [41] |
CURIALE J, BROMLEY B. Migration induced compositional changes in oils and condensates of a single field[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 1996, 24:1097-1113.
doi: 10.1016/S0146-6380(96)00099-X |
| [42] |
斯尚华, 赵靖舟, 刘俊邦, 等. 利用油包裹体荧光光谱确定齐家地区高台子油层致密油气成藏期次及其相对成熟度[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2018, 23(6):78-86.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2018.06.009 |
|
SI Shanghua, ZHAO Jingzhou, LIU Junbang, et al. Determination of accumulation periods and relative maturity of tight oil and gas in Gaotaizi oil reservoir of Qijia area by using fluorescence spectrum of oil inclusions[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2018, 23(6):78-86.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2018.06.009 |
|
||