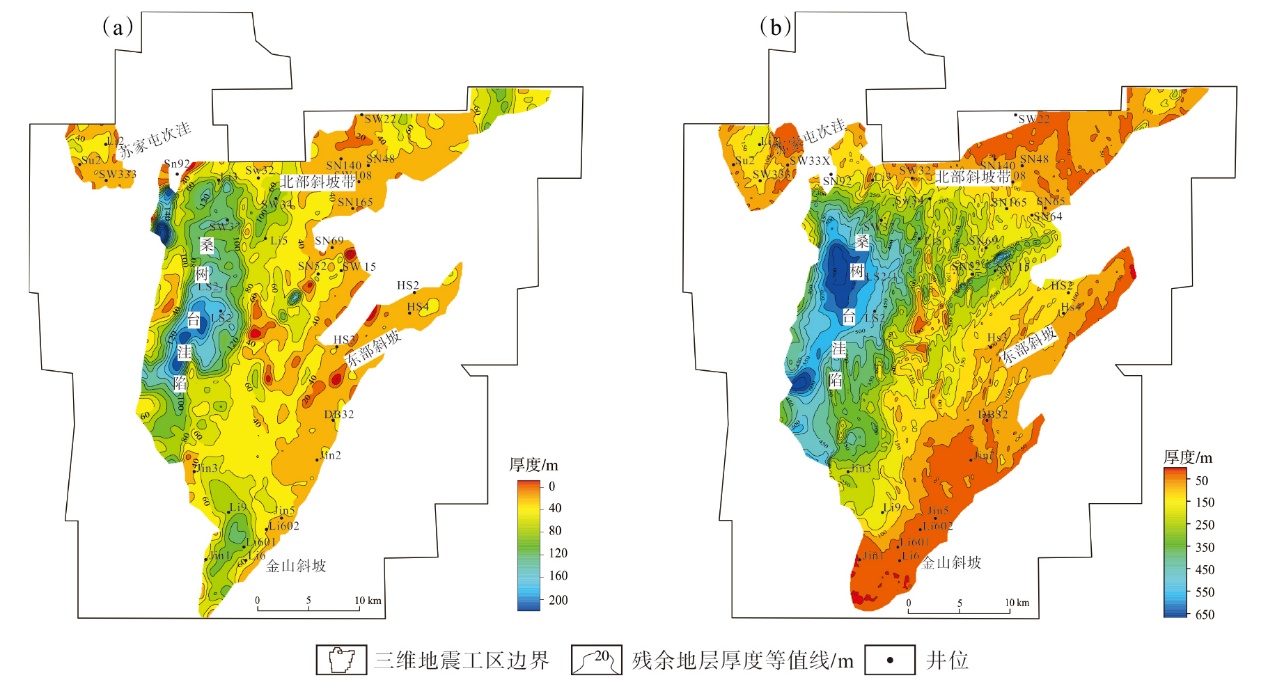
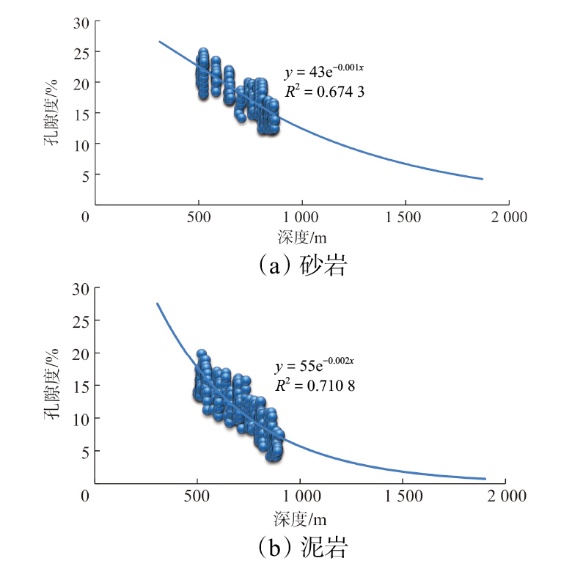
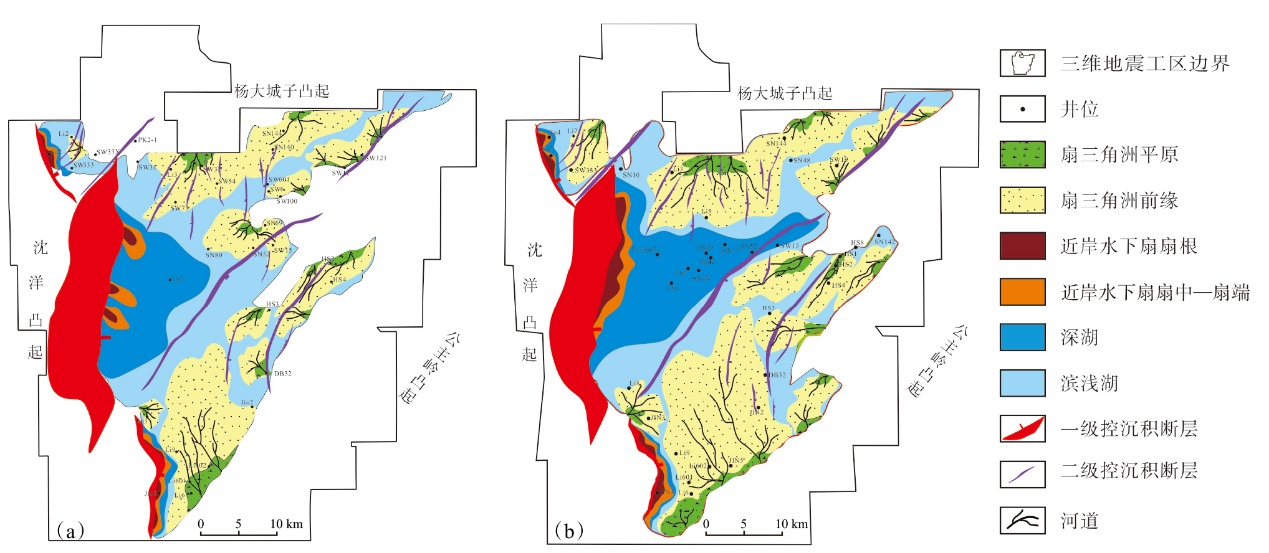
Lithologic Reservoirs ›› 2026, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (1): 146-161.doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20260113
• PETROLEUM EXPLORATION • Previous Articles
Paleogeomorphologic characteristics and sand control mechanisms of Cretaceous Shahezi Formation in Lishu fault depression, southern Songliao Basin
XIAO Meng1( ), ZHOU Yong2,3(
), ZHOU Yong2,3( ), WANG Ke2,3, YAN Jingchi2,3, ZHANG Yuejie2,3
), WANG Ke2,3, YAN Jingchi2,3, ZHANG Yuejie2,3
- 1
China Petroleum & Chemical Corporation Northeast Oil & Gas Branch Changchun 130062, China
2College of Geosciences ,China University of Petroleum (Beijing) Beijing 102249, China
3State Key laboratory of Petroleum Resources and Engineering ,China University of Petroleum (Beijing) Beijing 102249, China
CLC Number:
- TE121
| [1] | 蔡周荣, 殷征欣, 叶军, 等. 珠江口盆地向海阶梯状断裂特征及成因分析[J]. 中国科技论文, 2015, 10(3):322-326. |
| CAI Zhourong, YIN Zhengxin, YE Jun, et al. Characteristics and formation mechanism of the ladder-like faults towards the sea in Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. China Sciencepaper, 2015, 10(3):322-326. | |
| [2] |
赵文智, 魏国齐, 杨威, 等. 四川盆地万源—达州克拉通内裂陷的发现及勘探意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2017, 44(5):659-669.
doi: 10.11698/PED.2017.05.01 |
|
ZHAO Wenzhi, WEI Guoqi, YANG Wei, et al. Discovery of Wanyuan-Dazhou Intracratonic Rift and its exploration significance in the Sichuan Basin,SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2017, 44(5):659-669.
doi: 10.11698/PED.2017.05.01 |
|
| [3] | 马兵山, 漆家福, 王俊怀, 等. 南海北部珠江口盆地珠一坳陷西江凹陷与陆丰凹陷差异裂陷过程定量分析[J]. 高校地质学报, 2022, 28(5):669-687. |
| MA Bingshan, QI Jiafu, WANG Junhuai, et al. Quantitative analysis of differential rifting process in the Xijiang and Lufeng Sags of the Zhu 1 Depression,Pearl River Mouth Basin,Northern South China Sea[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2022, 28(5):669-687. | |
| [4] |
张翠梅, 刘晓峰, 任建业, 等. “构造-沉积分析”及其在沉积盆地中的应用[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2012, 31(3):128-136.
doi: 10.11978/j.issn.1009-5470.2012.03.017 |
|
ZHANG Cuimei, LIU Xiaofeng, REN Jianye, et al. Principle of the “tectono-sedimentary analysis” and its application in sedimentary basins[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2012, 31(3):128-136.
doi: 10.11978/j.issn.1009-5470.2012.03.017 |
|
| [5] | 王黎, 王果寿, 邱岐, 等. 松辽盆地梨树断陷深部层系沉积特征及演化分析[J]. 石油实验地质, 2014, 36(3):316-324. |
| WANG Li, WANG Guoshou, QIU Qi, et al. Sedimentary features and evolution of deep series in Lishu Fault Depression,Songliao Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2014, 36(3):316-324. | |
| [6] |
赵泽辉, 徐淑娟, 姜晓华, 等. 松辽盆地深层地质结构及致密砂砾岩气勘探[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2016, 43(1):12-23.
doi: 10.11698/PED.2016.01.02 |
|
ZHAO Zehui, XU Shujuan, JIANG Xiaohua, et al. Deep strata geologic structure and tight conglomerate gas exploration in Songliao Basin,East China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2016, 43(1):12-23.
doi: 10.11698/PED.2016.01.02 |
|
| [7] |
王宏语, 李瑞磊, 朱建峰, 等. 松辽盆地梨树断陷构造沉积学特征及发育机制[J]. 地学前缘, 2023, 30(4):112-127.
doi: 10.13745/j.esf.sf.2022.10.23 |
|
WANG Hongyu, LI Ruilei, ZHU Jianfeng, et al. Tectono-sedi-mentary characteristics and formation mechanism of the Lishu rift depression,Songliao Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2023, 30(4):112-127.
doi: 10.13745/j.esf.sf.2022.10.23 |
|
| [8] | 李耀华, 徐兴友, 张君峰, 等. 火山活动期断陷湖盆富有机质混积页岩形成条件:以松辽盆地南部梨树断陷沙河子组富有机质页岩为例[J]. 地球科学, 2022, 47(5):1728-1747. |
| LI Yaohua, XU Xingyou, ZHANG Junfeng, et al. Hybrid sedimentary conditions of organic-rich shales in faulted lacustrine basin during volcanic eruption episode:A case study of Shahezi Formaton (K1sh Fm.),Lishu Faulted Depression,South Songliao Basin[J]. Earth Science, 2022, 47(5):1728-1747. | |
| [9] | 陈永进, 李友. 基于米氏旋回的页岩高频层序划分与页岩有机质富集模式:以松辽盆地梨树断陷北斜坡营城组为例[J]. 石油科学通报, 2024, 9(4):535-548. |
| CHEN Yongjin, LI You. Division of high-frequency shale sequences and organic matter enrichment patterns in shales based on Milankovitch cycles:A case study of the Yingcheng Formation in the Northern Slope of the Lishu Fault Depression,Songliao Basin[J]. Petroleum Science Bulletin, 2024, 9(4):535-548. | |
| [10] | 鄢继华, 陈世悦, 姜在兴. 东营凹陷北部陡坡带近岸水下扇沉积特征[J]. 石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2005, 29(1):12-16. |
| YAN Jihua, CHEN Shiyue, JANG Zaixing. Sedimentary characteristics of nearshore subaqueous fans in steep slope of Dongying depression[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 2005, 29(1):12-16. | |
| [11] | 白立科, 邱隆伟, 杨勇强, 等. 近岸水下扇微相划分研究及意义初探:以滦平盆地下白垩统西瓜园组为例[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(8):2446-2459. |
| BAI Like, QIU Longwei, YANG Yongqiang, et al. Preliminary microfacies division and significance study of nearshore subaqueous fan:A case study from the Lower Cretaceous Xiguayuan Formation,Luanping Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(8):2446-2459. | |
| [12] | 曹辉兰, 华仁民, 纪友亮, 等. 扇三角洲砂砾岩储层沉积特征及与储层物性的关系:以罗家油田沙四段砂砾岩体为例[J]. 高校地质学报, 2001, 7(2):222-229. |
| CAO Huilan, HUA Renmin, JI Youliang, et al. Depositional characteristics of sandstone and conglomerate reservoirs of fan delta and relationship to reservoirs’ physical properties:Taking the Fourth Member of Shahejie Formation,Luojia Oilfield,Zhanhua Depression for an example[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2001, 7(2):222-229. | |
| [13] | 刘磊, 钟怡江, 陈洪德, 等. 中国东部箕状断陷湖盆扇三角洲与辫状河三角洲对比研究[J]. 沉积学报, 2015, 33(6):1170-1181. |
| LIU Lei, ZHONG Yijiang, CHEN Hongde, et al. Contrastive research of fan deltas and braided river deltas in half-graben rift lake basin in east China[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2015, 33(6):1170-1181. | |
| [14] | 向立宏, 赵铭海, 郝雪峰, 等. 济阳坳陷东营组沉积体系新认识[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2016, 23(3):8-13. |
| XIANG Lihong, ZHAO Minghai, HAO Xuefeng, et al. New understanding on sedimentary system of Dongying Formation in Jiyang depression[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2016, 23(3):8-13. | |
| [15] | 闫迪. 梨树断陷东部斜坡带断裂系统及控藏研究[D]. 大庆: 东北石油大学, 2016. |
| YAN Di. Study of fault system and its control of hydrocarbon accumulation in the Eastern Slope Zone,Lishu Fault Depression[D]. Daqing: Northeast Petroleum University, 2016. | |
| [16] | 武爱俊, 徐建永, 滕彬彬, 等. “动态物源”精细刻画方法与应用:以琼东南盆地崖南凹陷为例[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2017, 29(4):55-63. |
|
WU Aijun, XU Jianyong, TENG Binbin, et al. Fine description method of dynamic provenance and its application:A case from Yanan Sag,Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2017, 29(4):55-63.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2017.04.007 |
|
| [17] |
李想, 付磊, 魏璞, 等. 沉积古地貌恢复及古地貌对沉积体系的控制作用:以准噶尔盆地石西地区三叠系百口泉组为例[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2025, 37(2): 38-48.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20250204 |
|
LI Xiang, FU Lei, WEI Pu, et al. Restoration of sedimentary paleogeography and its control on sedimentary system:A case study of the Triassic Baikouquan Formation in Shixi area of Junggar Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2025, 37(2):38-48.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20250204 |
|
| [18] |
LIU Lei, CHEN Hongde, WANG Jun, et al. Geomorphological evolution and sediment dispersal processes in strike-slip and extensional composite basins:A case study in the Liaodong Bay Depression,Bohai Bay Basin,China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 110:73-90.
doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2019.07.023 |
| [19] |
叶蕾, 朱筱敏, 谢爽慧, 等. 沉积古地貌基本恢复方法及实例研究:以饶阳凹陷沙一段为例[J]. 古地理学报, 2023, 25(5):1139-1155.
doi: 10.7605/gdlxb.2023.05.077 |
| YE Lei, ZHU Xiaomin, XIE Shuanghui, et al. Restoration methods of sedimentary palaeogeomorphology and applications:A case study of the First Member of Paleogene Shahejie Formation in Raoyang sag[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography (Chinese Edition), 2023, 25(5):1139-1155. | |
| [20] | 杨桥, 漆家福. 碎屑岩层的分层去压实校正方法[J]. 石油实验地质, 2003, 25(2):206-210. |
| YANG Qiao, QI Jiafu. Method of delaminated decompaction correction[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2003, 25(2):206-210. | |
| [21] | 刘强虎. 渤海湾盆地沙垒田凸起古近系“源—渠—汇”系统耦合研究[D]. 北京: 中国石油大学(北京), 2016. |
| LIU Qianghu. “Source-to-sink” system coupling analysis of the Paleogene,Shaleitian Uplift,Bohai Bay Basin, China[D]. Beijing: China University of Petroleum (Beijing), 2016. | |
| [22] |
杨丽莎, 陈彬滔, 马轮, 等. 陆相湖盆坳陷期源—汇系统的要素特征及耦合关系:以南苏丹Melut盆地北部坳陷新近系Jimidi组为例[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2021, 33(3):27-38.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20210303 |
|
YANG Lisha, CHEN Bintao, MA Lun, et al. Element feature and coupling model of source-to-sink system in depression lacustrine basin:A case study of Neogene Jimidi Formation in Melut Basin,South Sudan[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2021, 33(3):27-38.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20210303 |
|
| [23] | MORLEY C K, NELSON R A, PATTON T L, et al. Transfer zones in the east African rift system and their relevance to hydrocarbon exploration in rifts[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1990, 74(8):1234-1253. |
| [24] | 付晓飞, 孙兵, 王海学, 等. 断层分段生长定量表征及在油气成藏研究中的应用[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2015, 44(2):271-281. |
| FU Xiaofei, SUN Bing, WANG Haixue, et al. Fault segmentation growth quantitative characterization and its application on sag hydrocarbon accumulation research[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2015, 44(2):271-281. | |
| [25] | 吴冬, 朱筱敏, 刘常妮, 等. Fula凹陷中央转换带对岩性油藏勘探的意义:以Abu Gabra组为例[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2017, 29(4):64-72. |
|
WU Dong, ZHU Xiaomin, LIU Changni, et al. Significance of central transfer zone on lithologic reservoir exploration:A case of Abu Gabra Formation in Fula Sag,Muglad Basin,Sudan[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2017, 29(4):64-72.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2017.04.008 |
|
| [26] |
何雁兵, 肖张波, 郑仰帝, 等. 珠江口盆地陆丰13洼转换带中生界陆丰7-9潜山成藏特征[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2023, 35(3):18-28.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20230302 |
|
HE Yanbing, XIAO Zhangbo, ZHENG Yangdi, et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation characteristics of Mesozoic Lufeng 7-9 buried hill in Lufeng 13 subsag transition zone,Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2023, 35(3):18-28.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20230302 |
|
| [27] |
侯宇光, 何生, 王冰洁, 等. 板桥凹陷构造坡折带对层序和沉积体系的控制[J]. 石油学报, 2010, 31(5):754-761.
doi: 10.7623/syxb201005009 |
|
HOU Yuguang, HE Sheng, WANG Bingjie, et al. Constraints by tectonic slope-break zones on sequences and depositional systems in the Banqiao Sag[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2010, 31(5):754-761.
doi: 10.7623/syxb201005009 |
|
| [28] | 冯有良, 胡素云, 李建忠, 等. 准噶尔盆地西北缘同沉积构造坡折对层序建造和岩性油气藏富集带的控制[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2018, 30(4):14-25. |
|
FENG Youliang, HU Suyun, LI Jianzhong, et al. Controls of syndepotitional structural slope-break zones on sequence architecture and enrichment zones of lithologic reservoirs in northwestern margin of Junggar Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2018, 30(4):14-25.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20180402 |
|
||