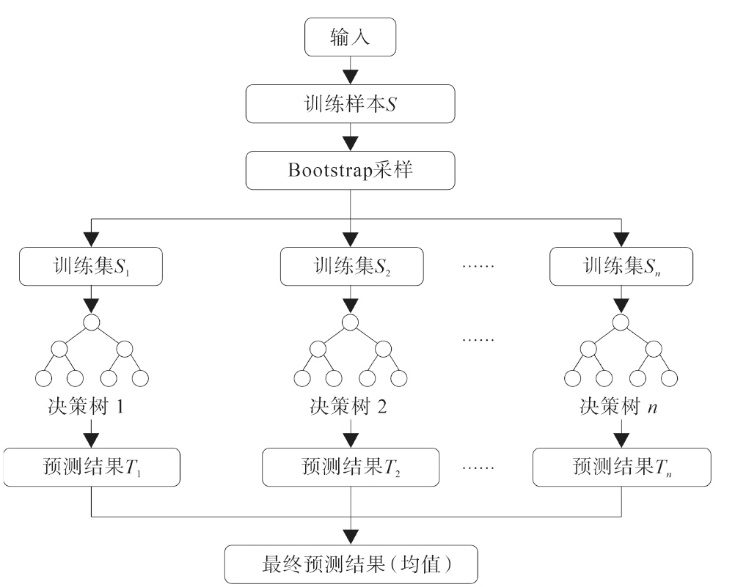
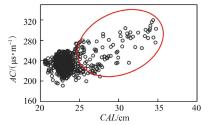
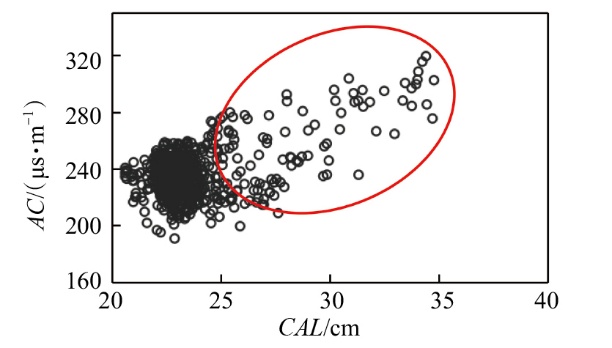
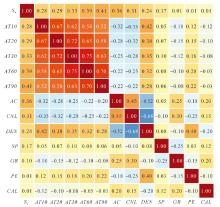
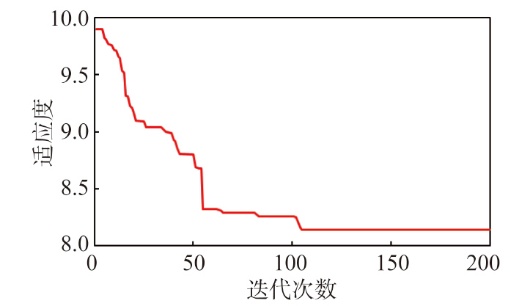
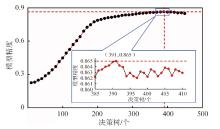
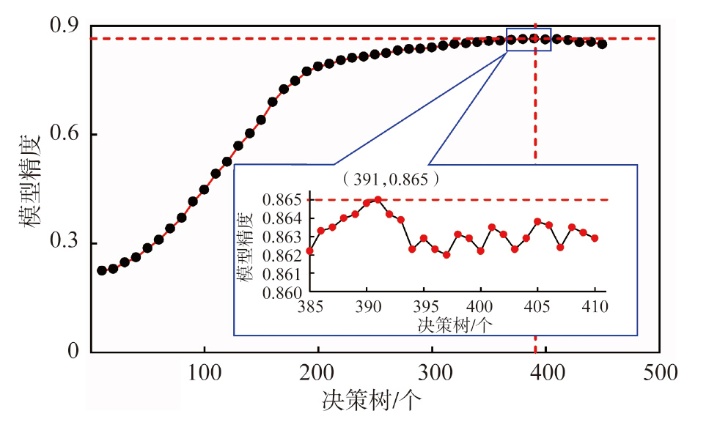
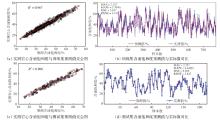
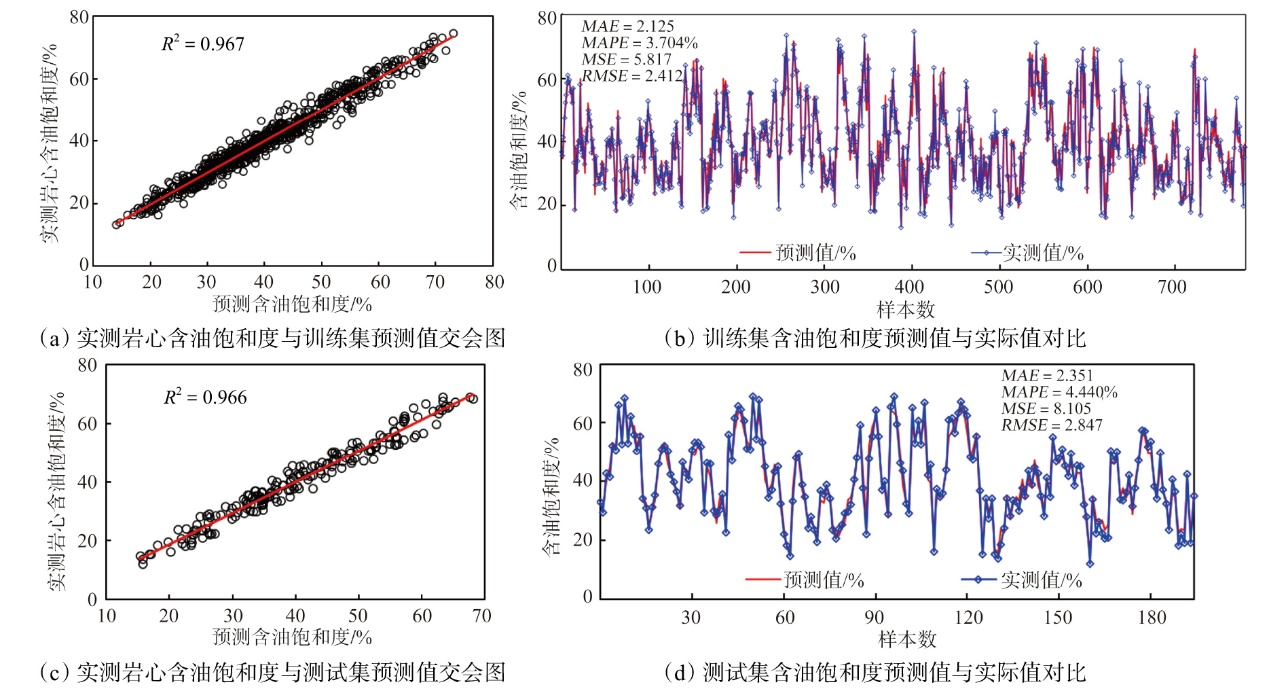
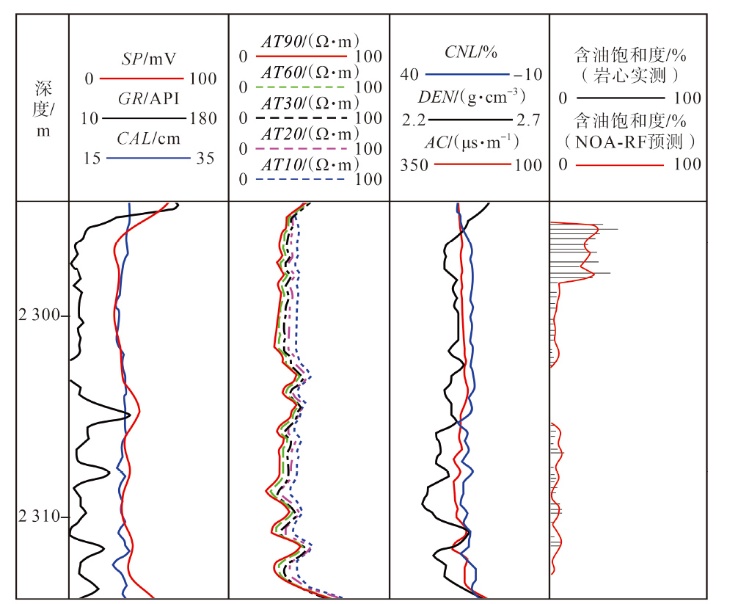
Lithologic Reservoirs ›› 2026, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (1): 55-66.doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20260105
• PETROLEUM EXPLORATION • Previous Articles Next Articles
Evaluation method for oil saturation in low resistivity reservoirs based on random forest optimization algorithm
YIN Jiang1( ), JIAO Xuejun2, LI Xiaolong3, LI Taifu4, SHEN Zhanyong4, LI Mengxi5, SUN Rui1, ZHU Yushuang1(
), JIAO Xuejun2, LI Xiaolong3, LI Taifu4, SHEN Zhanyong4, LI Mengxi5, SUN Rui1, ZHU Yushuang1( )
)
- 1
State Key Laboratory of Continental Evolution and Early Life/Department of Geology ,Northwest University Xi’an 710069, China
2China National Petroleum Corporation Shared Services Co. ,Ltd., Xi’an Center Xi’an 710069, China
3Well Operation Engineering Company ,Daqing Drilling Engineering Co., Ltd. Songyuan 138000, Jilin, China
4Oil Production Plant No. 7 ,PetroChina Changqing Oilfield Company Xi’an 710018, China
5Huanqing Company ,PetroChina Yumen Oilfield Qingyang 745799, Gansu, China
CLC Number:
- TE122
| [1] |
ARCHIE G E. The electrical resistivity log as an aid in determining some reservoir characteristics[J]. Transactions of the AIME, 1942, 146(1): 54-62.
doi: 10.2118/942054-G |
| [2] | SIMANDOUX P. Dielectric measurements in porous media and application to shaly formations[J]. Revue de l’Institut Français du Pétrole, 1963, 18(S1):193-215. |
| [3] |
CLAVIER C, COATES G, DUMANOIR J. Theoretical and experimental bases for the dual-water model for interpretation of shaly sands[J]. Society of Petroleum Engineers Journal, 1984, 24(2):153-168.
doi: 10.2118/6859-PA |
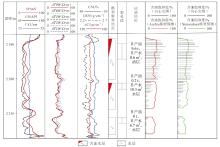
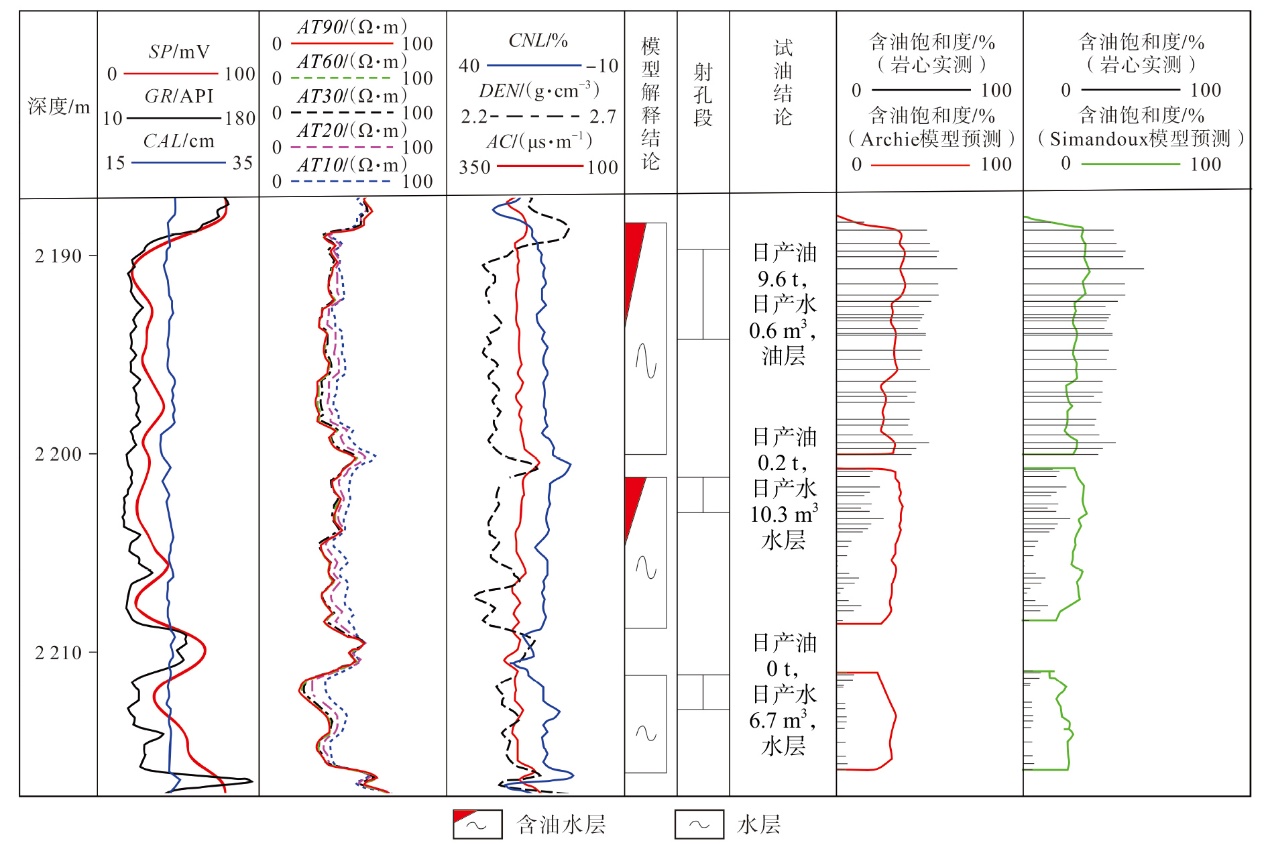
| [4] | 邢培俊, 孙建孟, 王克文, 等. 利用测井资料确定粘土矿物的方法对比[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 32(2):53-57. |
| XING Peijun, SUN Jianmeng, WANG Kewen, et al. Comparison of determination methods for clay minerals using log data[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 2008, 32(2):53-57. | |
| [5] | 陆云龙, 许赛男, 郑炀, 等. 黏土附加导电校正的低阻油层含水饱和度计算方法[J]. 中国海上油气, 2023, 35(1):63-69. |
| LU Yunlong, XU Sainan, ZHENG Yang, et al. Water saturation calculation method of low resistivity reservoir with clay additional conductivity correction[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2023, 35(1):63-69. | |
| [6] | REVIL A. Spectral induced polarization of shaly sands:Influence of the electrical double layer[J]. Water Resources Research, 2012, 48(2):1-23. |
| [7] |
GUO Zhihua, SONG Yanjie, TANG Xiaomin, et al. Conductivity model for pyrite-bearing laminated and dispersed shaly sands based on a differential equation and the generalized Archie equation[J]. Applied Geophysics, 2018, 15(2):208-221.
doi: 10.1007/s11770-018-0685-6 |
| [8] | 骆玉虎, 何胜林, 谭伟, 等. 北部湾盆地砂砾岩低阻油层成因及饱和度计算方法[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(6):33-41. |
| LUO Yuhu, HE Shenglin, TAN Wei, et al. Genetic mechanism and saturation calculation method of low resistivity sandy conglo-merate oil layers in Beibu Gulf Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(6):33-41. | |
| [9] |
CAI Jianchao, WEI Wei, HU Xiangyun, et al. Electrical conductivity models in saturated porous media:A review[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2017, 171:419-433.
doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.06.013 |
| [10] | 刘堂晏, 周灿灿, 马在田, 等. 球管孔隙模型的约束寻优及应用[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 2006, 34(11):1464-1469. |
| LIU Tangyan, ZHOU Cancan, MA Zaitian, et al. Restricted and optimized conditions of sphere-cylinder model and its applications[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Nature Science), 2006, 34(11):1464-1469. | |
| [11] |
赵军, 韩东, 何胜林, 等. 基于水气比计算的低对比度储层流体性质识别[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2021, 33(4):128-136.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20210414 |
|
ZHAO Jun, HAN Dong, HE Shenglin, et al. Identification of fluid properties of low contrast reservoir based on water-gas ratio calculation[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2021, 33(4):128-136.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20210414 |
|
| [12] |
GAD M, MAHMOUD A A, PANAGOPOULOS G, et al. Predicting water saturation in a Greek oilfield with the power of artificial neural networks[J]. ACS Omega, 2025, 10(1):557-566.
doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c07175 pmid: 39829518 |
| [13] | MELLAL I, LATRACH A, RASOULI V, et al. Water saturation prediction in the middle Bakken formation using machine learning[J]. Engineering, 2023, 4(3):1951-1964. |
| [14] |
桂金咏, 李胜军, 高建虎, 等. 基于特征变量扩展的含气饱和度随机森林预测方法[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2024, 36(2):65-75.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20240207 |
|
GUI Jinyong, LI Shengjun, GAO Jianhu, et al. A random forests prediction method for gas saturation based on feature variable extension[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2024, 36(2):65-75.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20240207 |
|
| [15] |
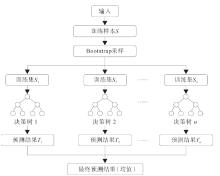
BREIMAN L. Random forests[J]. Machine Learning, 2001, 45(1):5-32.
doi: 10.1023/A:1010933404324 |
| [16] | 黄莉莎, 闫建平, 郭伟, 等. 基于随机森林回归算法的低电阻率页岩气储层饱和度评价[J]. 测井技术, 2023, 47(1):22-28. |
| HUANG Lisha, YAN Jianping, GUO Wei, et al. Evaluation of low resistivity shale gas reservoir saturation based on random forest regression method[J]. Well Logging Technology, 2023, 47(1):22-28. | |
| [17] | 吴保祥, 何金先, 张晓丽, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地地层埋藏演化与油气成藏分析[J]. 东北石油大学学报, 2012, 36(6):8-13. |
| WU Baoxiang, HE Jinxian, ZHANG Xiaoli, et al. Analysis of burial evolution of stratum and oil-gas reservoirs formation in Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Northeast Petroleum University, 2012, 36(6):8-13. | |
| [18] | 张岳桥, 董树文, 赵越, 等. 华北侏罗纪大地构造:综评与新认识[J]. 地质学报, 2007, 81(11):1462-1480. |
| ZHANG Yueqiao, DONG Shuwen, ZHAO Yue, et al. Jurassic tectonics of north China:A synthetic view[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2007, 81(11):1462-1480. | |
| [19] | 朱筱敏, 邓秀芹, 刘自亮, 等. 大型坳陷湖盆浅水辫状河三角洲沉积特征及模式:以鄂尔多斯盆地陇东地区延长组为例[J]. 地学前缘, 2013, 20(2):19-28. |
| ZHU Xiaomin, DENG Xiuqin, LIU Ziliang, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and model of shallow braided delta in large-scale lacustrine:An example from Triassic Yanchang Formation in Ordos Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2013, 20(2):19-28. | |
| [20] |
廖新武, 杨庆红, 李超, 等. 渤海湾盆地垦利6-1油田新近系明化镇组下段浅水三角洲沉积特征[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2025, 37(2):1-11.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20250201 |
|
LIAO Xinwu, YANG Qinghong, LI Chao, et al. Sedimentary characteristics of shallow water delta in the Neogene lower member of Minghuazhen Formation,Kenli 6-1 Oilfield in Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2025, 37(2):1-11.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20250201 |
|
| [21] |
白杨, 张晓磊, 刚文哲, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地平凉北地区上三叠统长8段储层低含油饱和度油藏特征及成因[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2023, 35(3):66-75.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20230306 |
|
BAI Yang, ZHANG Xiaolei, GANG Wenzhe, et al. Characteristics and genesis of Upper Triassic Chang 8 reservoir with low oil saturation in northern Pingliang area,Ordos Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2023, 35(3):66-75.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20230306 |
|
| [22] | 王鑫, 詹艳, 赵国泽, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地西缘构造带北段深部电性结构[J]. 地球物理学报, 2010, 53(3):595-604. |
| WANG Xin, ZHAN Yan, ZHAO Guoze, et al. Deep electrical structure beneath the northern section of the western margin of the Ordos Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2010, 53(3):595-604. | |
| [23] | 武娟, 罗仁泽, 雷璨如, 等. 基于大语言模型的致密砂岩储层测井含水饱和度预测[J]. 天然气工业, 2024, 44(9):77-87. |
| WU Juan, LUO Renze, LEI Canru, et al. Prediction of water saturation in tight sandstone reservoirs from well log data based on the large language models (LLMs)[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2024, 44(9):77-87. | |
| [24] | WAXMAN M H, SMITS L J M. Electrical conductivities in oil bearing shaly sand[J]. Society of Petroleum Engineers Journal, 1968, 42(3):107-122. |
| [25] | EFRON B, TIBSHIRANI R J. An introduction to the bootstrap[M]. Boca Raton: Chapman & Hall/CRC, 1994. |
| [26] | 方匡南, 吴见彬, 朱建平, 等. 随机森林方法研究综述[J]. 统计与信息论坛, 2011, 26(3):32-38. |
| FANG Kuangnan, WU Jianbin, ZHU Jianping, et al. A review of technologies on random forests[J]. Journal of Statistics and Information, 2011, 26(3):32-38. | |
| [27] |
MOHAMED A, REDA M, MOHAMMED J, et al. Nutcracker optimizer:A novel nature-inspired metaheuristic algorithm for global optimization and engineering design problems[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2023, 262:110248.
doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2022.110248 |
| [28] | WANG Tianze, NIE Yunli, WANG Shengli, et al. Depth control of ROV using the improved LADRC based on nutcracker optimization algorithm[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2024, 309(1):1-10. |
| [29] |
JAMEEL M, ABOUHAWWASH M. Revolutionizing optimization:An innovative nutcracker optimizer for single and multi-objective problems[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2024, 164:112019.
doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2024.112019 |
| [30] | 左银卿, 刘炜, 袁路波, 等. 含黄铁矿低电阻率储层测井评价技术[J]. 测井技术, 2007, 31(1):25-29. |
| ZUO Yinqing, LIU Wei, YUAN Lubo, et al. Logging evaluation technique for low resistivity reservoir containing pyrite[J]. Well Logging Technology, 2007, 31(1):25-29. | |
| [31] | 陈钢花, 杨叶. 利用常规测井资料确定黏土矿物含量的方法研究[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2011, 23(2):109-113. |
|
CHEN Ganghua, YANG Ye. Method of determining clay mineral content by using conventional logging data[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2011, 23(2):109-113.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2011.02.021 |
|
| [32] | 罗胜元, 陈孝红, 倪方杰. 自然伽马能谱测井在富有机质页岩评价和地质导向中的应用[J]. 测井技术, 2021, 45(3):297-304. |
| LUO Shengyuan, CHEN Xiaohong, NI Fangjie. Application of natural gamma spectroscopy logging in evaluation and guidance of black shale[J]. Well Logging Technology, 2021, 45(3):297-304. | |
| [33] |
宋宣毅, 刘月田, 马晶, 等. 基于灰狼算法优化的支持向量机产能预测[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2020, 32(2):134-140.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20200215 |
|
SONG Xuanyi, LIU Yuetian, MA Jing, et al. Productivity forecast based on support vector machine optimized by grey wolf optimizer[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2020, 32(2):134-140.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20200215 |
|
| [34] | 王光宇, 宋建国, 徐飞, 等. 不平衡样本集随机森林岩性预测方法[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2021, 56(4):679-687. |
| WANG Guangyu, SONG Jianguo, XU Fei, et al. Random forests lithology prediction method for imbalanced data sets[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2021, 56(4):679-687. |
|
||