岩性油气藏 ›› 2026, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (1): 136–145.doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20260112
• 地质勘探 • 上一篇
缝洞型碳酸盐岩岩溶体系表征及油气富集主控因素——以塔北地区轮古油田奥陶系为例
关宝珠1( ), 王爱萍2(
), 王爱萍2( ), 杨新影1, 裴明利2, 万超凡1, 倪祥龙2, 张强2, 杨巍2
), 杨新影1, 裴明利2, 万超凡1, 倪祥龙2, 张强2, 杨巍2
- 1
中国石油塔里木油田 勘探开发研究院 新疆 库尔勒 841000
2中国石油勘探开发研究院西北分院 兰州 730020
Characterization of fracture-cavity carbonate karst system and main controlling factors for hydrocarbon enrichment: A case study of Ordovician in Lungu Oilfield, Tabei area
GUAN Baozhu1( ), WANG Aiping2(
), WANG Aiping2( ), YANG Xinying1, PEI Mingli2, WAN Chaofan1, NI Xianglong2, ZHANG Qiang2, YANG Wei2
), YANG Xinying1, PEI Mingli2, WAN Chaofan1, NI Xianglong2, ZHANG Qiang2, YANG Wei2
- 1
Research Institute of Exploration and Development ,PetroChina Tarim Oilfield Korla 841000, Xinjiang, China
2PetroChina Research Institute of Petroleum Exploration and Development-Northwest Lanzhou 730020, China
摘要:
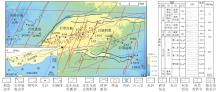
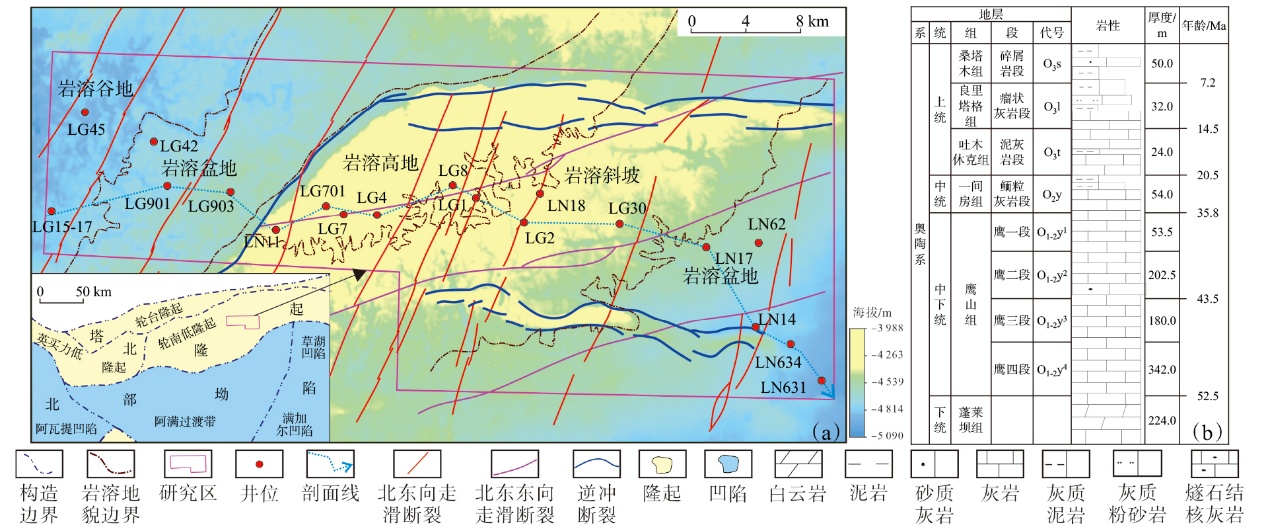
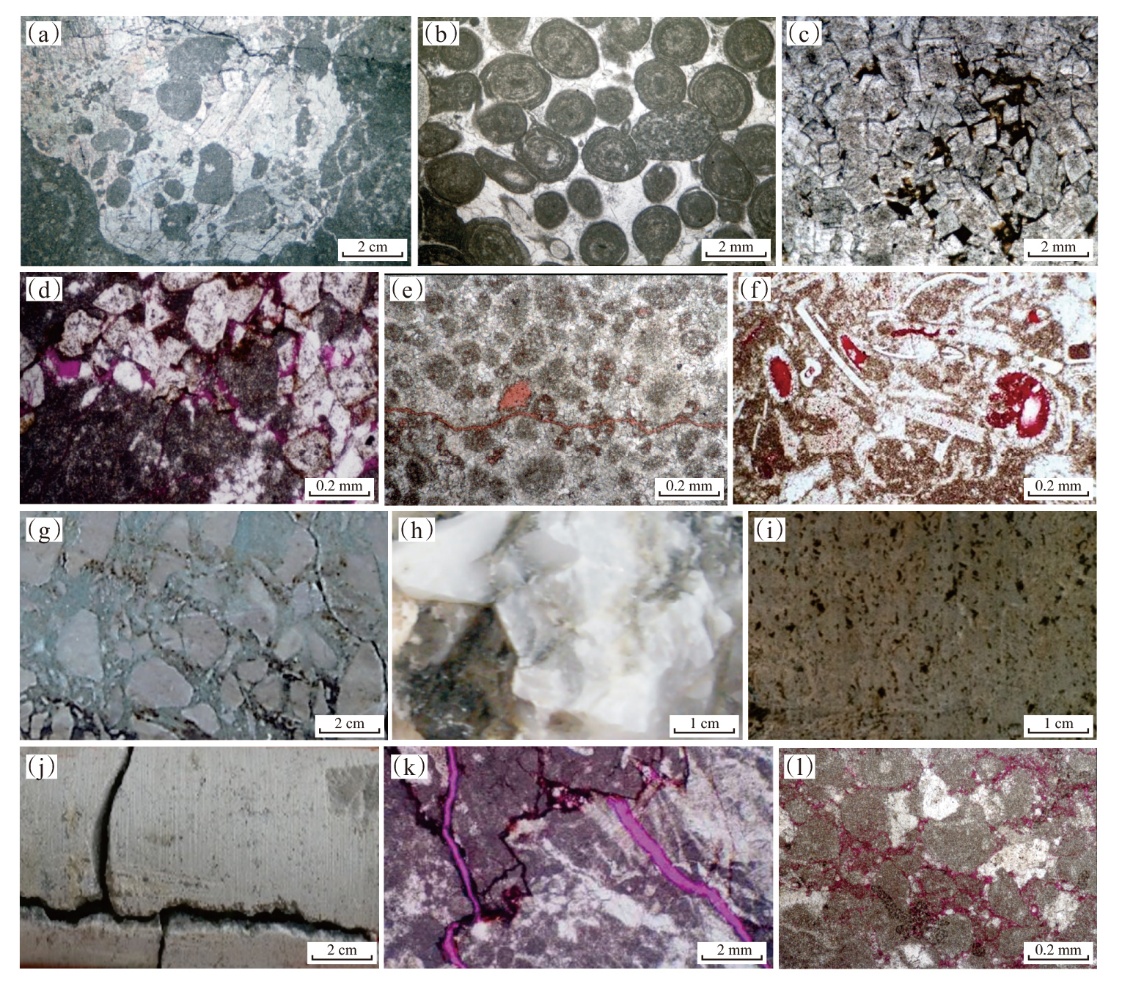
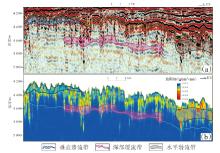
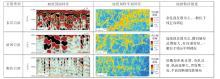
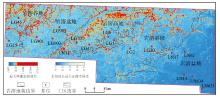
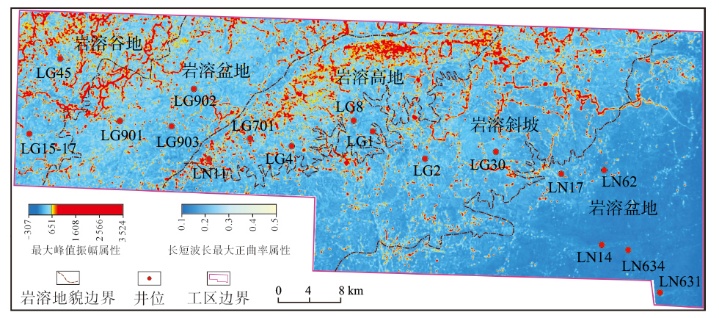
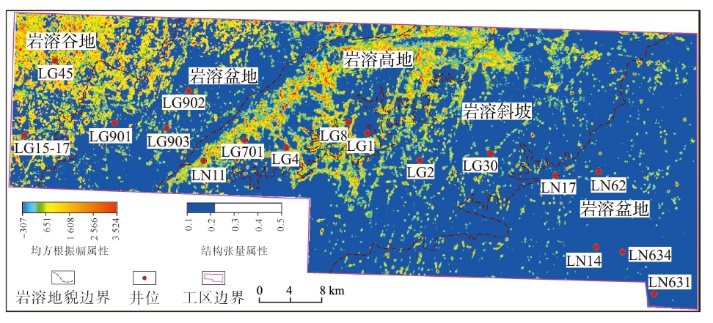
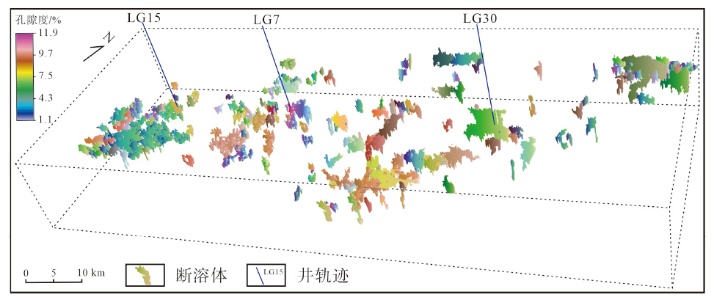
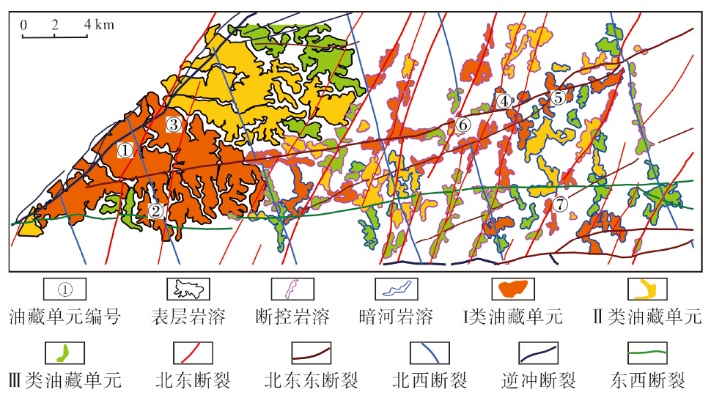
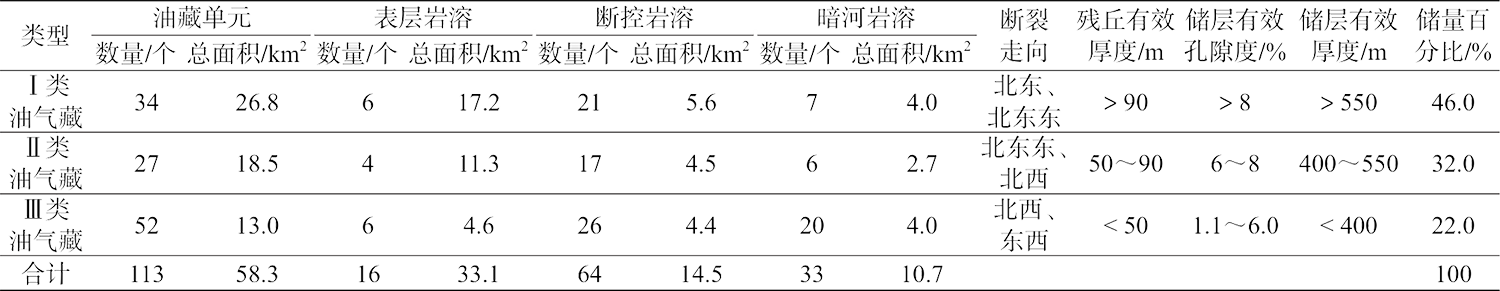
塔北地区轮古油田奥陶系缝洞型碳酸盐岩储层是中国超深层油气勘探的重要领域。基于高密度地震、测井及动态生产资料,构建了塔北地区轮古油田奥陶系缝洞型碳酸盐岩储层构造-岩溶-流体多场耦合储层预测理论框架,通过缝洞系统定量表征技术,系统揭示了储层发育规律与油气富集主控因素。研究结果表明:①轮古油田奥陶系储层非均质性较强,储集空间可划分为4种类型,晶间孔主要发育于晶粒白云岩中,孔径5~20 μm;粒间溶孔主要由鲕粒灰岩等颗粒灰岩经选择性溶蚀形成,孔径50~200 μm,为储层主要渗流通道;微裂缝宽度多小于10 μm;生物体腔孔主要发育于生物碎屑灰岩中,常见海百合茎等生物格架孔,孔径100~500 μm。②表层岩溶储层呈片状分布于古地貌高地,暗河岩溶储层沿古水系呈条带状展布,断控岩溶储层沿断裂带呈线状分布,多属性融合与三维地质建模技术可实现岩溶储层的三维空间整体雕刻。③油气的富集程度受岩溶相-断裂-储层规模控制,Ⅰ类高富集区集中于北东/北东东向断裂带、残丘厚度大于90 m、有效孔隙度大于8%,有效厚度大于550 m区域,为断裂-缝洞双输导、多期复式充注的成藏模式、“表层区侧向追踪、暗河区立体评价、断控区定向输导”的差异化开发策略可使产能提升15%~30%,新增储量大于200×104 t。
中图分类号:
- TE122.22
| [1] | 耿晓洁, 林畅松, 吴斌. 古地貌对塔中地区鹰山组岩溶结构及分布的控制作用[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2018, 30(4):46-55. |
|
GENG Xiaojie, LIN Changsong, WU Bin. Controlling of paleogeomorphology to characteristics and distribution of karst structures of Yingshan Formation in Tazhong area[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2018, 30(4):46-55.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20180405 |
|
| [2] | 贾永禄, 孙高飞, 聂仁仕, 等. 四重介质油藏渗流模型与试井曲线[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2016, 28(1):123-127. |
|
JIA Yonglu, SUN Gaofei, NIE Renshi, et al. Flow model and well test curves for quadruple-media reservoirs[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2016, 28(1):123-127.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2016.01.017 |
|
| [3] | 王清华, 杨海军, 汪如军, 等. 塔里木盆地超深层走滑断裂断控大油气田的勘探发现与技术创新[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2021, 26(4):58-71. |
| WANG Qinghua, YANG Haijun, WANG Rujun, et al. Disco-very and exploration technology of fault-controlled large oil and gas fields of ultra-deep formation in strike slip fault zone in Tarim Basin[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2021, 26(4):58-71. | |
| [4] | 程飞, 韩杰, 韩开飞, 等. 塔里木盆地轮古油田奥陶系储层特征及主控因素[J]. 东北石油大学学报, 2015, 39(3):15-24. |
| CHENG Fei, HAN Jie, HAN Kaifei, et al. Characteristics and main controlling factors of the Ordovician carbonate rock reservoirs in Lungu oilfield,Tarim basin[J]. Journal of Northeast Petroleum University, 2015, 39(3):15-24. | |
| [5] |
邓晓娟, 李勇, 刘志良, 等. 多尺度缝洞型碳酸盐岩油藏不确定性建模方法[J]. 石油学报, 2018, 39(9):1051-1062.
doi: 10.7623/syxb201809009 |
|
DENG Xiaojuan, LI Yong, LIU Zhiliang, et al. Uncertainty modeling method of multi-scale fracture-cave carbonate reservoir[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2018, 39(9):1051-1062.
doi: 10.7623/syxb201809009 |
|
| [6] | 乔俊程, 常少英, 曾溅辉, 等. 塔里木盆地北部富满地区超深层走滑断裂带碳酸盐岩油气差异成藏成因探讨[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2024, 45(5):1226-1246. |
| QIAO Juncheng, CHANG Shaoying, ZENG Jianhui, et al. Origin of differential hydrocarbon accumulation in ultra-deep carbonate reservoirs along strike-slip fault zones in the Fuman area,northern Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2024, 45(5):1226-1246. | |
| [7] | 陈思明, 侯明才, 房启飞, 等. 塔北隆起英买2地区奥陶系油气成藏特征及富集规律[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2015, 27(6):64-71. |
| CHEN Siming, HOU Mingcai, FANG Qifei, et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation and enrichment rule of Ordovician in Yingmai-2 area,northern uplift of Tarim Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2015, 27(6):64-71. | |
| [8] |
蔡振忠, 赵海涛, 王彭, 等. 考虑流固耦合作用的超深缝洞型碳酸盐岩储层连通性表征:以塔里木盆地富满油田满深区块为例[J]. 地学前缘, 2024, 31(5):301-312.
doi: 10.13745/j.esf.sf.2024.6.33 |
|
CAI Zhenzhong, ZHAO Haitao, WANG Peng, et al. Characte-rization of connectivity in ultra-deep fractured-caveate reservoirs considering fluid-solid coupling:A case study of the Manfen block in the Fuman oil field of the Tar Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2024, 31(5):301-312.
doi: 10.13745/j.esf.sf.2024.6.33 |
|
| [9] | 李阳. 塔河油田碳酸盐岩缝洞型油藏开发理论及方法[J]. 石油学报, 2013, 34(1):115-121. |
|
LI Yang. The theory and method for development of carbonate fractured-cavity reservoirs in Tahe oilfield[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2013, 34(1):115-121.
doi: 10.7623/syxb201301013 |
|
| [10] | 邓尚, 邱华标, 刘大卫, 等. 克拉通内走滑断裂成因与控藏机制研究进展[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2024, 45(5):1211-1225. |
| DENG Shang, QIU Huabiao, LIU Dawei, et al. Advances in research on the genetic mechanisms of intracratonic strike-slip fault system and their control on hydrocarbon accumulation:A case study of the northern Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2024, 45(5):1211-1225. | |
| [11] | LI You, WU Xinming, ZHU Zhenyu, et al. FaultSeg3D plus:A comprehensive study on evaluating and improving CNN-based seismic fault segmentation[J]. Geophysics, 2024, 89(5):N77-N91. |
| [12] |
LIU Yajing, WANG Lizhong, HONG Yi, et al. Coupled thermo-hydro-mechanical-chemical modeling of fines migration in hydrate-bearing sediments with CFD-DEM[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2023, 60(5):701-717.
doi: 10.1139/cgj-2022-0124 |
| [13] | 吕心瑞, 孙建芳, 李红凯, 等. 塔里木盆地深层碳酸盐岩缝洞型油藏精细地质建模技术[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2024, 45(5):1195-1210. |
| LYU Xinrui, SUN Jianfang, LI Hongkai, et al. Fine geological modelling technology for deep fractured-vuggy carbonate oil reservoirs in the Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2024, 45(5):1195-1210. | |
| [14] | 王伟力, 刘洛夫, 陈利新, 等. 塔里木盆地轮古东地区奥陶系碳酸盐岩储集层发育控制因素及有利区带预测[J]. 古地理学报, 2010, 12(1):107-115. |
| WANG Weili, LIU Luofu, CHEN Lixin, et al. Controlling factors and favorable zones prediction of the Ordovician carbonate reservoir in Lungudong area,Tarim Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography(Chinese Edition), 2010, 12(1):107-115. | |
| [15] | 高利君, 李宗杰, 李海英, 等. 塔里木盆地深层岩溶缝洞型储层三维雕刻“五步法”定量描述技术研究与应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(3):691-697. |
| GAO Lijun, LI Zongjie, LI Haiying, et al. The deep karst fissure and cavern reservoir in Tarim basin carved in three dimensions:Research and application of “five-step method” quantitative description technology[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(3):691-697. | |
| [16] | 漆家福, 陈石, 罗彩明, 等. 塔里木盆地阿-满过渡区走滑断裂系统及其控藏规律[J]. 地质学报, 2024, 98(12):3662-3682. |
| QI Jiafu, CHEN Shi, LUO Caiming, et al. Strike-slip fault system and its reservoir-controlling rules in Awati-Manger-transitional area,Tarim basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2024, 98(12):3662-3682. | |
| [17] | 李凤磊, 林承焰, 崔仕提, 等. 塔北地区奥陶系古地貌及走滑断裂差异性控储规律[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 46(6):48-58. |
| LI Fenglei, LIN Chengyan, CUI Shiti, et al. Analysis on diffe-rence of Ordovician fracture-cavity reservoirs controled by ancient landform and slip fault in Tabei area,Tarim Basin[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 2022, 46(6):48-58. | |
| [18] |
倪新锋, 沈安江, 乔占峰, 等. 塔里木盆地奥陶系缝洞型碳酸盐岩岩溶储层成因及勘探启示[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2023, 35(2):144-158.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20230214 |
|
NI Xinfeng, SHEN Anjiang, QIAO Zhanfeng, et al. Genesis and exploration enlightenment of Ordovician fracture-vuggy carbonate karst reservoirs in Tarim Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2023, 35(2):144-158.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20230214 |
|
| [19] | 邓兴梁, 李世银, 梁彬, 等. 轮古奥陶潜山油水界面识别方法及油气分布特征评价:以轮古LG7井区为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2013, 32(3):339-344. |
| DENG Xingliang, LI Shiyin, LIANG Bin, et al. Identification of oil-water interface and evaluation of oil and gas distribution in Ordovician buried hill reservoir in Lungu:A case in Lungu-well block 7[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2013, 32(3):339-344. | |
| [20] |
马永生, 蔡勋育, 李慧莉, 等. 深层—超深层碳酸盐岩储层发育机理新认识与特深层油气勘探方向[J]. 地学前缘, 2023, 30(6):1-13.
doi: 10.13745/j.esf.sf.2023.2.35 |
|
MA Yongsheng, CAI Xunyu, LI Huili, et al. New insights into the formation mechanism of deep-ultra-deep carbonate reservoirs and the direction of oil and gas exploration in extra-deep strata[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2023, 30(6):1-13.
doi: 10.13745/j.esf.sf.2023.2.35 |
|
| [21] | 张明, 李相文, 金梦, 等. 超深断控缝洞型储层迭代反演方法:以富满油田为例[J]. 物探与化探, 2023, 47(1):22-30. |
| ZHANG Ming, LI Xiangwen, JIN Meng, et al. Iterative inversion method for ultradeep fault-controlled fracture-vug reservoirs:A case study of the Fuman oilfield,Tarim Basin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(1):22-30. | |
| [22] | 吕修祥, 陈佩佩, 陈坤, 等. 深层碳酸盐岩差异成岩作用对油气分层聚集的影响:以塔里木盆地塔中隆起北斜坡鹰山组为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2019, 40(5):957-971. |
| LYU Xiuxiang, CHEN Peipei, CHEN Kun, et al. Effects of differential diagenesis of deep carbonate rocks on hydrocarbon zonation and accumulation:A case study of Yingshan Formation on northern slope of Tazhong uplift,Tarim Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2019, 40(5):957-971. | |
| [23] | 曹建文, 金意志, 夏日元, 等. 塔河油田4区奥陶系风化壳古岩溶作用标志及控制因素分析[J]. 中国岩溶, 2012, 31(2):220-226. |
| CAO Jianwen, JIN Yizhi, XIA Riyuan, et al. Marks and controlling factors of the paleo-karstification in the Ordovician weathered crust at the 4th block of Tahe oil field[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2012, 31(2):220-226. | |
| [24] | 崔立杰, 何幼斌, 王锦喜, 等. 基于层面的地震曲率属性在碳酸盐岩断裂预测中的应用:以塔里木盆地塔北某区块为例[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2012, 24(1):92-96. |
| CUI Lijie, HE Youbin, WANG Jinxi, et al. Application of seismic curvature based on horizon to carbonate fault prediction:An example of an area in Tabei,Tarim Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2012, 24(1):92-96. | |
| [25] | 李辉, 宁亚鑫. 超深层碳酸盐岩储集层天然裂缝发育差异性:以塔里木盆地YUEM地区为例[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2025, 46(2):144-153. |
| LI Hui, NING Yaxin. Differences in natural fracture development in ultra-deep carbonate reservoirs:A case study of YUEM area in Tarim Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2025, 46(2):144-153. | |
| [26] | 常少英, 邓兴梁, 戴传瑞, 等. 岩溶洞穴型油藏描述中的几种方法:以塔北轮古西油田为例[J]. 海相油气地质, 2016, 21(3):65-71. |
| CHANG Shaoying, DENG Xingliang, DAI Chuanrui, et al. Methods of reservoir description for karst caved reservoirs:An example from Lunguxi Oil Field,Tarim Basin[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2016, 21(3):65-71. | |
| [27] | 雷川, 陈红汉, 苏奥, 等. 塔河地区奥陶系深埋岩溶洞穴特征及保存机制初探[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2014, 26(2):27-31. |
|
LEI Chuan, CHEN Honghan, SU Ao, et al. Characteristics and preservation mechanism of the Ordovician deep burial karst caves in Tahe area[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2014, 26(2):27-31.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2014.02.005 |
|
| [28] | 王福焕, 王振宇, 张云峰, 等. 轮古东奥陶系断裂特征及其对油气成藏的控制[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2011, 16(1):15-20. |
| WANG Fuhuan, WANG Zhenyu, ZHANG Yunfeng, et al. Fault characteristics and their controlling roles to hydrocarbon pool-formation of Ordovician in Eastern Lungu[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2011, 16(1):15-20. |
| [1] | 黄诚, 朱莲花, 卜旭强, 曾溅辉, 隆辉, 廖文毫, 刘亚洲, 乔俊程. 塔里木盆地顺北地区走滑断裂特征及控藏作用[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2025, 37(6): 107-118. |
| [2] | 陆江, 王健, 吴楠, 李程善, 冯子飞. 鄂尔多斯盆地西缘奥陶系乌拉力克组页岩气勘探潜力[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2025, 37(5): 34-48. |
| [3] | 江山, 唐永建, 焦霞蓉, 李文亮, 黄成, 王泽. 塔里木盆地顺北油田4号断裂带断控体凝析气藏剩余气分布规律[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2025, 37(4): 84-94. |
| [4] | 陈钰桦, 施泽进, 李文杰, 易永杰, 刘恒, 田亚铭, 谭谦. 川东南习水地区下奥陶统层序地层特征及储层发育主控因素[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2025, 37(4): 147-158. |
| [5] | 熊昶, 王彭, 刘小钰, 王伟, 赵星星, 孙冲. 塔中隆起奥陶系油气性质及运聚富集模式[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2025, 37(1): 53-67. |
| [6] | 吴松, 冯冰, 于继良, 蓝宝锋, 李龙, 王胜, 沈家宁, 李刚权. 黔北正安地区安场向斜奥陶系五峰组—志留系龙马溪组页岩气富集规律[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2025, 37(1): 182-193. |
| [7] | 苏皓, 郭艳东, 曹立迎, 喻宸, 崔书岳, 卢婷, 张云, 李俊超. 顺北油田断控缝洞型凝析气藏衰竭式开采特征及保压开采对策[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2024, 36(5): 178-188. |
| [8] | 程静, 闫建平, 宋东江, 廖茂杰, 郭伟, 丁明海, 罗光东, 刘延梅. 川南长宁地区奥陶系五峰组—志留系龙马溪组页岩气储层低电阻率响应特征及主控因素[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2024, 36(3): 31-39. |
| [9] | 陈叔阳, 何云峰, 王立鑫, 尚浩杰, 杨昕睿, 尹艳树. 塔里木盆地顺北1号断裂带奥陶系碳酸盐岩储层结构表征及三维地质建模[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2024, 36(2): 124-135. |
| [10] | 杜江民, 崔子豪, 贾志伟, 张毅, 聂万才, 龙鹏宇, 刘泊远. 鄂尔多斯盆地苏里格地区奥陶系马家沟组马五5亚段沉积特征[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2023, 35(5): 37-48. |
| [11] | 宋兴国, 陈石, 杨明慧, 谢舟, 康鹏飞, 李婷, 陈九洲, 彭梓俊. 塔里木盆地富满油田FⅠ16断裂发育特征及其对油气分布的影响[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2023, 35(3): 99-109. |
| [12] | 卜旭强, 王来源, 朱莲花, 黄诚, 朱秀香. 塔里木盆地顺北油气田奥陶系断控缝洞型储层特征及成藏模式[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2023, 35(3): 152-160. |
| [13] | 倪新锋, 沈安江, 乔占峰, 郑剑锋, 郑兴平, 杨钊. 塔里木盆地奥陶系缝洞型碳酸盐岩岩溶储层成因及勘探启示[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2023, 35(2): 144-158. |
| [14] | 刘永立, 李国蓉, 何钊, 田家奇, 李肖肖. 塔北地区寒武系层序地层格架与台缘带展布特征[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2022, 34(6): 80-91. |
| [15] | 何文渊, 云建兵, 钟建华. 川东北二叠系长兴组碳酸盐岩云化成储机制[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2022, 34(5): 1-25. |
|
||






 甘公网安备 62010202002827号
甘公网安备 62010202002827号