岩性油气藏 ›› 2026, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (1): 115–125.doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20260110
• 地质勘探 • 上一篇
基于光流矢量的TI介质逆时偏移方法
- 1
中国石油勘探开发研究院 西北分院 兰州 730020
2中国海洋大学 海洋地球科学学院 山东 青岛 266100
Reverse-time migration in TI media based on optical flow vector
FENG Yancang1(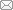 ), LIU Wenqing1, ZHANG Huixing2, WU Jie1, LI Dongsheng1
), LIU Wenqing1, ZHANG Huixing2, WU Jie1, LI Dongsheng1
- 1
PetroChina Research Institute of Petroleum Exploration and Development-Northwest Lanzhou 730020, China
2Ocean University of China Qingdao 266100, Shandong, China
摘要:
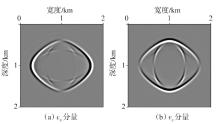
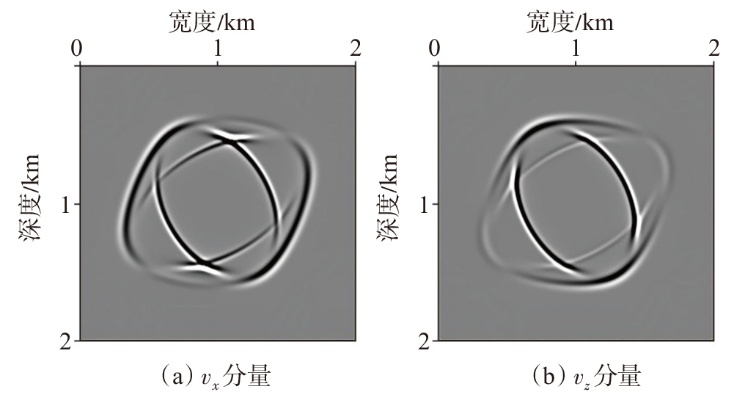
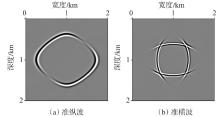
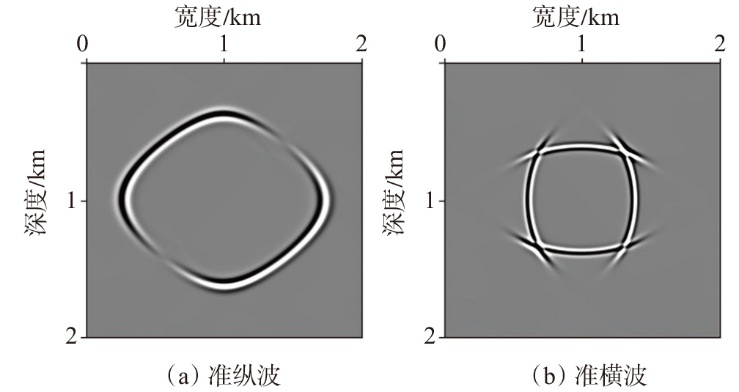
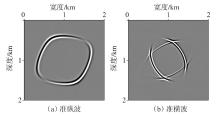
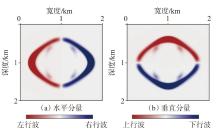
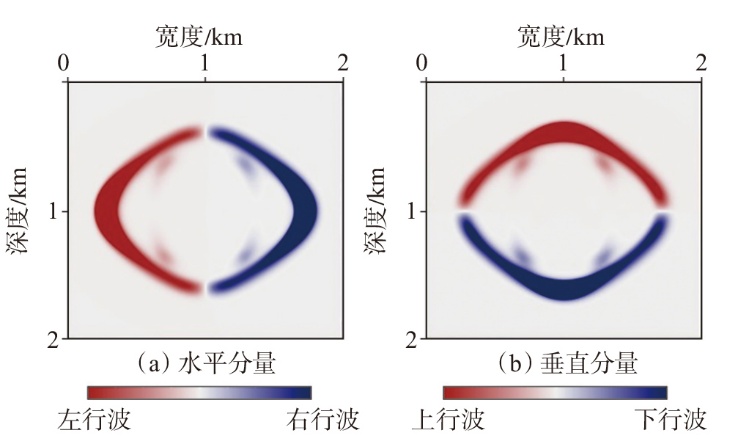
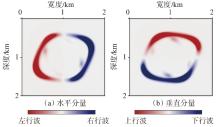
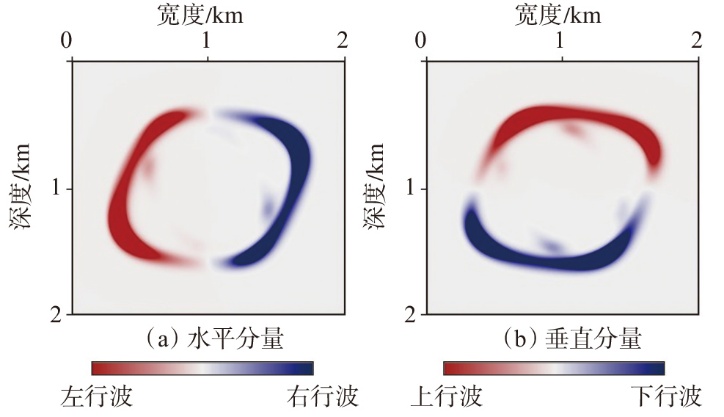
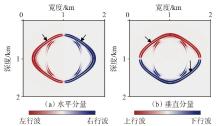
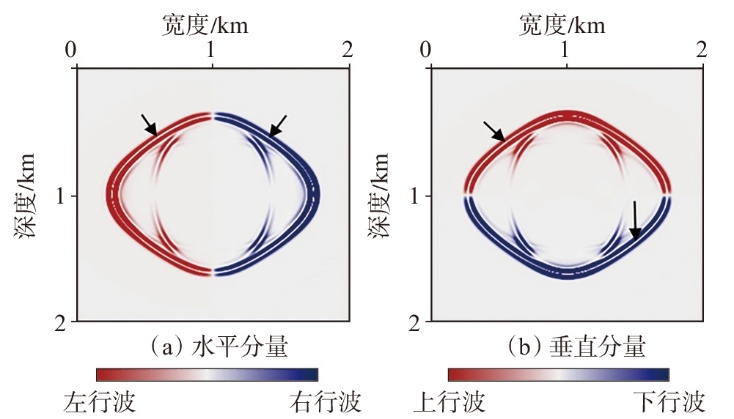
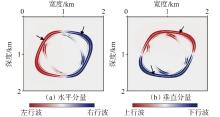
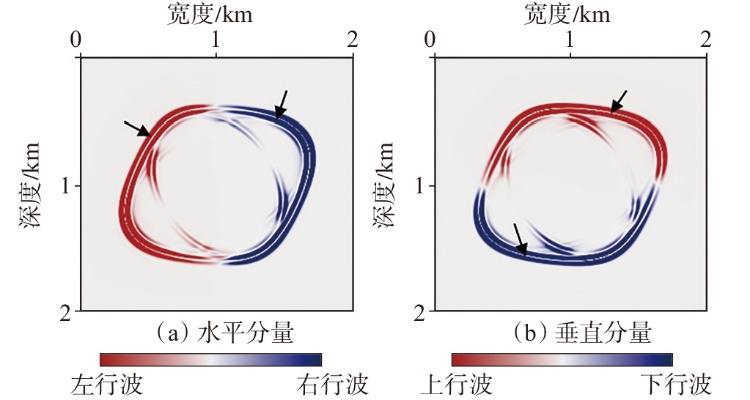
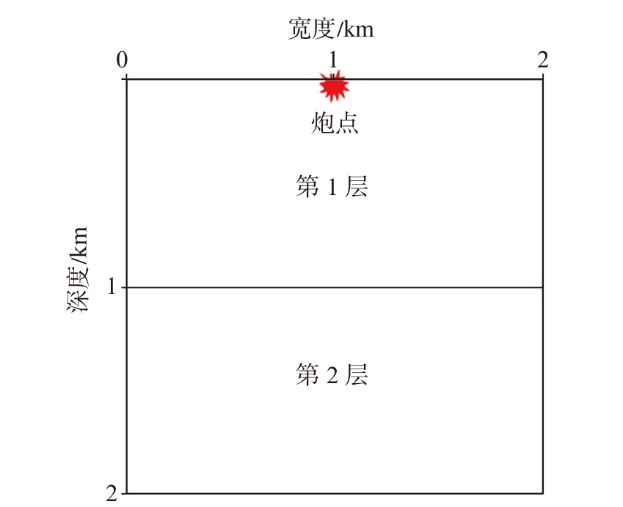
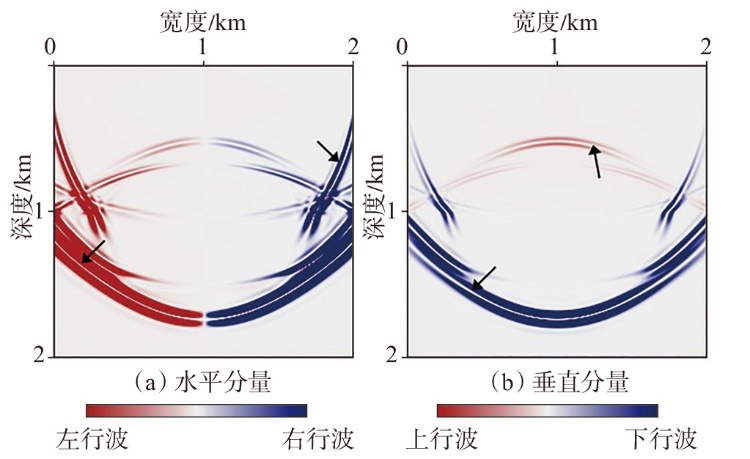
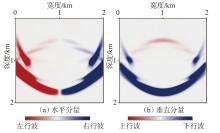
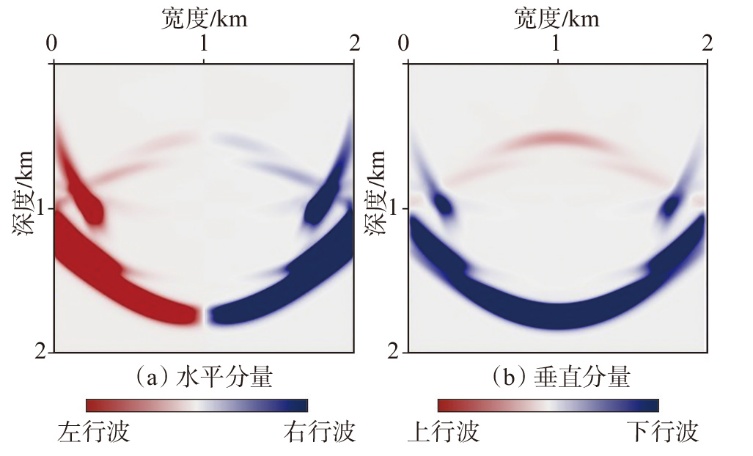
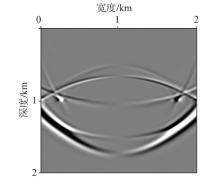
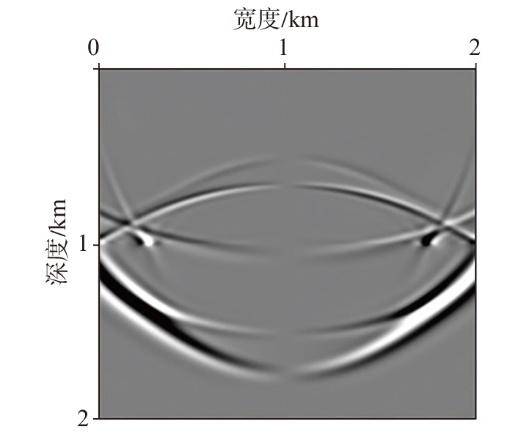
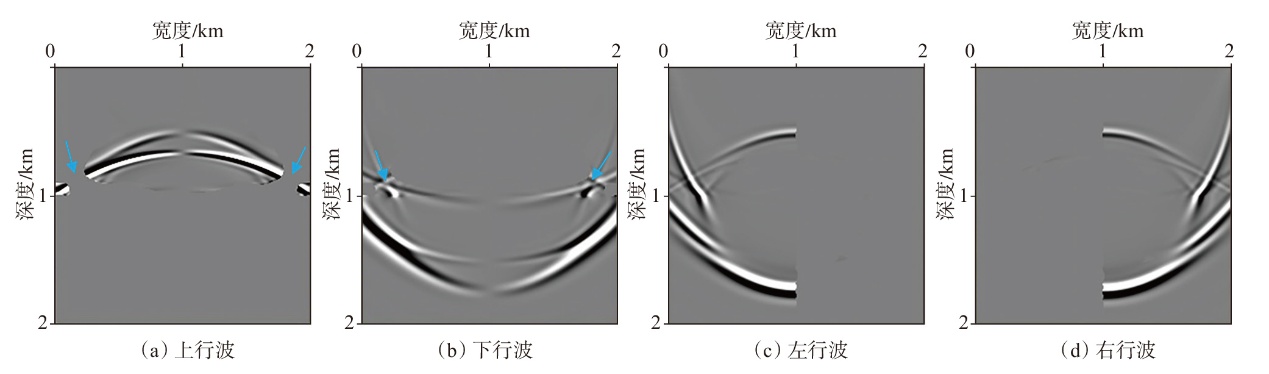
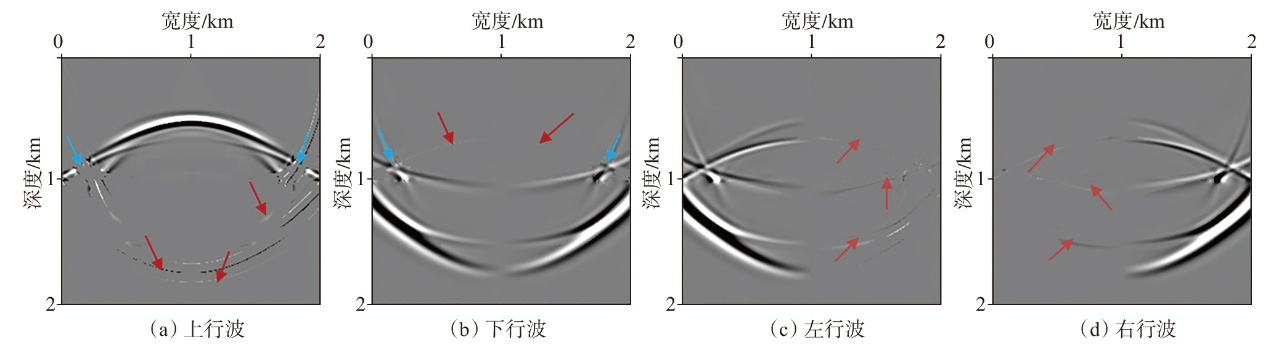
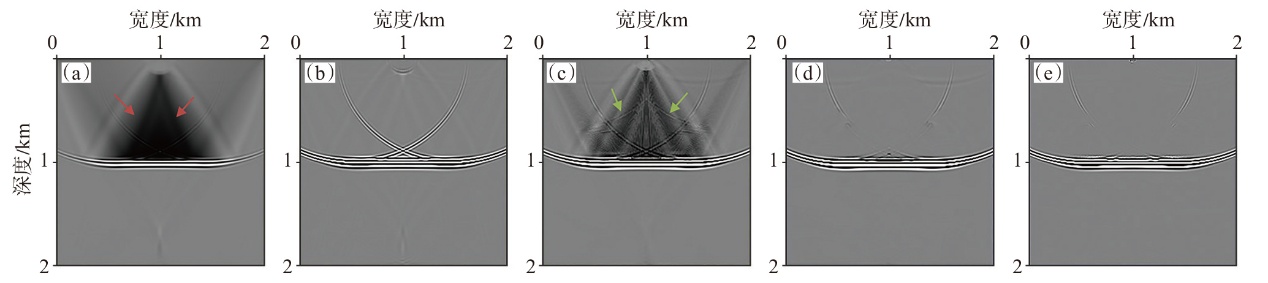
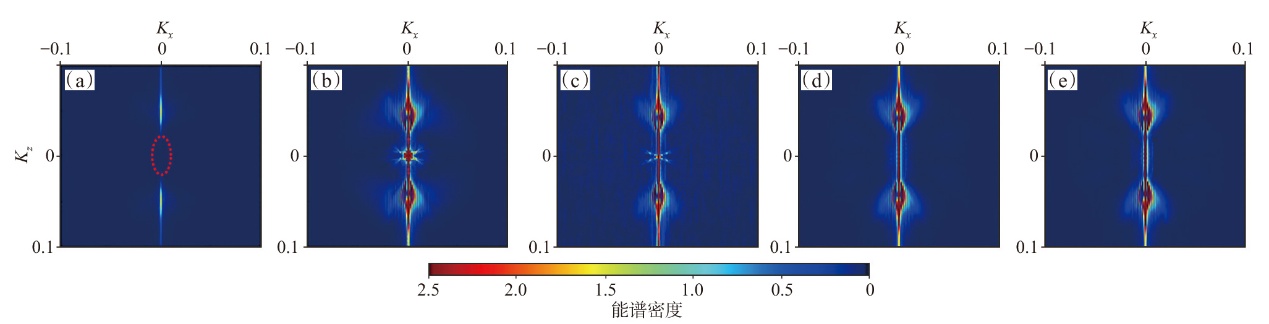
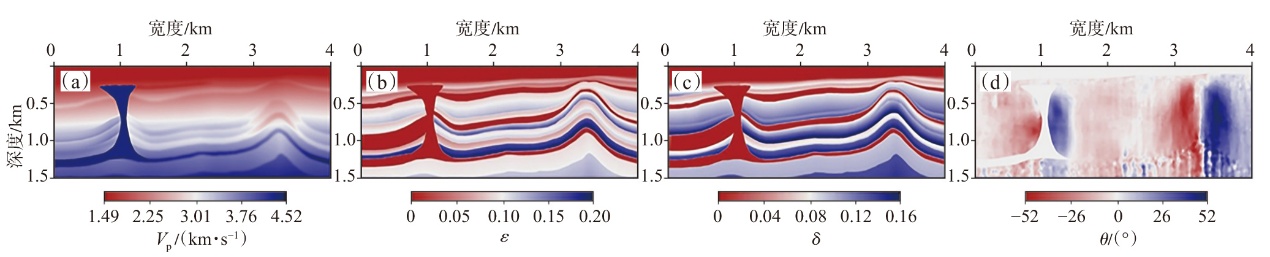
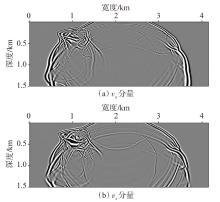
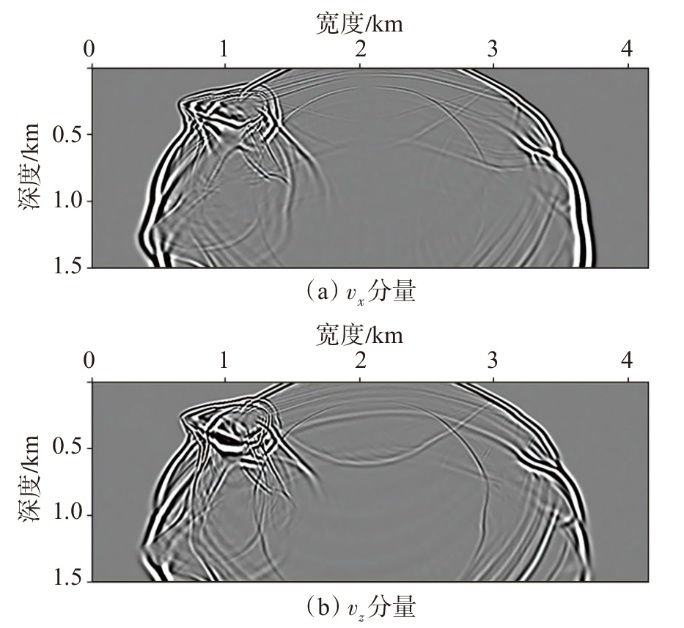
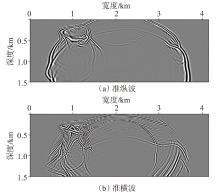
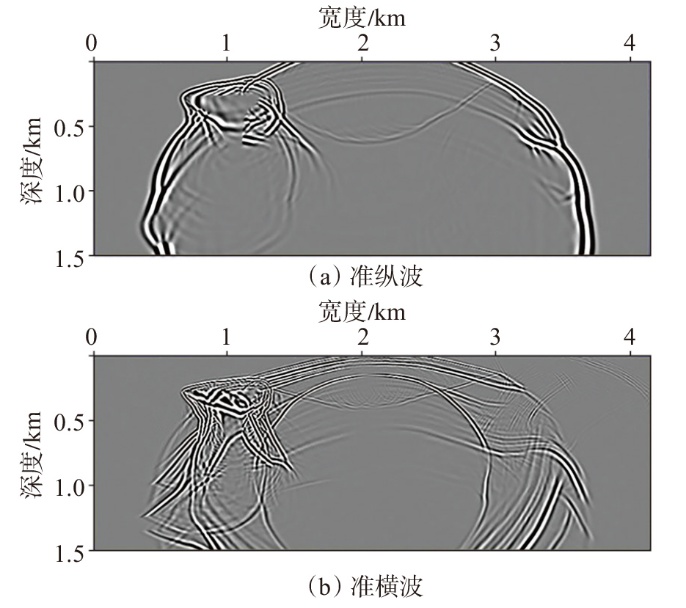
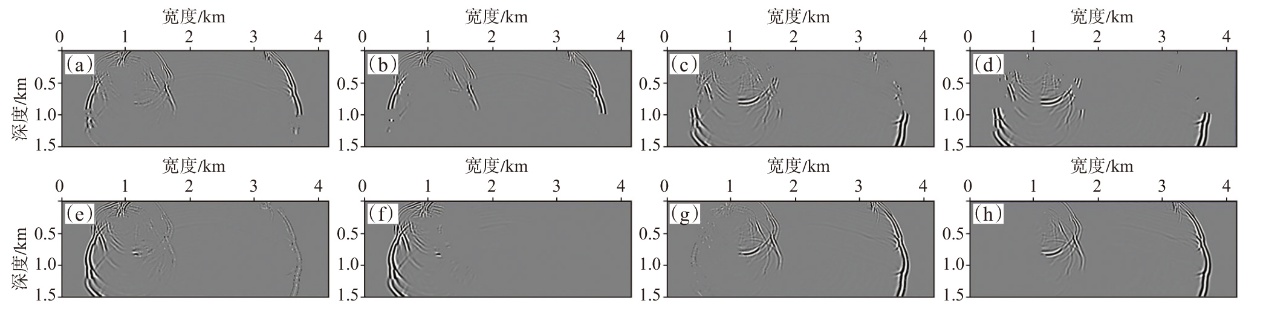
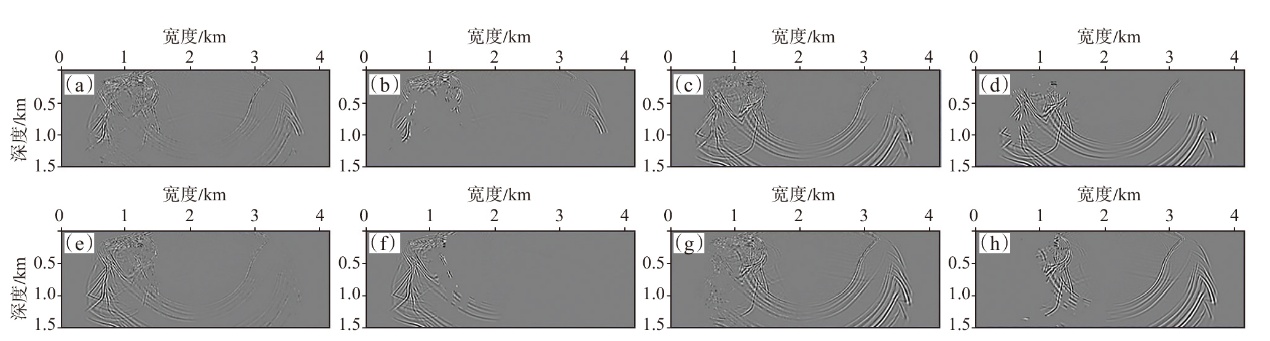
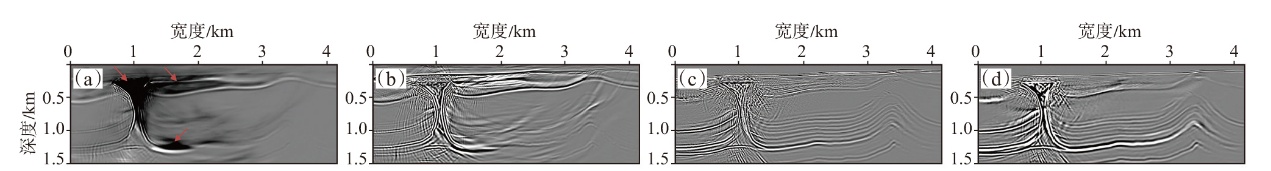
弹性波逆时偏移技术在面对复杂地质构造时,背向发育的反射波与正常传播的波场互相关易产生较强振幅的低频噪声。为了解决常规Poynting矢量的行波分离逆时偏移算法计算不稳定、行波分离精度不高等问题,开展了基于光流矢量的TI 介质逆时偏移方法研究,通过将光流学与各向异性介质弹性动力学相结合,经过多次迭代运算得到一个更逼近于真实波场传播方向信息的精确矢量,有效压制了偏移噪声。研究结果表明:①利用光流法相邻时间内波场不变的假设和在空间方向上波场光滑的假设得到的TI 介质的光流矢量可以有效避免Poynting矢量的不稳定隐患,能精确指示TI 介质中纵横波的传播方向。②基于光流矢量的行波分离方法可以精确地分离出波场的上、下、左、右行波。③基于光流矢量的TI 介质逆时偏移算法可以有效避免同路径波场的互相关成像,可压制偏移噪声。
中图分类号:
- TE121.34
| [1] | 陈可洋. 基于拉普拉斯算子的叠前逆时噪声压制方法[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2011, 23(5):87-95. |
|
CHEN Keyang. Pre-stack reverse-time noise suppressing method based on Laplacian operator[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2011, 23(5):87-95.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2011.05.018 |
|
| [2] |
刘梦丽, 徐兴荣, 王小卫, 等. 预条件弹性介质最小二乘逆时偏移[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2020, 32(5):133-142.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20200514 |
|
LIU Mengli, XU Xingrong, WANG Xiaowei, et al. Preconditioning elastic least-squares reverse time migration[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2020, 32(5):133-142.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20200514 |
|
| [3] |
芦永明, 张剑锋, 杨凯, 等. 二维TI介质非结构网格弹性波矢量逆时偏移[J]. 地球物理学报, 2017, 60(12):4776-4789.
doi: 10.6038/cjg20171219 |
| LU Yongming, ZHANG Jianfeng, YANG Kai, et al. Vector elastic reverse time migration based on unstructured mesh for 2D tilted TI medium[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2017, 60(12):4776-4789. | |
| [4] | 周进举, 王德利, 李博文, 等. 基于解耦传播的波场分解方法在VTI介质弹性波逆时偏移中的应用[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 2018, 48(3):909-921. |
| ZHOU Jinju, WANG Deli, LI Bowen, et al. Application of wave-field decomposition based on decoupled propagation in elastic RTM for VTI media[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 2018, 48(3):909-921. | |
| [5] | 陈沫. 横向各向同性介质地震波场逆时偏移[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2009, 21(4):78-81. |
|
CHEN Mo. The seismic wave field reverse-time migration in transversely isotropic media[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2009, 21(4):78-81.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2009.04.015 |
|
| [6] | 杜启振, 秦童. 横向各向同性介质弹性波多分量叠前逆时偏移[J]. 地球物理学报, 2009, 52(3):801-807. |
| DU Qizhen, QIN Tong. Multicomponent prestack reverse-time migration of elastic waves in transverse isotropic medium[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2009, 52(3):801-807. | |
| [7] | ZHOU Yang, WANG Huazhong. Efficient wave-mode separation in vertical transversely isotropic media[J]. Geophysics, 2016, 81(2):C35-C47. |
| [8] | YANG Kai, ZHANG Jianfeng. Determination of the phase-velocity directions in anisotropic media using a direction vector[J]. Geophysics, 2022, 87(6):C125-C138. |
| [9] |
DU Qizhen, GUO Chenfeng, ZHAO Qiang, et al. Vector-based elastic reverse time migration based on scalar imaging condition[J]. Geophysics, 2017, 82(2):S111-S127.
doi: 10.1190/geo2016-0146.1 |
| [10] | XIAO Xiang, LEANEY W S. Local vertical seismic profiling (VSP) elastic reverse-time migration and migration resolution:Salt-flank imaging with transmitted P-to-S waves[J]. Geophy-sics, 2010, 75(2):S35-S49. |
| [11] |
LI Zhiyuan, LIU Youshan, LIANG Guanghe, et al. First-order particle velocity equations of decoupled P- and S-wavefields and their application in elastic reverse time migration[J]. Geophysics, 2021, 86(6):S387-S404.
doi: 10.1190/geo2020-0452.1 |
| [12] |
TANG Chen, MCMECHAN G A, WANG Deli. Two algorithms to stabilize multidirectional Poynting vectors for calculating angle gathers from reverse time migration[J]. Geophysics, 2017, 82(2):S129-S141.
doi: 10.1190/geo2016-0101.1 |
| [13] | LI Zhiyuan, WANG Jiquan, MA Xiaona, et al. Calculation of the stable Poynting vector using the first-order temporal derivative of the seismic wavefield[J]. Geophysics, 2022, 87(1):S17-S25. |
| [14] |
BRUHN A, WEICKERT J, SCHNORR C. Lucas/Kanade meets Horn/Schunck:Combining local and global optic flow methods[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2005, 61(3):211-231.
doi: 10.1023/B:VISI.0000045324.43199.43 |
| [15] | SZELISKI R. Computer vision:Algorithms and applications[M]. 2nd ed. New York: Springer, 2022. |
| [16] |
GONG Ting, NGUYEN B D, MCMECHAN G A. Polarized wavefield magnitudes with optical flow for elastic angle-demain common-image gathers[J]. Geophysics, 2016, 81(4):S239-S251.
doi: 10.1190/geo2015-0518.1 |
| [17] |
吴成梁, 王华忠, 冯波, 等. 基于CLG光学流和波场分解的逆时偏移角度道集提取方法研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2021, 64(4):1375-1388.
doi: 10.6038/cjg2021O0088 |
| WU Chengliang, WANG Huazhong, FENG Bo, et al. RTM angle gathers based on the Combining Local and Global (CLG) optical flow method and wavefield decomposition method[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2021, 64(4):1375-1388. | |
| [18] |
XIE Chuang, WANG Jianhua, SONG Peng, et al. Elastic reverse time migration based on first-order velocity-dilatation-rotation equations using the optical flow vector[J]. Geophysics, 2024, 89(4):S325-S337.
doi: 10.1190/geo2023-0198.1 |
| [19] |
VIRIEUX J. P-SV wave propagation in heterogeneous media:Velocity-stress finite-difference method[J]. Geophysics, 1986, 51(4):889-901.
doi: 10.1190/1.1442147 |
| [20] |
THOMSEN L. Weak elastic anisotropy[J]. Geophysics, 1986, 51(10):1954-1966.
doi: 10.1190/1.1442051 |
| [21] |
SAENGER E H, BOHLEN T. Finite-difference modeling of viscoelastic and anisotropic wave propagation using the rotated staggered grid[J]. Geophysics, 2004, 69(2):583-591.
doi: 10.1190/1.1707078 |
| [22] | 杨哲, 刘威, 胡自多, 等. 时空域波动方程混合网格有限差分数值模拟[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2018, 30(2):93-109. |
| YANG Zhe, LIU Wei, HU Ziduo, et al. Mixed-grid finite-diffe-rence methods for wave equation numerical modeling in time-space domain[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2018, 30(2):93-109. | |
| [23] | 陈可洋. 各向异性弹性介质方向行波波场分离正演数值模拟[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2014, 26(5):91-96. |
|
CHEN Keyang. Wave field separating numerical simulation of anisotropic elastic medium directional one-way wave[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2014, 26(5):91-96.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8926.2014.05.017 |
|
| [24] |
BERENGER J P. A perfectly matched layer for the absorption of electromagnetic waves[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1994, 114(2):185-200.
doi: 10.1006/jcph.1994.1159 |
| [25] | MORSE P M, FESHBACH H. Methods of theoretical physics:I[M]. New York: McGraw-Hill Book Company, 1953. |
| [26] |
DELLINGER J, ETGEN J. Wave-field separation in two-dimensional anisotropic media[J]. Geophysics, 1990, 55(7):914-919.
doi: 10.1190/1.1442906 |
| [27] |
HORN B K P, SCHUNCK B G. Determining optical flow[J]. Artificial Intelligence, 1981, 17:185-203.
doi: 10.1016/0004-3702(81)90024-2 |
| [28] | ZHANG Qie. RTM angle gathers and Specular Filter (SF) RTM using optical flow[R]. Houston: Society of Exploration Geophysicists, 2014. |
| [1] | 王立德, 王小卫, 周辉, 吴杰, 张志强, 王建乐, 王德英, 冯刚. 一种基于改进共轭梯度法的弹性波全波形反演速度分层建模方法[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2023, 35(4): 61-69. |
| [2] | 闫建平, 罗静超, 石学文, 钟光海, 郑马嘉, 黄毅, 唐洪明, 胡钦红. 川南泸州地区奥陶系五峰组—志留系龙马溪组页岩裂缝发育模式及意义[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2022, 34(6): 60-71. |
| [3] | 张猛. 基于GPU并行加速的黏声最小二乘逆时偏移及应用[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2022, 34(1): 148-153. |
| [4] | 徐兴荣, 苏勤, 孙甲庆, 曾华会, 肖明图, 刘梦丽. 高精度组合剩余静校正方法及其应用[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2021, 33(5): 132-139. |
| [5] | 刘梦丽, 徐兴荣, 王小卫, 胡书华, 刘金涛. 预条件弹性介质最小二乘逆时偏移[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2020, 32(5): 133-142. |
| [6] | 吴伟, 邵广辉, 桂鹏飞, 张虔, 魏浩元, 李国利, 任盼亮. 基于电成像资料的裂缝有效性评价和储集层品质分类——以鸭儿峡油田白垩系为例[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2019, 31(6): 102-108. |
| [7] | 刘冬冬, 杨东旭, 张子亚, 张晨, 罗群, 潘占昆, 黄治鑫. 基于常规测井和成像测井的致密储层裂缝识别方法——以准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷芦草沟组为例[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2019, 31(3): 76-85. |
| [8] | 李玉凤, 孙炜, 何巍巍, 杨云飞, 章新文, 严移胜. 基于叠前反演的泥页岩地层压力预测方法[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2019, 31(1): 113-121. |
| [9] | 赵搏志, 林畅松, 李浩, 王媛, 孙彦达, 何海全, 王清龙. 南哈Marsel探区Asa区块下石炭统岩溶储层精细刻画及分布特征[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2018, 30(1): 97-111. |
| [10] | 陈可洋. 逆时成像技术在大庆探区复杂构造成像中的应用[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2017, 29(6): 91-100. |
| [11] | 唐海全. 随钻方位伽马数据成像处理方法[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2017, 29(1): 110-115. |
| [12] | 周 文,尹太举,张亚春,李伟强,王冬冬 . 蚂蚁追踪技术在裂缝预测中的应用——以青西油田下沟组为例[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2015, 27(6): 111-118. |
| [13] | 张大权,邹妞妞,姜 杨,马崇尧,张顺存,杜社宽 . 火山岩岩性测井识别方法研究——以准噶尔盆地火山岩为例[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2015, 27(1): 108-114. |
| [14] | 陈可洋. 各向异性弹性介质方向行波波场分离正演数值模拟[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2014, 26(5): 91-96. |
| [15] | 陈可洋,陈树民,李来林,吴清岭,范兴才,刘振宽. 地震波动方程方向行波波场分离正演数值模拟与逆时成像[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2014, 26(4): 130-136. |
|
||



 甘公网安备 62010202002827号
甘公网安备 62010202002827号