岩性油气藏 ›› 2026, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (1): 172–179.doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20260115
• 石油工程与油气田开发 • 上一篇
页岩油藏CO2吞吐渗流场-应力场耦合数值模拟方法
张庆福( ), 张世明, 曹小朋, 吕琦, 李宗阳, 于金彪, 汪勇
), 张世明, 曹小朋, 吕琦, 李宗阳, 于金彪, 汪勇
中国石化胜利油田分公司 勘探开发研究院 山东 东营 257015
Numerical simulation on the coupling of flow and geomechanics during CO2 huff and puff in shale oil reservoirs
ZHANG Qingfu( ), ZHANG Shiming, CAO Xiaopeng, LYU Qi, LI Zongyang, YU Jinbiao, WANG Yong
), ZHANG Shiming, CAO Xiaopeng, LYU Qi, LI Zongyang, YU Jinbiao, WANG Yong
Exploration and Development Research Institute ,Sinopec Shengli Oilfield Company Dongying 257015, Shandong, China
摘要:
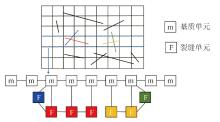
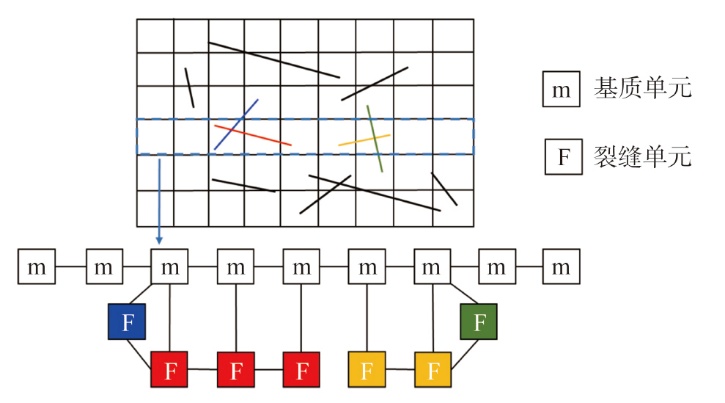
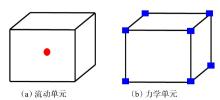
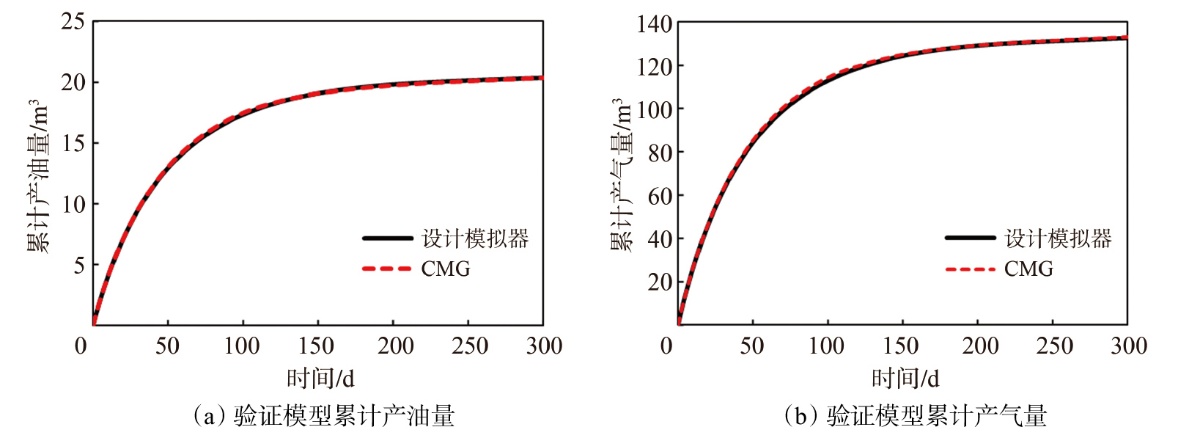
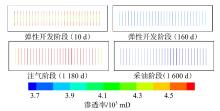
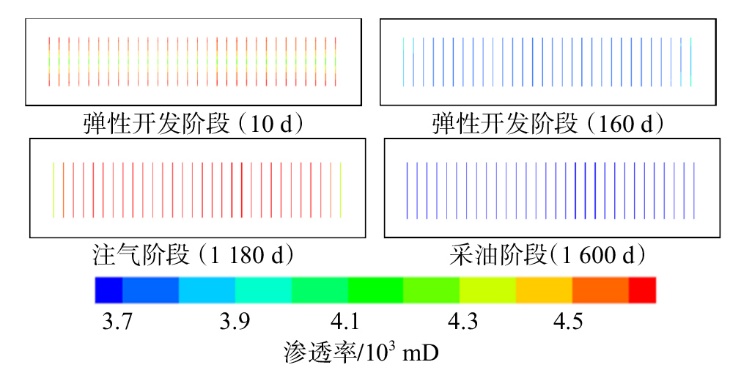
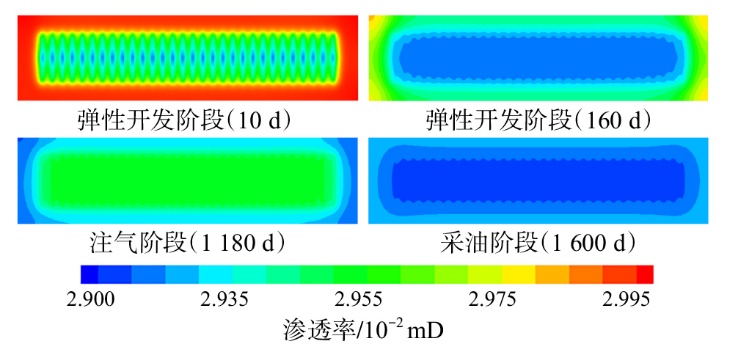
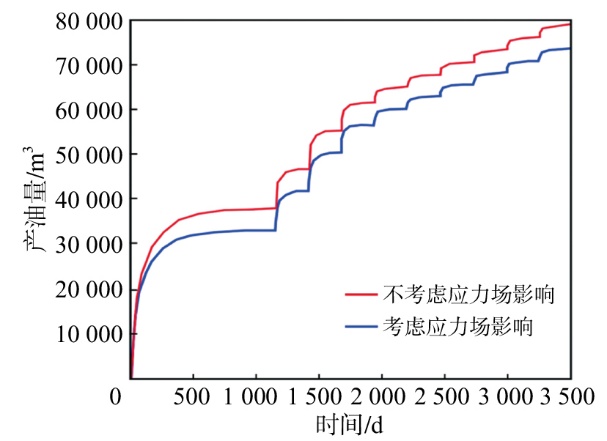
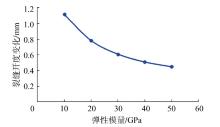
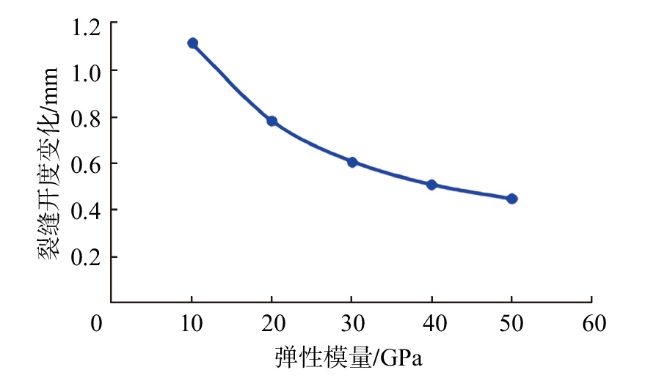
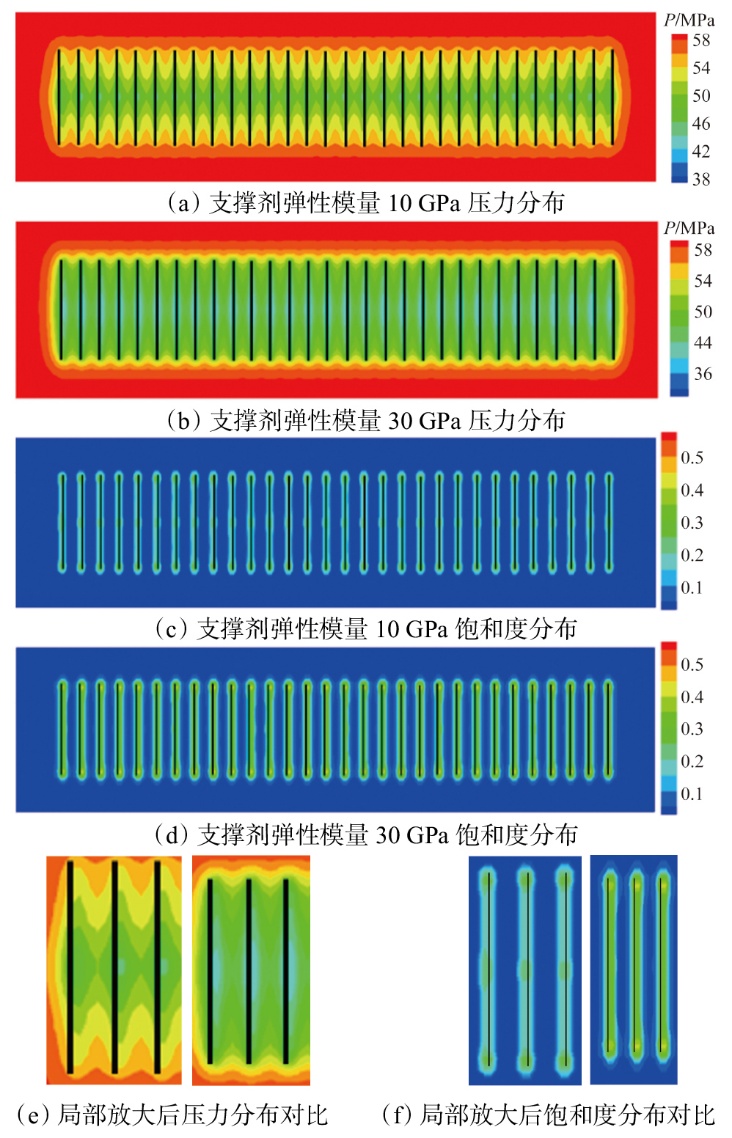
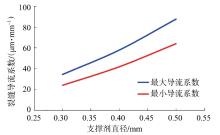
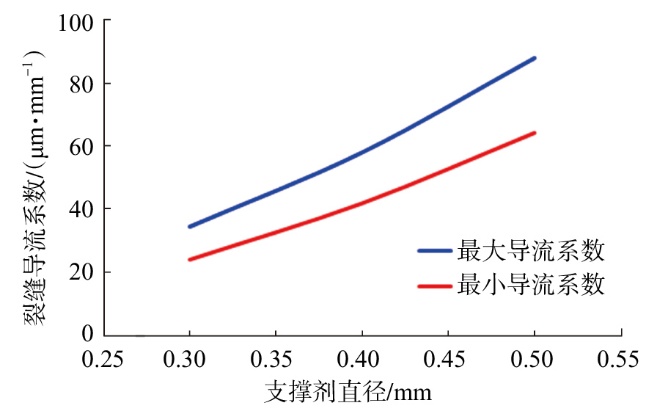
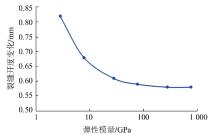
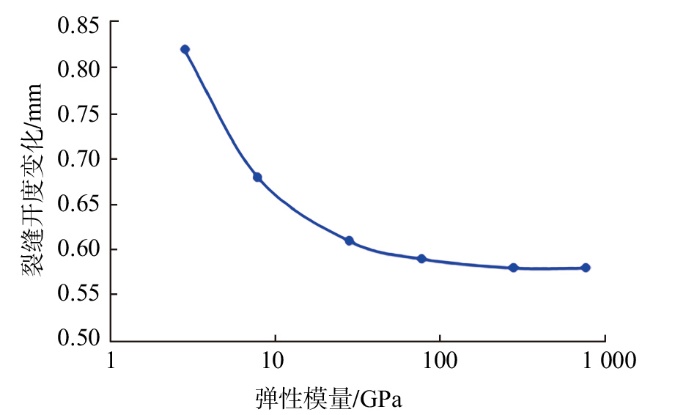
采用组分模型描述流体流动和相态变化特征,构建嵌入式离散裂缝模型以表征人工裂缝,建立了基质和压裂裂缝-支撑剂本构关系,研究了不同力学和开发参数下的应力场对人工裂缝导流能力和开发效果的影响。研究结果表明:①页岩油藏CO2吞吐开发是一个多组分多场耦合的复杂过程,伴随页岩油藏CO2吞吐,地层压力场和应力场反复变化。在流固耦合效应的影响下,支撑剂会发生变形和嵌入裂缝边界层,导致页岩油藏的人工裂缝开度、导流系数与基质孔隙度、渗透率均发生改变,对页岩油藏开发效果影响明显。②支撑剂弹性模量越大,开发过程中支撑剂越不容易变形,裂缝闭合量越小;支撑剂直径越大,越有利于保持裂缝开度。③基质弹性模量越大,支撑剂越难嵌入基质,裂缝闭合越小,有利于裂缝维持导流能力。
中图分类号:
- TE349
| [1] | 苏皓, 雷征东, 张荻萩, 等. 致密油藏体积压裂水平井参数优化研究[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2018, 30(4):140-148. |
| SU Hao, LEI Zhengdong, ZHANG Diqiu, et al. Volume fractu-ring parameters optimization of horizontal well in tight reservoir[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2018, 30(4):140-148. | |
| [2] |
李继庆, 刘曰武, 黄灿, 等. 页岩气水平井试井模型及井间干扰特征[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2018, 30(6):138-144.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20180617 |
|
LIU Jiqing, LIU Yuewu, HUANG Can, et al. Multi-stage fracturing horizontal well interference test model and its application[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2018, 30(6):138-144.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20180617 |
|
| [3] |
刘博, 徐刚, 纪拥军, 等. 页岩油水平井体积压裂及微地震监测技术实践[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2020, 32(6):172-180.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20200617 |
|
LIU Bo, XU Gang, JI Yongjun, et al. Practice of volume fractu-ring and microseismic monitoring technology in horizontal wells of shale oil[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2020, 32(6):172-180.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20200617 |
|
| [4] |
HUGHES J D. A reality check on the shale revolution[J]. Nature, 2013, 494(7437):307-308.
doi: 10.1038/494307a |
| [5] | CLARK A J. Determination of recovery factor in the Bakken Formation,Mountrail county,ND[R]. New Orlean,SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, 2009. |
| [6] | 刘佳慧, 苏玉亮, 李蕾, 等. 基于微流控实验的页岩油CO2吞吐提高采收率微观机理研究[R]. 西安,油气田勘探与开发国际会议, 2022. |
| LIU Jiahui, SU Yuliang, LI Lei, et al. Study on micro mechanism of enhanced oil recovery by CO2 huff-n-puff of shale oil based on microfluidic experiment[R]. Xi’an,The International Field Exploration & Development Conference, 2022. | |
| [7] | 杨明, 薛程伟, 李朝阳, 等. 页岩油CO2吞吐影响因素及微观孔隙动用特征[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 2023, 42(4):148-156. |
| YANG Ming, XUE Chengwei, LI Chaoyang, et al. Influencing factors of CO2 huff and puff and micro-pores producing characteristics of shale oil[J]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing, 2023, 42(4):148-156. | |
| [8] | 李凤霞, 王海波, 周彤, 等. 页岩油储层裂缝对CO2吞吐效果的影响及孔隙动用特征[J]. 石油钻探技术, 2022, 50(2):38-44 |
| LI Fengxia, WANG Haibo, ZHOU Tong, et al. The influence of fractures in shale oil reservoirs on CO2 huff and puff and its pore production characteristics[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techni-ques, 2022, 50(2):38-44. | |
| [9] | 叶安平, 郭平, 王绍平, 等. 利用PR状态方程确定CO2驱最小混相压力[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2012, 24(6):125-128. |
| YE Anping, GUO Ping, WANG Shaoping, et al. Determination of minimum miscibility pressure for CO2 flooding by using PR equation of state[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2012, 24(6):125-128. | |
| [10] | 张海龙. CO2混相驱提高石油采收率实践与认识[J]. 大庆石油地质与开发, 2020, 39(2):114-119. |
| ZHANG Hailong. Practice and understanding of enhancing the oil recovery by CO2 miscible flooding[J]. Petroleum Geology & Oilfield Development in Daqing, 2020, 39(2):114-119. | |
| [11] |
程杰成, 朱维耀, 姜洪福. 特低渗透油藏CO2驱油多相渗流理论模型研究及应用[J]. 石油学报, 2008, 29(2):246-251.
doi: 10.7623/syxb200802016 |
|
CHENG Jiecheng, ZHU Weiyao, JIANG Hongfu. Study on mathematical models for multi-phase porous flow in CO2 drive of extra-low permeability reservoir and field application[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2008, 29(2):246-251.
doi: 10.7623/syxb200802016 |
|
| [12] |
周瑞, 苏玉亮, 马兵, 等. 随机分形体积压裂水平井CO2吞吐模拟[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2020, 32(1):161-168.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20200118 |
|
ZHOU Rui, SU Yuliang, MA Bing, et al. CO2 huff and puff simulation in horizontal well with random fractal volume fracturing[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2020, 32(1):161-168.
doi: 10.12108/yxyqc.20200118 |
|
| [13] | GAMADI T D, ELLDAKLI F, SHENG J J. Compositional simulation evaluation of EOR potential in shale oil reservoirs by cyclic natural gas injection[R]. Denver,SPE/AAPG/SEG Unconventional Resources Technology Conference, 2014. |
| [14] | YU Wei, LASHGARI H, SEPEHRNOORI K. Simulation study of CO2 huff-n-puff process in Bakken tight oil reservoirs[R]. Denver,SPE Western North American and Rocky Mountain Joint Meeting, 2014. |
| [15] |
LI Sheng, DONG Mingzhe, LUO Peng. Simulation study on dissolved oil release from kerogen and its effect on shale oil production under primary depletion and CO2 huff-n-puff[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2021, 200:108239.
doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2020.108239 |
| [16] | DENOYELLE L C, LEMONNIER P. Simulation of CO2 huff and puff using relative permeability hysteresis[R]. Dallas,SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, 1987. |
| [17] |
WAN T, SHENG J J. Evaluation of the EOR potential in hydraulically fractured shale oil reservoirs by cyclic gas injection[J]. Petroleum Science and Technology, 2015, 33(7):812-818.
doi: 10.1080/10916466.2015.1010041 |
| [18] |
MOLERO P Z, YU Wei, XU Yifei, et al. Simulation study of CO2-EOR in tight oil reservoirs with complex fracture geo-metries[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6:33445.
doi: 10.1038/srep33445 |
| [19] | 张英林. 页岩油藏储集性能及应力敏感性评价[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2020. |
| ZHANG Yinglin. Evaluation of reservoir property and stress sensitivity in shale reservoir[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum (East China), 2020. | |
| [20] |
LI Kewen, GAO Yuanping, LYU Youchang, et al. New mathe-matical models for calculating proppant embedment and fracture conductivity[J]. SPE Journal, 2015, 20(3):496-507.
doi: 10.2118/155954-PA |
| [21] | LACY L L, RICKARDS A R, BLLDEN D M. Fracture width and embedment testing in soft reservoir sandstone[J]. SPE drilling & completion, 1998, 13(1):25-29. |
| [22] | 张庆福. 页岩油藏注CO2增能开发数值模拟研究[J]. 计算力学学报, 2024, 41(4):755-761. |
| ZHANG Qingfu. Numerical simulation of CO2-EOR in shale oil reservoirs[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics, 2024, 41(4):755-761. | |
| [23] | 刘礼军. 缝洞型碳酸盐岩油气藏流固耦合数值模拟研究[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2021. |
| LIU Lijun. Numerical simulation of coupled flow and geomechanical process in fractured karst carbonate reservoirs[D]. Qingdao: China University of Petroleum (East China), 2021. |
| [1] | 詹盛云, 童建祥, 王振东, 白玉婷, 王泰超. 底水油藏不同注采井模式SAGD开发特征及合理注采压差[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2025, 37(6): 180-190. |
| [2] | 江山, 唐永建, 焦霞蓉, 李文亮, 黄成, 王泽. 塔里木盆地顺北油田4号断裂带断控体凝析气藏剩余气分布规律[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2025, 37(4): 84-94. |
| [3] | 杨旭, 白鸣生, 龚汉渤, 李皋, 陶祖文. 川西新场地区三叠系须二段构造裂缝特征及定量预测[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2025, 37(3): 73-83. |
| [4] | 赵艾琳, 赖强, 樊睿琦, 吴煜宇, 陈杰, 严双栏, 张家伟, 廖广志. 基性火山岩核磁共振响应机理及孔隙结构评价方法——以四川盆地西南部二叠系峨眉山玄武岩组为例[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2025, 37(3): 153-164. |
| [5] | 张庆龙, 毛元元, 冯建松, 袁学生, 周微, 朱福金, 轩玲玲. 裂缝-孔隙型碳酸盐岩油藏加密井井位部署新方法——以渤海湾盆地黄骅坳陷唐海油田寒武系油藏为例[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2025, 37(3): 165-175. |
| [6] | 徐有杰, 任宗孝, 向祖平, 樊晓辉, 于梦男. 非均质储层致密气藏压裂井复杂缝多井干扰数值试井模型[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2025, 37(3): 194-200. |
| [7] | 何岩, 许维娜, 党思思, 牟蕾, 林少玲, 雷章树. 准噶尔盆地陆梁地区侏罗系西山窑组钙质夹层成因及勘探意义[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2025, 37(1): 90-101. |
| [8] | 陈肖, 缪云, 李伟, 谢明英, 施浩, 王伟峰. 海上边水驱砂岩油田合理油水井数比计算方法[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2025, 37(1): 194-200. |
| [9] | 崔传智, 李静, 吴忠维. 扩散吸附作用下CO2非混相驱微观渗流特征模拟[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2024, 36(6): 181-188. |
| [10] | 刘仁静, 陆文明. 断块油藏注采耦合提高采收率机理及矿场实践[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2024, 36(3): 180-188. |
| [11] | 包汉勇, 刘超, 甘玉青, 薛萌, 刘世强, 曾联波, 马诗杰, 罗良. 四川盆地涪陵南地区奥陶系五峰组—志留系龙马溪组页岩古构造应力场及裂缝特征[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2024, 36(1): 14-22. |
| [12] | 李丰丰, 倪小威, 徐思慧, 魏新路, 刘迪仁. 斜井各向异性地层随钻侧向测井响应规律及快速校正方法[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2023, 35(3): 161-168. |
| [13] | 吕栋梁, 杨健, 林立明, 张恺漓, 陈燕虎. 砂岩储层油水相对渗透率曲线表征模型及其在数值模拟中的应用[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2023, 35(1): 145-159. |
| [14] | 程丹华, 焦霞蓉, 王建伟, 庄东志, 王政军, 江山. 黄骅坳陷南堡凹陷古近系沙一段页岩油储层特征及油气意义[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2022, 34(3): 70-81. |
| [15] | 张威, 李磊, 邱欣卫, 龚广传, 程琳燕, 高毅凡, 杨志鹏, 杨蕾. A/S对断陷湖盆三角洲时空演化的控制及数值模拟——以珠江口盆地陆丰22洼古近系文昌组为例[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2022, 34(3): 131-141. |
|
||

 甘公网安备 62010202002827号
甘公网安备 62010202002827号